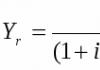31.05.2018 17:59:55 1C:Servistrend ru
Registration of a new division in the 1C program: Accounting 8.3
The “Divisions” directory is used in all sections of accounting, acts as analytics in many accounting and tax accounts and is one of the key objects of the system. In this article we will look at the features of adding a new division to the organization structure in the program.
The initial filling of the directory is carried out when the program is put into commercial operation, along with other regulatory and reference information. Subsequent changes are made in accordance with the orders of the enterprise.
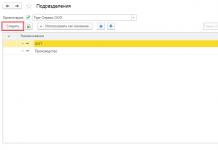
For internal accounting purposes, organizations issue an order to introduce a new division (cost center). Next, the documents are sent to the person responsible for setting up and adding regulatory and reference information. Having received the document, the user follows the navigation path to create a new division: Directories / Enterprise / Divisions.
In the open form of the directory element “Divisions”, the person responsible for setting up master data fills in the following fields:
- Name – custom name of a department or group of departments;
- Organization – fill in the current organization;
- Group – indicates the element that is the parent in the structure.

The directory of departments is hierarchical; there is a division into elements and groups. The user is given the opportunity to build a structure of divisions containing up to 10 nesting levels. To move units to a new group, the user can specify the required value in the “Group” field on the card.

To use a department as the main one in documents, you need to click the “Use as main department” command in the form of the list of departments.

It is worth noting that the directory of departments reflects the structure of the organization for personnel records, calculation and reflection of salaries, accounting and tax accounting, etc. Thus, it is recommended to fill out this directory based on the actual structure of the enterprise, also taking into account the groupings of divisions in the context of which it is necessary to build reports.
Organizations should also establish procedures for renaming and closing departments in accordance with accounting needs. When closing, information about the current status and closing date can be added to the name of the unit for convenience and to prevent errors by users. When renaming a division, the options are to change the name on the card or create a new division in the structure.
Still have questions? We'll tell you about adding divisions to 1C as part of a free consultation!
We bring to your attention an article about reflecting enterprise divisions in the 1C: Trade Management 8 program (rev. 11.3). As an example, a demo base in the standard delivery was used.
Settings
The use of departments in the program can be enabled or disabled using a flag in the enterprise settings:
Master data and administration – Setting up master data and sections – Enterprise
If the use of departments is disabled, the corresponding directory will not be available. There will be no “Division” field in documents and directories.
Where are units used?

Direct maintenance of separate accounting is included in the form of the unit itself.
Directory "Enterprise structure"
Filling out the directory
Divisions are entered into a directory called “Enterprise Structure”:
Master data and administration – Master data – Enterprise structure
This reference book implements a hierarchy of elements. This means that one division can be created directly "inside" another, without the use of groups. For example, in the image below you can see that the trade sales department includes other departments:

When creating a department, you must enter its name. If this unit is included in a higher one, it is also indicated in the corresponding field. It is possible to specify the head of the department (optional parameter):

Important. In the 1C: Trade Management program, divisions are not tied to an organization (individual entrepreneur or legal entity), but relate to the entire enterprise.
Separate accounting of goods

To do this, the appropriate setting must be installed in the program (see paragraph 2 of this article).
Features of reflecting holding divisions
If an enterprise is a holding company that includes several organizations, the question arises: how to enter the divisions of these organizations into the information database?
The holding includes two legal entities, each of which has an administration, a sales department and a purchasing department.
The reflection of such divisions in the directory depends on the situation at the enterprise. There are two options:

Legal entities have the right to create separate divisions for various purposes. The legislation regulates in detail the conditions and procedure for their creation. Separate divisions simultaneously have two main characteristics:
- The address of a separate division differs from the address of the organization indicated in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities;
- At the location of the separate unit, at least one stationary workplace is equipped for a period of more than a month.
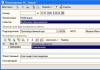
In the 1C:Accounting 3.0 program, created on the 1C:Enterprise 8.3 platform, registration of a separate division is carried out in the menu “Directories - Enterprises - Divisions”.
Fig.1
You need to create a new division in 1C: check the “Separate division” box, fill in all the details, indicate the head division. The division will have its own checkpoint, and the TIN will be common for all divisions and the parent company.

Fig.2
After filling out, the document must be recorded, and then it will be reflected in accounting.

Fig.3
In the 1C program, you can create, configure and maintain records of several organizations and departments at the same time. At the same time, it is possible to separately calculate wages with the submission of tax reports to different Federal Tax Service Inspectors. Let's look at an example of how to keep records for separate divisions in terms of wages.
In the main menu, select “Administration – Program settings – Accounting parameters”.

Fig.4
In the accounting parameters, select “Salary settings”.

Fig.5
In the “Payroll calculation” section, check the “Payroll calculation by separate departments” checkbox.

Fig.6
In the department card you can enter the details of the tax office to which the reports will be submitted.

Fig.7
Payroll
First we need to hire employees for our division. To do this, go from the main menu to “Salaries and personnel – Personnel records – Hiring”.

Fig.8
Through “Create” we go to the employment document. We fill in the following information:
- The organization is our organization;
- Division – a separate subdivision;
- Position – position of an employee of a separate unit;
- Employee – an employee of a separate unit;
- Reception date – fill in the required date;
- Probation period – fill in if one is provided;
- Type of employment – in our case it is internal part-time work.

Fig.9
Now let’s calculate the salary of the employee of the main and separate division. Salaries in 1C 8.3 are calculated in the section “Salaries and Personnel - Salaries - All Accruals”.

Fig.10
Using the “Create” button, we calculate wages for employees of the main department. For example, let's take data for one employee. We will fill out and post the “Payroll” document.


Fig.12
Generation of 2-NDFL certificates
So, we have calculated wages for two employees of the main and separate departments. Next, we will generate 2-NDFL certificates for these employees. To do this, from the main menu go to “Salaries and personnel – personal income tax – 2-NDFL for transfer to the Federal Tax Service”.

Fig.13
We create a certificate for an employee of the main department. The 1C 8.3 program offers the opportunity to select a tax office according to OKTMO and KPP. We select the one we need and fill in the remaining data. The employee data should be filled in automatically. The help displays the following information:
- The tax rate is in our case 13%;
- Income – accrued salary to an employee;
- Taxable income - if there were no deductions, then the amounts are the same;
- Tax – the amount of accrued personal income tax;
- Withheld – personal income tax is withheld at the time of salary payment, our salary has only been accrued, so in our case the value in this cell is “0”;
- Listed – this field will be filled in after the tax is paid to the budget, so for now it is also “0”.


Fig.15
Next, fill out a certificate for an employee of a separate unit. We generate the certificate in a similar way, changing the data in the OKTMO/KPP field when paying income. Data from the Federal Tax Service at the address of the separate division. Similar to the previous certificate, the employee’s data, his income, tax rate and tax amount are filled in automatically.

Fig.16
Just like for the previous certificate, you can display a printed form in which we see the Federal Tax Service code different from the first one.

Fig.17
In this article, we looked at how to create a separate division, as well as the possibilities offered by the 1C 8.3 program for payroll, tax calculation, as well as submitting reports for employees of the main and separate divisions to different tax inspectorates. Thanks to them, maintaining a separate unit in the program will not be difficult for users.
08.09.2016
To create a separate division, the taxpayer must fulfill a number of obligations in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation. These include the need to register with the tax authorities, calculation and payment of taxes/fees both at the location of the enterprise and at the location of separate divisions / Art. 19 Tax Code of the Russian Federation/.
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the taxpayer is obliged to notify the tax authority about the creation of a separate division, paragraphs 1 and 4 of Art. 83 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation regulate the need for registration with the tax authorities at the location of the separate division. Please note that if the taxpayer is already registered with one of the tax authorities, there is no need to register with the same tax authority, but on a different basis / paragraph 39 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of Russia dated February 28, 2001 No. 5 “On some issues of application of part first of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation"/.
In Articles 23 and 83 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation you can find information about the deadlines for filing an application for tax registration at the location of a separate division:
Taking into account the information that when registering a taxpayer for tax purposes when creating a separate division, it is necessary to focus on the location of the division. Thus, a corresponding application is submitted to the tax authority, taking into account the territorial jurisdiction, while the specifics of accounting for private groups in specialized tax authorities are not taken into account. Specialized groups include tax authorities of an industry or subject area (construction, motor transport, etc.). This conclusion is confirmed by the special provisions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which provide for the distribution of tax obligations, including the location of the designated separate divisions. Because part of the tax obligations is usually distributed to the budgets of additional territories, we can conclude that there are territorial bodies involved in monitoring the payment of taxes in the specified territory.
However, it is impossible to make an unambiguous interpretation of the term “separate division”, which, within the framework of tax legal relations, should lead to the mandatory payment of taxes by the taxpayer to various budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation or municipalities. Otherwise, the peculiarity of a separate division will consist only in territorial isolation, and therefore the amount of the taxpayer’s tax obligations will remain unchanged. The courts did not recognize this argument as fair, despite its apparent logic.
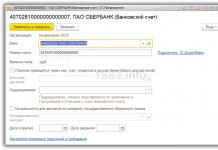
When making a transaction with a separate division, you must enter both values in the directory of counterparties: legal entity - head division and separate division.
To add a separate division to the directory, you must select the “Separate division” type, then select an element in the directory of counterparties that corresponds to the legal entity (head division), and also enter the checkpoint and address of the separate division.
Then, in order to formalize a transaction with a counterparty - a separate division - in the sales/receipt document, in the “Counterparty” field, you must indicate the element of the directory of counterparties corresponding to the legal entity - the head division, in the “Consignee” field - a separate division.
First, let's figure out where counterparties are located in 1C 8.3. The Counterparties directory can be called from the Directories section:
Or through the All functions command in the Main menu:

Step 1. Filling out the fields of the counterparty card
How to create a counterparty
When filling out the Counterparty Type field, 4 values are available for selection: Legal entity, Individual, Separate division, Government institution:

If the counterparty is a legal entity
Indicate the name, full name (shown in printed forms), INN (10 digits), KPP (9 digits), OKPO code.
For this type of counterparty, after filling out the short name, the Fill in by name button is available. When you click on it, a window of the contractors found by the current name appears:

After the user selects the desired counterparty, the 1C 8.3 program compares its details with the details filled in by the user and:
- or fills in empty details;
- or, if there are discrepancies, offers to refill such details.
Thus, in 1C 8.3 the details are automatically filled in: name, abbreviated legal name, checkpoint, telephone, legal address.
To use the autofill service by name, you must connect the Internet user support service through the Administration – Service – Internet support section.
If the counterparty is an individual
Indicate your full name, INN (12 digits), OKPO code, series and number of the certificate, identification document:

If the counterparty is a separate division
The composition of the fields is similar to filling out the Legal Entity type, but an additional field, Head Counterparty, is added. The selection of the value to fill in this field also comes from the Counterparties directory, therefore the Head Counterparty must first be entered in this directory.
For a separate division in 1C 8.3, the TIN is filled in automatically according to the TIN of the head counterparty, and the checkpoint depends on the location of the division, the name of the division:

If the counterparty is a government agency
Used to enter information about government agencies into the 1C 8.3 database: for example, the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Federal Tax Service, the Social Insurance Fund. In this case the following are indicated:
- Name – the name of the recipient, understandable to the user;
- Full name – name of the payee in the payment order for transfer to the budget;
- Government body:
- Tax authority - if the recipient is the Federal Tax Service;
- FSS body - if the recipient is the FSS;
- Pension Fund body - if the recipient is the Pension Fund;
- Other – if the recipient is another body.
- TIN – TIN of the payment recipient;
- Checkpoint – payee checkpoint:

Filling out the remaining fields of the Counterparty card
- Full name– full name of the counterparty (to be inserted into printed forms). Able to store a history of name changes.
- Country of registration– it is important to indicate, since if the counterparty is registered abroad, it becomes possible to enter the tax and registration number in the format of the country of registration.
- Completed details main bank account, addresses And phones, contact faces from the card are automatically inserted into documents when selecting a counterparty.
- TIN and checkpoint counterparty - when filling out these details, their correctness is checked, as well as their absence in the database to avoid duplication.
For all types of counterparties, with the exception of a separate division, in 1C 8.3 it is possible to automatically fill in the details according to the TIN. Wherein:
- Filling out the TIN also works when connecting to Internet support.
- If information about the counterparty is available in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, the following details will be filled in: checkpoint, short and full name, legal address, manager as the main contact person, telephone.
- The checkpoint attribute has the ability to store the history of its changes (starting from version 3.0.39). If the checkpoint has changed, then you need to click on the History link and add a new line, indicating the start date of the new value:

The counterparty card at the top provides access to details and documents associated with this counterparty:

Let's look at each of them in more detail.
A list of bank accounts for this counterparty opens:

New bank accounts must be entered through the counterparty card. You can also add a new bank through the current account entry form:

To correctly fill out a bank in 1C 8.3, it is better to use the Bank Classifier, which is filled out by downloading the bank classifier from the RBC agency website or from the ITS disk (read in our article).
After the classifier is loaded into 1C 8.3, you need to find the desired bank in the folder with the name of the required region and click the Select button. After this, the bank will be added to the Banks directory and from there you can add it to the Bank field of the Current Account creation window:

The checkbox for the “Payments are made through a correspondent account opened in another bank (settlement bank)” checkbox is selected if settlements are made through a bank’s correspondent account in another bank. Valid only for Russian bank accounts.
A list of contact persons for this counterparty opens. The contact person selected as the main one is inserted into documents and printed forms. For example, the contact person is inserted into the Signatures section of the contract of this counterparty:

When creating a contact person, fill in the following fields:
- Main tab- FULL NAME;
- Addresses tab– address, telephone, E-mail, other contact information;
- Tab Additional details– position, role, date of birth, other additional information.
- The Role field is filled in to clarify the value specified in the Position field. For example, Position = Accountant, and the clarifying role can be = Accountant, Materials Accountant, Fixed Asset Accountant, etc.
When you start filling out, the contact person is filled in with the form Counterparty contact person:

But after recording the element on the Home tab, 2 more types of contacts are added for selection: personal contact and other contact person, so that if the contact is no longer a contact person for this counterparty, then in the future it will be possible to assign another type to it and the contact will appear in the Contact persons directory, but will no longer be listed as a contact of this counterparty and will not appear in the list of its contact persons:

A list of settings for settlement accounts for this counterparty opens:

This window has only informative value, since it is better to set up accounts with counterparties through the information register of the same name, so that the settings are correct and the picture of the settings is complete. To do this, go to the section Directories – Purchases and sales – Accounts for settlements with counterparties:

The figure shows that two lines with account settings have been entered:
- The settings of the first line are valid for all organizations, all counterparties and for all contracts and for settlements in the registry currency. accounting, since none of the values in the columns are selected.
- The second line already specifically applies to the organization Confetprom for settlements with the counterparty Cafe Skazka under a specific agreement and for settlements in registry currency. accounting.
Thus, the substitution of accounts in the first line will be valid in all cases except those specified in the second line. In this case, no fewer fields must be filled in in the new setting than in the previous settings.
The information register of the same name opens with the selection of licenses for this counterparty. This information is used to draw up a declaration on retail volumes:

A list of electronic document management settings for this counterparty opens. can be found in the Administration section – Setting up the exchange of electronic documents:

Step 2. Working with counterparty documents in 1C 8.3
On the tab Documentation The Journal of Operations with selection for this counterparty opens, in which you can additionally set selections by agreement and organization, as well as by other details through the More – Set up list button:

Step 3. Working with counterparty agreements in 1C 8.3
How to choose a counterparty agreement
The availability of accounting under contracts in 1C 8.3 is included in the Main section - Functionality - Calculations tab - Accounting under contracts checkbox.
On the tab Treaties a list of all contracts that have ever been entered into the 1C 8.3 database for this counterparty opens. In the list, you can select by organization and select existing contracts for a specific date.
The 1C Accounting 3.0 configuration allows you to designate several contracts for a counterparty as the main ones, depending on the organization with which the contract was concluded and the type of contract. That is, 2 main contracts with the type Other and With the buyer can be assigned to one organization, but one organization cannot have 2 main contracts with the type With the buyer:

Incorrect indication of a contract in 1C can lead to duplication of contracts. What errors this can lead to, how to find and correct such errors, see our video:
How to create an agreement with a counterparty in 1C 8.3
Filling out the general details of the contract:
- The following details are always filled in: name, number and date of the contract;
- Settlement currency – contract currency;
- Type of calculations – additional analytics for calculations. Allows the user to combine contracts of different counterparties. For example, into groups according to some criterion;
- Price type – used for substitution when selecting a contract in a document.
When creating a new contract, the key field is Contract Type. Expansion of the list for selecting types of contracts in 1C 8.3 Accounting 3.0 is determined by enabling the settings in the Main section – Functionality – Trade tab:

The type of agreement determines, for example, the availability of the agreement for selection from the list of agreements when entering documents (receipts, sales, etc.) into the 1C 8.3 database:

What errors can result from incorrectly specifying the type of contract, see our video lesson:
Filling out the details of the contract with the supplier in 1C 8.3
If in the field Currency If a non-regulated accounting currency is selected, the field becomes available Payment in and choice of payment currency.
Checkbox The payment deadline has been established under the contract– is established if the contract provides for a payment period that is different from the payment period specified in the organization’s accounting policies. If the checkbox is checked, the Contract payment due date field becomes visible.
Checkbox The organization acts as a tax agent for the payment of VAT– established if the organization acts as a tax agent for the payment of VAT. The ability to set this checkbox is enabled in the Main section - Functionality - Calculations tab - VAT tax agent.
In this case you need to indicate:
- Type of agency agreement (rent, sale of property, non-resident);
- Generalized name of goods for the tax agent invoice - it will be substituted in the invoice during automatic registration of tax agent invoices.
If in the field Currency If a non-regulated accounting currency is selected and the organization does not act as a tax agent for VAT, then the checkbox becomes available Calculations in conventional units. This checkbox must be selected if the contract is entered in conventional units. Possibility to make payments in USD is included in the Main section - Functionality - Calculations tab - Calculations in currency and monetary units.
Filling out the details of the contract with the buyer in 1C 8.3
In the Procedure for registering invoices field, you need to select from the list the order for registering invoices for advance payments under the contract.
Generalized name of goods for advance invoices - it will be substituted in the invoice when automatically registering advance invoices.
Filling out the details of the agreement with the principal (principal) in 1C 8.3
To automatically calculate commission (agency) remuneration in 1C 8.3, you need to specify the calculation method that will be entered during registration.
The Organization acts as a tax agent for the payment of VAT checkbox – is selected if the organization acts as a tax agent for the payment of VAT. Then, by default, the Type of agency agreement is set to Non-Resident (clause 2 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Filling out the details of the agreement with the commission agent (agent) in 1C 8.3
To automatically calculate commission (agency) remuneration, you need to specify Calculation method, which will be substituted during registration.
The following calculation methods are available: Not calculated, Percentage of the difference between the sales and receipt amounts, Percentage of the sale amount.
Filling out details of other contracts in 1C 8.3
For such contracts, only general details and the Validity period details must be filled in.
Validity– depending on the validity period, the agreement is considered short-term (less than a year) or long-term and entails the establishment of accounting accounts for credit and loan transactions: 66.01 “Short-term loans” and 67.01 “Long-term loans”.
Filling out an agreement card with a counterparty in 1C 8.3
In the agreement card at the top there are sections: documents, attached files, accounts of settlements with counterparties.
- Documentation– a list of all documents (including those not posted) opens, when creating which this agreement was specified:

- Attached files– a list of files loaded for this agreement opens. For example, a scan of a printed copy of the contract itself or an additional conditions for it:

How to load an agreement with a counterparty in 1C 8.3
When you press the button Add You can upload either a file or an image from the scanner. When adding from a scanner, a window for working with the scanner will open. Uploaded files are stored in separate folders that are created for each object.
If you click the More button to select Preview, then when viewing attached images in a special window you can view its contents:

Pictogram Electronic signature and encryption offers a list of commands to choose from:

Working with a contract template in 1C 8.3
By button Agreement– you can print the contract by first selecting a template for forming the contract.
You can choose any ready-made suitable template and form an agreement. can also be called from a document Buyer's invoice:

Important: before creating a contract in 1C 8.3, you must check that all information about the organization is filled in: name, list of responsible persons, payment details; by counterparty: name, contact person, payment details; and the agreement – signature section:

After this, a correct contract will be formed in which all the necessary data is filled in:

If the printed form of the contract contains yellow fields, this means that there is incomplete data in the 1C 8.3 database:

How to create your own contract template in 1C 8.3
Section Directories – Purchases and sales – Contract templates – Create – New template:

A form for creating a template will open. It is a text editor with clear icons for editing. Let's add manual text and insert details that must be filled out according to the information base. This is the contract number and contract date. Let's save:

A new template has appeared in the list of templates:

After this, we will create a ready-made agreement using this template:

The 1C 8.3 program produced a printed form using a new template. That is, when creating a template, you can insert any text and set the filling of changing data using values from the database.

You can also send by email by clicking the button Send.
Step 4. Set up sending documents by email to counterparties in 1C 8.3
To send emails, you must first make the settings described. More details on how to set up mail in 1C 8.3 can be seen in our video tutorial:
After successful setup, you will be able to send attached files by email.
Step 5. Delete duplicate counterparties in 1C 8.3
In some cases, in 1C 8.3 it is necessary to search for duplicate elements of the Counterparties directory. For example, in the Counterparties directory there was a selection based on some criterion and the user did not notice that the counterparty had already been entered (since it was hidden) and entered it again.
To eliminate this situation, Search and remove duplicates processing is used. (in BP 2.0, ZUP 2.5, ZiK 1.0 similar processing Search and replace values). Section Administration – Support and Maintenance.
You can read more about searching and deleting duplicates in 1C 8.3.
How duplication of counterparties occurs in the Counterparties directory and what errors this duplication causes, see our video:
Step 6. Checking the counterparty in 1C 8.3
This feature appeared in the 1C Enterprise Accounting 3.0 configuration, starting with release 3.0.40.31 and allows the user to obtain information about the counterparty to assess reliability, the scale of financial activity, etc.
The dossier can be called up using the button of the same name in the counterparty’s card:

A window opens with a report for this counterparty:

By switching between sections (Main, Unified State Register of Legal Entities, Program data, Accounting statements, Reporting analysis, Financial analysis, Inspections), you can obtain comprehensive information about the counterparty of interest.
Important: after a report on a counterparty is generated in 1C 8.3 Accounting 3.0, each of its sections can be saved in mxl, pdf, xls formats.
- Chapter Main– information collected and summarized from data from other sections is displayed.
- Chapter Unified State Register of Legal Entities– information is displayed in the context of legal addresses, managers, authorized capital, founders.
- Chapter Program data– the data specified in the program from the counterparty’s card is displayed.
- Chapter Financial statements– reporting for 2012-2013 is displayed according to Rosstat.