Spring is a favorable time for arranging a plot with raspberries. Regardless of the variety, it must be protected from diseases and pests, pruned, fed, and watered. Only with good care will raspberries produce a bountiful and tasty harvest.
Treatment of bushes is carried out at the beginning of the growing season and during budding (5-7 days before flowering).
During raspberry flowering, any preventive or therapeutic measures should be excluded. Processing the bushes during this period leads to the death of pollinating insects and, as a result, to a deterioration in the harvest.
What to process
Treatment is carried out both with chemicals (urea, copper sulfate, dolomite flour, Bordeaux mixture) and folk remedies (mustard, soda, boiling water, infusions of herbs and flowers).
To strengthen the plants, treatment with urea is carried out in early spring. Take 15-20 grams per square meter. Urea saturates the bushes with nitrogen and makes them less susceptible to disease.
Treating raspberries with copper sulfate helps avoid the appearance of fungal diseases (gray rot, anthracnose). The raspberry stems and the soil around the bushes are processed. For spraying, take 50 grams of vitriol per 5 liters of water.
During the growing season and during active plant growth, treatment with copper sulfate cannot be carried out. It accumulates in berries and stems.
When fighting anthracnose, rust and powdery mildew, treating bushes with a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture or iron sulfate, Topaz, Nitrofen helps.
The main reasons for the development of infections are high humidity and high acidity of the soil. Reducing watering reduces humidity. Acidity can be reduced using wood ash, slaked lime, and dolomite flour. Take 150 grams per square meter.
Mustard protects raspberries from weevil larvae.
For spraying, take 20 grams of dry mustard per 10 liters of water, mix everything and leave for 12 hours. Spraying the bushes is carried out in several passes.
Instead of mustard, you can take baking soda, dilute 2 tablespoons in 10 liters of water.
Treating the bushes and root circle with boiling water allows you to get rid of most pests. The procedure is carried out after the snow has melted and the soil has warmed up.
If the affected area is small, raspberry beetle larvae can be collected manually. Before flowering, the plant is treated with an infusion of wormwood and marigold. When using Agravertine and Agravertine, the treatment is carried out twice.
During budding, raspberries can be sprayed with tansy infusion.
For the infusion, take 350 grams of dry herbs or a kilogram of freshly harvested raw materials, 5 liters of water. The tansy is infused for a day, then boiled for half an hour, filtered and diluted with the same amount of water.
Mulching with pine needles protects against weevils and gray rot.
Main pests and diseases of raspberries with photos, descriptions and control measures
Pests
The main pests of raspberries are:
- stem gall midge,
- raspberry beetle,
- stem fly,
- weevil,
- spider mite,
- bud moth,
- raspberry nutcracker,
- raspberry glass.

The presence of swellings on the stems and shoots of raspberries indicates that the plant is affected by stem gall midge. Such shoots are pruned and burned.
For prevention, in early spring the soil is loosened to a depth of 5-10 centimeters and sprayed with karbofos or Fufanon.
When the buds appear, re-treatment with Fufanon or Actellik is carried out.

Aphids feed on plant sap and accumulate on the lower part of the foliage. To destroy the pest during bud break, karbofos or Actellik are used.

To prevent stem fly, mulching the soil around the bushes is used. Mulch makes it difficult for insects to escape from the ground. The first treatment is carried out after the snow melts, using karbofos. At the beginning of May (before flowering), treatment is carried out with Fitoverm, Actellik or Agravertin.

Raspberry gallworm attacks raspberry stems. The larvae feed on stem tissue and cause tissue cracking and swelling. The swellings reach 10 centimeters in length. Sick plants are removed from the site. To prevent healthy bushes, treatment is carried out with karbofos.

When raspberry bushes are damaged by a weevil, the plants are treated with karbofos, metaphos or Actellik. Treatment is carried out a week before flowering.

To combat bud moths in early spring (before the buds swell), the bushes are treated with Bordeaux mixture, Confidor, Iskra, Decis. When leaves appear, a 10% solution of karbofos is used.

The raspberry beetle damages the leaves, buds and berries of the plant. The berries become smaller and spoil quickly.
To protect against the raspberry beetle, the bushes and the ground around (immediately after the snow melts, pruning and gartering the bushes) are sprayed with a 10% solution of karbofos, Nitrafen, Decis, Konfidor, Iskra and covered with mulch.

When raspberry glass appears, the damaged stems are pruned and burned; the caterpillars damage the stems and roots and lead to weakening and death of the bushes.

Spider mites can be identified by white punctures on the surface of raspberry leaves. With severe damage, plants begin to wither and die.
When fighting spider mites, karbofos, phosphamide, metaphos, colloidal sulfur, Cidial are used. Spraying is carried out in the evening.
Diseases
Raspberries are affected
- anthracnose,
- rust,
- white and purple spotting,
- powdery mildew,
- vercillous wilt,
- gray rot,
- streak,
- mosaic,
- mycoplasma disease (growth),
- curliness,
- bactericidal root cancer,
- root rot.

Anthracnose (leaf curling) occurs when there is a lack of boron or potassium in the soil. With a lack of potassium, the leaves turn inward. You can correct the situation with the help of ash. The lack of boron can be compensated by adding a solution of boric acid.
In early spring, raspberries are treated with Nitrafen solution against gray rot and anthracnose.. When the buds open, spray with Bordeaux mixture. You can use Fitosporin at any time.
If mottling, streaks, or spots appear on the leaves (viral diseases), they must be removed immediately. Pruning old shoots, thinning and fertilizing plants allows you to avoid these diseases. 
To avoid verticillium wilt when planting, the roots should be dipped in a weak solution of potassium permanganate for 10 minutes.. When leaf spots appear, Bordeaux mixture is used.

Raspberry chlorosis

Pests (mites, aphids, nematodes) penetrate the stems through cuts and breaks. These insects are carriers of viral diseases (chlorosis, jaundice). The leaves turn yellow, the stems become depleted, the berries become smaller and dry out quickly.
At the first signs of chlorosis, the plants need to be dug up and burned; healthy bushes and the soil around them are treated with protective drugs.
Mycoplasma disease leads to the formation of a large number of non-fruiting thin shoots with a length of 30-50 centimeters (about 200 pieces per bush). At the first manifestations of the disease, the bush is dug up and removed from the site.
Leads to yellowing of foliage. When transplanting or planting bushes, you need to pay attention to the roots. If there is swelling, they are removed, and the cut areas are treated with a 1% solution of copper sulfate. 

When raspberry curl appears, the leaves become very small, become wrinkled, and hard. The undersides of the leaves turn brown. The berries become sour, deformed and dry out. The plant dies within 3 years. Sick bushes are immediately removed and sent to the fire.
Spring treatment of raspberries from pests/Raspberry stem fly/Spraying raspberries: video
In addition to treating raspberries against pests and diseases, care includes:
- pruning,
- feeding,
- tying,
- watering and weeding.
To prevent raspberry bushes from getting sick, the roots and stems need to be protected from mechanical damage. Shrubs can grow in one place for no more than 7 years. They can be planted on the previous site after 4 years.
Planting should be done in fertilized soil. The seedlings must be healthy, strong, with a well-developed, powerful root system, without any damage.

Treatment with copper-containing preparations (1% Bordeaux mixture, Oksikhom, Abiga-Pik, Khom, Copper Oxide) saves raspberries from infections. In rainy weather, spraying should be repeated after 1.5-2 weeks.
To combat diseases of raspberry bushes, it is necessary to provide the plants with a high level of agricultural technology (correctly chosen planting site, fertilizing, timely watering, loosening, weeding, tying and mulching).
If raspberries dry out, there are reasons for this: lack of nitrogen, lack of moisture and dense planting. Eliminating problems allows you to improve the yield several times.

Pruning is done from the second year of plant life.
One of the more important stages of raspberry care is pruning.
First of all, shoots that are not expected to bear fruit (frozen, damaged and young) are pruned; they are cut at the root. If the shoot is partially damaged, it is cut back to a healthy place.
Regardless of planting, the bushes should not be thickened. With a bush form, 8-12 stems should grow, with a ribbon form, no more than 25 stems.
The second pruning is done when the raspberries begin to grow.
The tops of raspberries are pruned by 12-15 centimeters (to the first bud), this stimulates the development of the plant and lateral buds. The height of the stem should not exceed 1.5 meters.

The most necessary nutrients for raspberries are potassium, phosphorus, nitrogen and organic matter.
- Potassium improves the yield and winter hardiness of plants.
- Phosphorus strengthens shoots.
- Nitrogen accelerates plant growth. Any variety of raspberry produces a good harvest in soil rich in organic matter.
To increase the yield, spring fertilizing is carried out in several stages.
Any type of raspberry feeding is done after watering and loosening the soil.
For the first feeding, after the snow melts (before loosening the soil), urea or saltpeter is used. Granular fertilizer is applied under the bush immediately after watering. Take 15 grams of saltpeter or 20 grams of urea per square meter. To enhance the effect, a glass of wood ash is scattered under the bush.
After loosening the soil, rotted manure, peat or compost is distributed on the site. The organic matter will serve as mulch.
In May, raspberries need to be fed with mullein. Mullein is filled with water in a ratio of one to one and infused for a week. The resulting infusion is diluted with cool water (2 liters per 10 liters of water) and poured under the bushes.
When laying the ovary, feeding is done with superphosphate. After this procedure, the bushes become strong, resistant to diseases, and productivity increases.
During flowering, 1 glass of superphosphate, a glass of ash and 100 grams of urea are introduced.
The mixture is diluted in a bucket of water and poured under the bushes.
Feeding raspberries with chicken droppings increases the yield and strengthens the plants. The litter is diluted in water in a ratio of one to five and infused for 5 days. The finished infusion is diluted one to twenty and used for its intended purpose.
Raspberries. The struggle for the harvest begins in spring: video
Proper processing of raspberries in the spring and good care allows you to get a bountiful harvest every year.
Work should begin immediately after the snow melts, even before the growing season begins. Spraying is acceptable during the period of swelling, bud break and before flowering. Later, beneficial insects will begin to pollinate flowers; it is important to preserve them. In critical cases, when the raspberry tree is overcome by disease or a serious pest invasion is observed, the bushes are treated during flowering and immediately after it.
Spring raspberry care includes a set of activities that gardeners must begin sequentially. Before the first spraying, pruning and clearing of the raspberry tree is carried out. Procedure:
- even before the start of sap flow (until the earth warms up and the plants begin to grow), you need to have time to remove the frostbitten tops of the shoots;
- all dry, poorly overwintered branches are cut off at the root;
- shoots growing inside the bush must also be removed;
- leaves, old twigs and other plant debris are raked out of the raspberry tree and burned, since harmful insects and pathogens often overwinter in them.
When preparing raspberries for processing, use clean, well-sharpened garden tools. The cuts need to be made even, smooth, torn and crooked ones take longer to heal, which means that these places are susceptible to pests and the development of diseases.
All spraying is carried out in the morning and evening in calm weather without rain. The bushes must be treated carefully, touching every twig and leaf; most pests and diseases develop in various lesions on the bark or young tissue of the shoots. If several different varieties grow nearby, the entire raspberry tree is sprayed.
What to process
When choosing a product or processing method, you can rely on the general advice of experienced gardeners, which indicates approximate dates and recommended drug options. But more often the focus is on the characteristics of certain varieties. Taking into account the characteristics of resistance or vulnerability to diseases and pests, it is easier to identify possible risks and decide how and with what to treat raspberries in the spring.
Perhaps the raspberry bushes already caught some kind of disease last season; in the fall they went through the first stage of treatment. In the spring, you need to continue the fight against the existing disease and protect weakened bushes from pests as much as possible. Chemicals can be used only before flowering begins; after, if there is an urgent need, you need to select something from folk recipes or biological preparations.
Chemical substances

Such tools help quickly solve problems that have already arisen and serve as reliable long-term protection. There are many opponents of chemistry, but experienced gardeners advise not to give up such drugs, but to use them correctly.
How to work with chemicals, safety precautions, first aid:
- The treatment is carried out using protective equipment - a respirator, goggles, gloves and protective clothing.
- While working, you must not smoke, drink, or eat.
- After spraying, wash your hands and face with soap, rinse your mouth, and rinse your eyes well with running water.
- Preparation of the solution is not permitted in food containers.
- The drugs should be stored away from food products and out of the reach of children and pets.
- Chemicals should be stored and handled away from sources of ignition.
- Be sure to read the instructions for the drug.
- If chemicals come into contact with your skin or eyes, immediately rinse these areas thoroughly. If droplets of drugs enter the digestive tract, drink 4 glasses of water, induce vomiting, take several tablets of activated charcoal and go to the hospital. For severe neuralgic symptoms, you need to drink 10–20 mg of diazepam.
Let's look at the most common chemicals for the prevention and elimination of pests and diseases of raspberries.
Nitrafen
The drug is intended to combat the wintering stages of fungal diseases and pests. Active substances not only kill up to 70% of fungal spores and pest pupae, they significantly slow down the development of the remaining ones. To enhance the effect, the soil is loosened before processing.
The only negative is the average toxicity of the drug, but if used in a timely manner, this will not affect human health in any way.
Purpose:
- scale insects;
- leaf rollers;
- anthracnose;
- septoria;
- rust;
- powdery mildew.
The treatment is carried out as soon as the snow melts. The bushes and soil are irrigated abundantly. 100 grams of the drug are dissolved in 5 liters of water. For 10 square meters of raspberry plantings you will need from 1.5 to 2.5 liters of solution.
Fufan (Fufanon)

A broad-spectrum insecticide used to control sucking and gnawing insects such as raspberry beetles, weevils, aphids, and mites. When treating raspberries, the drug is effective for up to 14 days. The substance, when it gets on the bodies, respiratory and digestive organs of insects, first causes complete paralysis, then the pest dies.
Fufanon should be stored in a dark, dry, cool place. When heated to 28 degrees, the drug melts.
Despite the serious toxicity of Fufanon, when used correctly it will not harm plants or humans. Spraying is carried out before flowering, only the bushes are treated, trying not to get on the soil, more attention is paid to places of mass accumulation of the pest.
It is important that it does not rain within 4 days after spraying; part of the preparation will flow with precipitation into the soil, it will be absorbed by the roots and transferred to the fruits. One ampoule of 47% Fufanon is designed for a liter of water, and 57% for 2 liters. For 10 raspberry bushes you will need about 2–2.5 liters of solution.
Advantages:
- the result is noticeable the next day;
- Fufanon does not have a strong specific odor;
- the product is used economically;
- The drug is universal, acts on many pests of various crops.
The only disadvantage is the complicated process of diluting the product in water. It is time-tested and always gives good results. With timely spring treatment, you don’t have to worry about the safety of the bushes during the fruiting period.
Aktellik

A universal insecticide designed to combat spider mites, weevils, aphids, scale insects, flies, leafhoppers, cutworms, mowers and blackheads. The substance causes paralysis in insects, they cannot eat or move. The effect is noticeable the next day; adults, larvae, and caterpillars located on the back of the leaves die.
Actellik is used before the buds appear. The ampoule is diluted in 2 liters of water. You need to process the bushes carefully, trying to touch the back side of the leaves. The procedure can be carried out when there is no risk of precipitation for about 5 days; the bushes must also be dry, so evening hours are allocated for the procedure. The prepared solution cannot be stored. The substance may cause poisoning and skin rashes.
Advantages:
- instant result, protective effect lasts from 3 to 15 days;
- the product penetrates into leaf tissue, kills mining pests;
- Actellik is compatible with many drugs, except alkaline ones;
- availability, low price.
Flaws:
- insects that produce many generations per season quickly develop resistance to the active substance;
- processing cannot be carried out in the heat; at temperatures above 29 degrees, the drug loses its properties;
- strong pungent odor, toxicity;
- danger to beneficial insects.
Judging by the reviews from gardeners, Actellik is very easy to use; it helps to quickly get rid of pests when they colonize raspberries in small colonies. It is not designed for insect prevention, but only for control.
Chlorophos

A contact insecticide that blocks vital processes in the body of insects. The product gives excellent results in the fight against fleas, ticks, flies, gall midges and caterpillars of various butterflies, including cutworms. Chlorophos cannot be used together with drugs that have an alkaline environment and mineral oils.
Attention!
The drug has a medium hazard class; it can harm beneficial insects only through direct contact. In the human or animal body, Chlorophos quickly disintegrates.
For spraying, prepare a solution of 20 grams of Chlorophos per bucket of water. The treatment is carried out when the soil warms up to +13 degrees, after 10 days or during the period of swelling of the buds, the procedure is repeated. For better wetting of the shoots, 2 grams of the drug OP-7 or OP-8 can be added to the solution; soap cannot be used. Raspberries should be processed strictly in dry weather.
The drug has low volatility, but it is quickly absorbed into raspberry leaves and tissues. In bright, intense lighting, the active ingredients are quickly destroyed; prepared solutions can only be stored in plastic, glass or enamel containers in a dark room.
Topaz

Fungicide for the elimination and prevention of powdery mildew, rust, scab, gray rot and spotting, it suppresses infection, spores do not germinate. The substance quickly spreads throughout the plant, moving from old branches to young shoots. The effect lasts up to 2 weeks, regardless of the weather. The drug should not be used for more than 3 years in a row.
Topaz is one of the few products approved for use in private gardens, and it does not leave marks on the leaves and stems of raspberries. The drug is mixed with other pesticides; particular effectiveness is observed in tandem with Kuproxat.
To prepare a mixture against most diseases, take 1 ml of the drug per 5 liters of water, and when fighting rust, prepare a more concentrated solution - 2 ml per half a bucket of water. For one bush and the soil around it, use no more than 2 liters of the mixture. Treatment occurs during the period of bud formation. Bushes should be sprayed in dry weather, when there is no risk of precipitation.
Kemifos

The insecticide has a short action time, high toxicity and an unpleasant odor, but it very quickly destroys even the largest colonies of harmful insects. If you follow the safety rules described above, Kemifos will not harm humans. Application area:
- scale insects;
- flies;
- moth;
- caterpillars;
- weevil;
- raspberry beetle;
- ticks.
The substance has a contact, fumigation and intestinal effect on the pest, the result is noticeable almost immediately. Kemifos paralyzes insects, as a result of which they die, and auxiliary substances destroy the larvae and eggs of pests.
Pros of Kemifos:
- fast and reliable protection of raspberries;
- preventing the appearance of pests;
- low risk to human health.
- negative impact on beneficial insects and soil microorganisms;
- pungent, specific smell.
The first spraying is carried out as soon as the buds begin to swell, and the second, if necessary, before flowering. They cultivate the bushes and soil. It is not recommended to spray Kemifos in the wind; the optimal temperature for work will be 12–25 degrees.
To treat raspberries, take 20 ml of the drug per 20 liters of water and mix the solution. For 10 bushes you will need about 2 liters of mixture. The product cannot be mixed with anything, but in order to avoid insects becoming accustomed to the active ingredients, it is alternated with other insecticides.
Alatar

Insecticide to combat raspberry beetle and weevil. The product contains 2 potent substances - malathion and cypermethrin, which destroy the most resistant, unpretentious insects, as well as their offspring (eggs, pupae).
After treatment, the substance remains on the stems and leaves for a long time; rain washes it off weakly. However, you should be careful when using it, Alatar is highly toxic and can cause serious poisoning, neuralgia, burns, and allergies. Be sure to study the safety rules.
To prepare the solution you will need 5 ml of the drug per 10 liters of water, mix the liquid well. Use 2 liters of the mixture per bush; in the spring, the raspberry tree can be sprayed once, when the pest appears, but not later than the beginning of flowering.

A drug to eliminate fungal diseases. The period of protective action lasts a little more than 30 days. The substance slows down the growth and development of fungal cells, gradually destroys and destroys them. Copper sulfate is effective in the fight against anthracnose, curl, scab, spots, rust, septoria, as well as various rots and bacterioses.
The drug not only protects raspberries, but is also a foliar feeding; copper deficiency is often observed in plants planted on peaty and acidic soils. How to dilute and use:
- To treat raspberries you will need 50 or 75 grams of powder (depending on the degree of damage). First, half a liter of warm water is taken into a plastic bucket, the drug is poured, the liquid is thoroughly mixed until the crystals are completely dissolved, then, stirring, gradually add water to 10 liters. Metal containers cannot be used;
- before pouring the mixture into the sprayer, it must be filtered through a fine-mesh sieve;
- use 2 liters of solution on a raspberry bush, and also spray the soil. Copper sulfate is used in early spring before the buds swell.
The drug may cause irritation to the mucous membrane upon contact with solution or powder; follow safety rules. It is moderately toxic to bees and beneficial insects. With the correct dosage, the drug does not leave burns on the leaves.
Urea
Most summer residents, especially among beginners, are accustomed to perceiving urea (carbamide) exclusively as a nitrogen fertilizer. And experienced gardeners say that spring treatment of raspberries with urea leaf by leaf strengthens the plants and increases their immunity to a range of diseases and pests.
The bushes need to be treated before the buds swell, during the period when the daytime temperature is within 5 degrees Celsius. How to prepare the mixture:
- prepare 2 buckets, pour a liter of warm water into them;
- pour 500 grams of urea into one bucket, and 50 grams of copper sulfate into the second, mix the liquids thoroughly until the drugs are completely dissolved;
- Add 4 liters of cold water to each bucket and combine the liquids;
- strain the solution.
The bushes are sprayed so that the solution gets into every crack in the bark of the stems; it is in these places that harmful microorganisms and pest pupae overwinter. The soil around the bushes and between the rows is also cultivated.
Treatment with urea slows down the growing season; flowering will occur 10–15 days later than usual. This will protect the raspberries from late return frosts.
Urea, entering the plant, is absorbed by it through the bark and buds, which serves as a starting fertilizer for raspberries. 3 liters of product is enough for 10 square meters. The solution cannot be stored; it is used on the same day. If this amount of liquid is too much for a small raspberry tree, treat other garden trees and shrubs.

The drug consists of two dry components – copper sulfate and calcium oxide (in different bags inside the package), from which a “Bordeaux mixture” solution is prepared for treating raspberries against bacterial and fungal diseases:
- anthracosis;
- bacteriosis;
- leaf curl;
- scab;
- rot;
- spotting;
- rust;
- septoria.
The main components destroy the structure of bacteria and fungi, and when they come into contact with leaves and delicate tissues of the stems, they do not cause serious burns. The solution is not washed off by rain, the drug is valid for up to 30 days, which means it can be used for preventive purposes. Treatment is carried out as soon as the snow melts. You need to thoroughly irrigate the bushes and the soil, which is loosened before processing.
Bordeaux mixture cannot be used together with any drugs that are destroyed in an alkaline environment. If you use the product for several years in a row, copper will accumulate in the soil, which will cause the ovaries and leaves to fall off at the beginning of the season. The drug is toxic to humans, follow safety rules when working.
Depending on the degree of damage and the stage of development of the disease, the mixture is prepared in different concentrations, 1% for the prevention and elimination of the first symptoms of the disease, 3% for the treatment of advanced diseases.
Helpful Tips:
- When slaked with water, high-quality lime will dissolve rapidly and release heat. If, during the dissolution process, lime forms a lot of sediment with flakes and gives a weak reaction to water, it means that the material is of poor quality and cannot be used;
- Before filtering, you need to check the liquid - put a rusty nail in it; the presence of a red coating on the nail indicates a lack of lime. Plant tissue can be severely damaged by treatment. Lime mortar is prepared separately and gradually added to the mixture until the plaque disappears with repeated tests;
- Often the manufacturer puts litmus paper in the package to check the mixture; it is better to use it. Since if there is too much lime in the finished solution, the nail will remain clean, but the solution itself will lose its fungicidal properties;
- the copper solution is poured into lime; the opposite can only be done by adding the missing lime;
- Use only enameled, plastic, wooden or glass containers; a dry stick is suitable for mixing.
A 3% solution can burn already swollen buds, so it is important to carry out spring treatment as early as possible and not experiment when the plants begin to flow sap. When buds form, it is permissible to treat with a 1% mixture.

Broad-spectrum fungicide, effective in the treatment of fungal diseases. Spring treatment of raspberries with Oxychom is more of a preventive nature, helping to protect the bushes from purple spotting. With a low degree of fungal infection, the result of using the product is noticeable after a few hours, and it lasts for a long time.
The drug must not be mixed with anything. Treatments are carried out in dry weather, without wind, in the morning or evening. Spraying occurs during the period when young shoots grow 15 cm, before flowering. The drug enters the vessels of the plant through leaves, young bark and roots, protecting it from the inside.
To prepare the solution, take 30 grams of Oxychom per 5 liters of water, there is no specific consumption rate, the bushes must be treated carefully, paying maximum attention to the leaves and stems, and not the soil. The finished product cannot be stored.

Fungicide for the control of purple spot and powdery mildew, has a protective, eradicating, systemic effect. The substance penetrates the plant organs through roots, leaves and young bark, protecting them for a month. Fundazol helps cope with mites and aphids; it causes the death of the embryo or larvae inside the egg.
Attention!
Treatments with Fundazol cannot be carried out annually, otherwise resistance will occur. The drug is used once every 2 years.
Over the years, no shortcomings have been identified, but Fundazol has many advantages:
- the drug is not toxic to plants;
- increases winter hardiness;
- effective in all climate zones;
- long-lasting therapeutic and protective effect;
- possibility of mixing with other preparations, except lime and alkaline;
- the effect occurs a few hours after treatment.
Preventive spraying is carried out at the beginning of the growing season. Later spraying makes sense only when signs of disease appear; in advanced cases, when treating raspberries with Fundazol, the soil is also treated. Take 15 grams of the drug per bucket of water.
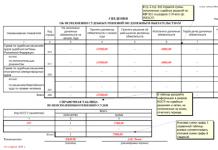
Score

Contact fungicide for the prevention and control of all fungal diseases of raspberries. The drug quickly eradicates not only developed fungi, but also spores; when used correctly, it protects plantings for a long time. The substances quickly spread throughout the plant, the greatest effectiveness is observed at temperatures from +14 to 25 degrees. It is better to use Skor at the first signs of illness.
Advantages:
- strengthening plant immunity;
- the drug helps to increase the length of shoots and the size of leaves, bushiness;
- increase in productivity;
- preservation of green mass until late autumn;
- ability to penetrate all plant organs;
- maintaining the effect in hot weather or during prolonged rainy periods;
- low toxicity for bees, animals and humans.
Flaws:
- frequent use causes resistance to fungi, the drug can be used once every 2 years;
- unpleasant odor;
- decreased activity at low temperatures.
For prevention, the bushes are sprayed before flowering, as soon as the day and night temperatures are above 14 degrees. To prepare the solution (to treat 100 square meters of plantings) you will need 4 ml of Skor per 10 liters of water. The finished mixture cannot be stored; it is prepared before spraying.
Skor can be mixed with drugs such as Topaz, Karate and Actellik, and joint use with products that have an alkaline reaction is unacceptable. You can add a little soap to the solution. When processing, the leaves are well moistened on both sides.
Hom

Contact fungicide based on copper, intended for the treatment and prevention of fungal diseases of raspberries. To prepare the solution you will need 20 grams of Homa per 5 liters of water. Metal containers cannot be used; first pour a liter of warm water, dissolve the powder, constantly stirring the liquid, add cold water to the required volume.
For 10 square meters use 1.5 liters of solution. Treatments are carried out in dry weather before flowering. If there is rain in the forecast, half a liter of milk is added to the finished mixture, so the solution will stay on the plant longer. The product is harmful to beneficial insects.
The finished mixture cannot be stored; the drug can be combined with other products except lime. How long the effect will last depends on the weather; in rainy spring, re-treatment may be required. Spraying should not be carried out at temperatures above 29 degrees.

Insecticide against aphids, mites, scale insects, moths, weevils, leafhoppers and whiteflies. The duration of activity is from 5 days to 2 weeks, the result is noticeable almost immediately. Spraying is carried out at the beginning of the raspberry growing season, as soon as the buds begin to bloom. During this period, adult individuals emerge from the pupae and eggs of pests; the drug is effective only against adults; it is not suitable for prevention.
You will need 75 grams of Karbofos per bucket of water; at least 1.5 liters of the mixture are used per bush. Spraying is carried out in calm, cool weather (from 15 to 18 degrees). The drug has a sharp, unpleasant odor that dissipates quite quickly.
Manufacturers produce the drug in different forms and concentrations; before preparing the solution, be sure to look at the information on the packaging (recipe and consumption rate for berry growers).
Karbofos is a contact chemical, it is not absorbed by the plant, it harms insects only with direct contact, so spraying is carried out very carefully, abundantly irrigating the leaves and stems from all sides. The product is alternated with other drugs, insects quickly get used to the components.

The best drug for fighting spider mites, and it also does an excellent job of treating and preventing fungal diseases (powdery mildew and rust). Sulfur does not penetrate into the plant; it releases vapors that stop the development of mites and destroy fungal spores. The protection lasts about 10 days, the first results are noticeable after 3 days.
Sulfur can be used with pesticides other than iron sulfate and those containing phosphorus compounds or mineral oils. There is a separate recipe for solving a specific problem.
The prepared solution cannot be stored. Spraying should not be carried out in heat and drought, as this can lead to burns on the leaves. The optimal temperature range is from 20 to 30 degrees.
Antitlin
The drug against aphids and caterpillars, made from tobacco dust, affects adults, eggs, pupae and larvae. Antitlin quickly affects pests, is not dangerous for humans or animals, is not phytotoxic, but can harm beneficial insects. Spraying can be carried out only before the raspberries begin to bloom, you need to carry out 2 treatments with an interval of 10–14 days. 500 grams of the drug are dissolved in 10 liters of water, and the soil is also irrigated.

The product helps to cope with many pests and diseases at any stage of development, however, DNOC is not recommended for use in private gardens. If there are no other options, you should follow all safety rules, in addition to the tips described above, you need to remember the following:
- the drug can only be used when the raspberry patch is located at a distance of 1 kilometer from the dwelling;
- DNOC is used no more than once every 3 years;
- Before processing, it is advisable to cover the ground around the bushes and between the rows with polyethylene; along with harmful organisms, the chemicals will destroy all the beneficial microflora of the earth;
- spraying is permissible only before the raspberry buds begin to bloom;
- there should be no people or animals nearby at the time of processing;
- DNOC cannot be used with other chemicals;
- the temperature during the treatment period should not be higher than 5 degrees; when it gets colder, the effect weakens, and in the heat the drug quickly evaporates.
Failure to adhere to the spraying schedule for young plants that are dormant can lead to burns on the bark and growth inhibition. The solution is prepared uniformly for all shrubs in the garden (50 grams of the drug per bucket of water). First, the powder is diluted in 2 liters of water, then, stirring, brought to the desired volume. Consumption – 15 liters per hundred square meters of plantings.

A systemic fungicide designed to protect against fungal diseases. Raspberries are rarely treated with it, but the substance copes well with the treatment and prevention of ailments such as gray rot, powdery mildew and white spotting. The active substance prevents the entry and growth of fungal mycelium on raspberry tissues. Spraying is carried out as soon as the temperature rises to +3 degrees.
Advantages:
- the drug penetrates the tissues a couple of hours after irrigating the plants;
- lack of phytotoxicity;
- low consumption of funds;
- When released into the soil, Horus causes virtually no harm to microflora.
Flaws:
- the drug does not penetrate into adult leaves, it is more effective at the early stage of raspberry growing season;
- efficiency decreases at temperatures above 25 degrees.
The effect lasts for 10 days; spraying should be done when the buds open. Take 2 grams of Horus per bucket of water. The resulting mixture is enough for 10 square meters of plantings.

Insecticide against aphids, mites, weevils and flea beetles. The drug acts very quickly on pests, the effect is noticeable within a few seconds after spraying. The substance causes nervous excitement in insects and damage to motor processes. The protection lasts about 2 weeks. Decis cannot be mixed with alkaline preparations.
To process raspberries, 1 gram of the drug is diluted in 10 liters of water, the mixture is enough for 100 square meters. There is practically no odor, the liquid or powder dissolves well in water. Spraying can be done before flowering begins. If it rains after treatment, you don’t have to worry, the precipitation will not wash away the drug. The bushes are treated completely, affecting the lower part of the leaves and young growth.
In Russia, the drug is produced in gram bags and 600 gram bottles; ampoules or 10 ml bottles are counterfeit.
Decis is not phytotoxic; after treatment there are no traces on the leaves and green stems of raspberries. You should work with the drug with extreme caution; if it comes into contact with the skin, it causes an allergic reaction and non-healing wounds appear. Ingestion of particles threatens serious poisoning, resulting in ataxia, weakness, and convulsions. Decis poses a serious danger to beneficial insects.
Biological agents
The basis of biological preparations are living antagonist microorganisms and their metabolic products. Accumulating in the soil, they negatively affect the development of fungi, bacteria and viruses, providing plants with long-term protection and strong immunity. The products are completely or low toxic, but do not neglect safety rules when using them.
Unlike chemistry, biological products do not give instant results; they act slowly, so it is better to use them as a preventive measure or at the very beginning of the development of diseases. There is no need to doubt the reliability of natural remedies; they have been tested by many gardeners around the world and have a lot of positive reviews.

Insecticidal, bacterial preparation for protection against winged insects, spider mites and beetles. Bitoxibacillin affects larvae, caterpillars and adult pests through the intestines, the effect is noticeable the very next day, insects cannot feed and die quite quickly. The favorable temperature threshold for Bitoxibacillin is +15–32 degrees.
You will need 70 grams of the drug per bucket of warm water, mix the mixture thoroughly and immediately begin spraying. The prepared solution cannot be stored; the raspberry tree is irrigated abundantly, touching all the bushes, branches, leaves on both sides and the soil. The first treatment should be carried out as soon as it gets warmer and the buds begin to bloom; if necessary, the procedure is repeated after 3 weeks. If after the first treatment it rains within 3 days, spraying should be repeated immediately.

Insectoacaricide against various types of mites, aphids, cutworms and other gnawing, sucking insects. The substance penetrates the body, causing paralysis and rapid death. However, individuals often experience addiction.
The product is safe for the environment, quickly disintegrates in water or soil, and is effective even in hot weather. The effect occurs 8–15 hours after processing the raspberry, the effect lasts from 5 to 15 days, it depends on the weather. The waiting period from processing to harvesting is 3 days. Fitoverm does not leave burns on plants; it is not advisable to mix it with other drugs.
Attention!
The effectiveness of Fitoverm directly depends on the weather. When the temperature drops to +17–24 degrees, the toxicity of the drug for pests decreases, and when it rises to 32 degrees, it increases significantly.
When applied to the soil, the substance does not penetrate the roots; it is advisable to carry out only superficial but thorough spraying (wetting the leaves on both sides).
To treat 10 raspberry bushes you will need 20 ml of Fitoverm per bucket of water. The drug is first dissolved in a small amount of water heated from the sun, then gradually, stirring the liquid, water is added to the required amount. A liter of solution is consumed per bush. The treatment is carried out in calm weather, when there is no risk of precipitation, the first time as soon as the pest appears, the second time after 7 or 10 days. Experienced gardeners recommend not using the drug more than 2 times during the entire season.
Agrovertin

The drug is intended to combat aphids, mites, scale insects, flies, mites and cutworms on raspberries. The substance paralyzes the insect, which leads to its death; the effect is noticeable within 3 or 4 hours after treatment. The leaves are sprayed evenly and thoroughly; it is advisable to treat the bushes at a temperature of 12–25 degrees, always in calm weather.
Despite the biological origin of the drug, it is toxic and poses a moderate danger to humans, animals and beneficial insects. Be sure to read the instructions and follow the safety rules. If the concentration is maintained, the substance will not harm plants.
The first spraying should be carried out as soon as the buds open, the next one after 2 or 3 weeks. Agrovertin should not be stored or mixed with other drugs. First, 500 ml of water is poured into a bucket, 5 ml of the drug is added, the liquid is thoroughly mixed, and another 3.5 liters of water are added.

Biofungicide to protect raspberries from gray, white, black and root rot, bacterial cancer, anthracnose, powdery mildew, and wilt. The spores and mycelium of the Trichoderma fungus inhibit pathogens by competing for food, releasing enzymes, antibiotics and other biological substances. The product is mixed with all biological products, except Mikosan.
To treat one hundred square meters of raspberry plantings you will need 40 grams of dry preparation or 100 ml of liquid per bucket of water. Spraying is carried out in early spring, as soon as the snow melts, the plants and soil are treated. The procedure helps suppress inactive pathogens and enrich the soil with beneficial microflora. Before flowering, you can carry out another, consolidating spraying.
3 or 4 days before treatment, the powder is diluted in 3 liters of warm water, mixed, covered and left to activate, then the required amount of water is added. Raspberries should be sprayed in calm, cloudy weather or in the evenings at temperatures above 8 degrees.
No protective measures are required when working with the drug; it is safe for humans, animals, insects and the environment as a whole. The prepared solution must be used within 6 hours after the second addition of water.

A drug for the elimination and prevention of all fungal and bacterial diseases. Fitosporin begins to act instantly, but the results will be noticeable in a day or two. The active substance is a spore culture, which in the process of life secretes fungicidal oligopeptides, they quickly spread throughout the vascular system of raspberries, suppressing the proliferation of pathogens.
Fitosporin is low-toxic, it can be used in private areas, it does not harm humans, pets, beneficial insects, plants, and it does not destroy soil microflora. The effect of the drug remains even after freezing and thawing.
Advantages:
- quick results;
- Possibility of use throughout the raspberry growing season;
- safety of use;
- the berries can be eaten even on the day of processing, the main thing is to rinse them well with running water;
- reliable protection for a long period of time.
Flaws:
- bacteria die in bright sun; bushes should only be sprayed in the evening or in cloudy weather;
- relatively high price.
The drug is compatible with many pesticides, stimulants and growth regulators, but it cannot be mixed with products that have an alkaline reaction. The method of preparing the Fitosporin mixture depends on the form in which it is produced.
| Type of drug | How to use |
| Powder | The product is diluted 1 or 2 hours before spraying, take 5 grams of powder per 10 liters of water, mix thoroughly. The first time the upper part of the leaves and the soil are sprayed, after 15–20 days the procedure is repeated, but now the foliage is irrigated from below. |
| Paste | This type of Fitosporin contains the biological fertilizer GUMI. To spray raspberries over the leaves and water them, take 3 teaspoons of paste in a bucket of water, mix, and let it brew for 2 hours. The product can be used at any stage of disease development, the effect is especially noticeable when the bushes are weakened and depressed. |
| Liquid | The product is used to root the growth of raspberry seedlings. The solution is prepared from 10 drops of Fitosporin and 200 ml of water, just this amount of the mixture is enough to water one bush. |
| Fitosporin-M Reanimator | A concentrate containing antibiotics, vitamins, enzymes and amino acids of natural origin. A biological product of this type helps restore the growth of weakened bushes due to diseases and other negative factors. To prepare the solution, take 1 part of the concentrate to 20 parts of water. Spraying is carried out twice with an interval of 10 days. |
The consumption of any spraying solution is liter per 10 square meters of raspberry plantings. You need to water the bushes with Fitosporin no more than 2 times a month; the solution is poured at the root after the main, abundant watering. Treatments can be carried out in any weather; the protective film is washed off by rain, but only partially. During periods when there is a lot of rainfall, the intervals between spraying are no more than 7 days, you need to have time to carry out the procedure 2 hours before the rain or immediately after.
Polyversum WP

The drug is based on a live predatory fungus, protects raspberries from diseases, strengthens the immune system and has a positive effect on the quality of the berries. The fungus creates a symbiosis with the root of the plant, protecting it from the penetration of pathogenic species of fungi. The product helps protect raspberry plantings from root canker, gray rot and dying shoots.
The first treatment should be carried out at the very beginning of the growing season, the second when the shoots grow to 20 cm. The emulsion is prepared strictly according to the instructions, it is given on the packaging. The product is safe for warm-blooded animals, it does not harm the environment, and has a beneficial effect on the composition of the soil.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies for protecting raspberries do not always live up to expectations, especially if the plants are severely affected by diseases and pests. However, studying the experience of experienced gardeners, we can conclude that in some situations they have a positive effect.
In order not to waste energy preparing solutions, decoctions and infusions, and to get good results, use folk recipes as an addition to the main treatment. Chemical preparations cannot be used after raspberry flowering, but infusions can be used, but the last treatment is carried out 2 weeks before the start of harvest, especially if the recipe is based on the use of bitter herbs.
When processing raspberries with folk remedies, branches, leaves, and soil around the bushes, in the inter-row spaces, are abundantly irrigated. Treatments are carried out in dry, windless weather, when there is no risk of precipitation. If it rains after the procedure, it is repeated immediately. You can irrigate plants only in the morning and evening. Prepared infusions and decoctions should be stored in closed containers in a dark, cool room.
 Marigolds are an excellent remedy for controlling aphids and cutworms. Biologically active substances found in plant tissues disinfect the soil and destroy pathogens of fungal diseases. For infusion, all parts of the marigold bush are used, including the roots. Cooking process:
Marigolds are an excellent remedy for controlling aphids and cutworms. Biologically active substances found in plant tissues disinfect the soil and destroy pathogens of fungal diseases. For infusion, all parts of the marigold bush are used, including the roots. Cooking process:
- the bucket is half filled with crushed marigolds, filled to the top with warm water, covered with a lid, and placed in a dark room for 48 hours;
- The infusion is squeezed out, filtered, and 40 grams of laundry soap are added.
To completely destroy aphids, you need to carry out 3-7 treatments every 3 or 4 days. The aroma of the infusion will drive away ants and cutworms. Spraying begins as early as possible so that aphids do not leave traces of their vital activity (twisted, gnawed young leaves and tips of shoots). In spring, fresh marigolds are not so easy to find; you can use dried flowers in the same quantity.
Tincture of bitter wormwood
The product is intended to combat the raspberry beetle, which can cause enormous damage to berry plantings. Wormwood infusion is rarely used in its pure form; for faster and better results it is mixed with marigold tincture.
To prepare the mixture, take 100 grams of dry, crushed plants (the amount of each ingredient is calculated for 5 liters of water). Marigolds infuse for 48 hours, and wormwood for 2 hours. Then both infusions are filtered, combined and 40 grams of laundry soap are added.
Female raspberry beetles arrive at the beginning of flowering, lay eggs in flowers and rosettes of young leaves, so the first repellent treatment must be carried out before flowering, the next fixative spraying is repeated after 2 or 3 days.
The smell of onions cannot be tolerated by aphids and mites; to prepare the infusion, take a half-liter jar of onion husks in 2 liters of water, leave for 2 days in a closed container. The strained concentrate is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:2, 20 grams of soap are added. Spraying is carried out once a week, paying more attention to the underside of the leaves. The first treatment occurs during the period when the first leaves begin to appear.
Birch tar
The product helps to cope with aphids and weevils on raspberries; the tar does not kill the pest, but repels adults with its pungent odor. Therefore, the mixture should be used when the raspberry buds begin to bloom. To work with tar, use old containers, because the product is difficult to wash off.
To combat aphids, rub 50 grams of tar soap on a fine grater, pour a liter of hot water into the shavings, and stir until completely dissolved. Add 5 ml of tar to the soap solution and pour the liquid into 20 liters of cold water and mix.
A suspension for getting rid of weevils is prepared from 10 liters of water and 60 ml of tar. The product does not dissolve well in ordinary water, so first add a tablespoon of liquid soap to it, only then add tar. The treatment is carried out when the leaves bloom and before the raspberries bloom.

An infusion of tangerine or orange peels is a good remedy against aphids and small caterpillars that infest raspberries in early spring. You can use dry raw materials, but fresh skins twisted through a meat grinder will give a greater effect. How to prepare the mixture:
- 1.5 kilograms of crushed fresh skins or a kilogram of dry skins are placed in a glass container, filled with 5 liters of warm water, closed with a lid and left for 5 days in a warm, dark room;
- the mixture is filtered through cheesecloth, 100 grams of the finished tincture is diluted in 10 liters of water, a tablespoon of liquid soap is added and the bushes are sprayed;
- the first treatment should be carried out at the beginning of the raspberry growing season, when the buds begin to open, the next 2 or 3 procedures are repeated with an interval of 7 days;
- the remaining concentrate is poured into separate containers with tight lids and stored in a cool place.
The same infusion helps not only drive away aphids, but also ticks; the treatment must be carried out very carefully, irrigating the bushes and soil.

Soda against aphids is a proven remedy; its advantages include quick results and the absence of any harm to plants. The substance increases productivity and, thanks to its bactericidal properties, protects against diseases. To combat aphids, baking soda and soda ash are used, but preference should be given to the second option, this product will saturate the plants with calcium.
When a soda solution gets on the insect’s body, it causes irritation and leaves minor damage. Pests try to leave the uncomfortable zone, but they are prevented by soap, which not only deters the enemy, but also increases the duration of the product. How to prepare the solution:
- 300 grams of laundry soap or 100 grams of tar soap are grated and dissolved in a liter of warm water;
- Add a teaspoon of soda ash to the mixture and mix thoroughly.
Aphids appear in raspberry fields in early spring, when the buds open and young shoots grow, carefully monitor the bushes, if the first individuals appear, begin to carry out treatments, usually 1 or 2 sessions are enough to completely get rid of the insect.
Whey or sour milk
The products are useful in treating raspberries against rust and late blight. Add 10–15 drops of pharmaceutical iodine to a liter of sour milk or whey, mix, and filter the solution. To treat other fungal diseases, prepare a solution from a liter of water, 500 grams of sour milk and 100 grams of salt. The bushes and soil are irrigated at the beginning of the growing season and at the first symptoms of diseases.

During the period of active growth of green mass and the growth of young shoots, raspberry bushes need additional nutrition. If you ignore fertilizing in the spring, the bushes will spend all their energy on growth, their immunity to diseases and pests will weaken, and the yield and quality of the fruit will decrease. Mullein is a complex fertilizer, which comes in handy in the spring!
Attention!
Before using organic fertilizers in the spring, you should assess the degree of soil fertility. For example, if you applied bird or cow droppings in the fall, it is better to refuse additional spring feeding with the same fertilizers.
A liter of fermented mullein is mixed with 10 liters of water, watering is carried out immediately after the snow melts, it is good if the solution is warm. It is not advisable to pour fertilizer under the roots of young bushes; it is better to distribute it along the rows. The solution cannot be stored; it is used immediately.

Ash is good for raspberries because it does not contain chlorine; the substance is harmful to the crop. The wood combustion product enriches the bushes with useful substances and protects them from various pests, especially aphids. Recipe for preparing ash-soap solution:
- 300 grams of ash are boiled in 10 liters of water for about 30 minutes;
- cool the liquid, add 40 grams of grated laundry soap or a tablespoon of liquid soap;
- The mixture is thoroughly mixed and used immediately; there is no need to strain it.
You can prepare not a decoction, but an infusion - 300 grams of ash are poured into 10 liters of water, the container is covered with a lid and left for 2 days. Add 40 grams of soap to the finished infusion and mix well. The treatment is carried out when the first greenery appears and 2 weeks before the start of flowering, the bushes are not just sprayed, they are literally bathed in such a solution.

Kerosene emulsion helps get rid of gall midges and stem flies. The product is not widely used among gardeners, it is rarely written about in blogs, but it is in vain that it gives very good results. Dilute 400 grams of laundry or green soap in a liter of hot water, add 800 ml of kerosene little by little and pour the mixture into 9 liters of water. The resulting emulsion is used immediately; the bushes are treated in the period before the buds swell, in calm weather.
Garlic and mustard tincture
Volatile substances in garlic drive away pests; the plant is effective against many fungal and bacterial diseases. If you combine garlic and mustard infusions, you get double protection for raspberries from many ailments and unwanted guests. How to prepare the mixture:
- 100 grams of cloves or green garlic are passed through a meat grinder, poured with a liter of water, covered with a lid, and left to infuse for a day;
- the resulting infusion is filtered and diluted in 5 liters of water;
- 50 grams of mustard are poured into a five-liter bucket of water and left for 2 or 3 hours;
- Combine both infusions, add 40 grams of soap, mix.
The first treatment is carried out when the raspberries acquire young leaves, subsequent sessions every 7 or 10 days. In total you need to carry out 3-4 sprayings.
Boiling water treatment
The procedure allows you to destroy pupae, weevil larvae and other pests overwintering in the soil, as well as fungal spores. Watering the bushes with hot water (75–80 degrees) is carried out after the snow has melted, when the sun is already warming the soil, but the buds have not yet begun to swell. Plants are watered with a watering can so that water falls on the stems and roots. Frozen ground will prevent boiling water from harming the plant. About a liter of water is poured under the bush.
In spring, raspberries need to be provided with the most reliable protection. For example, choose something from chemical or biological agents and supplement them with folk recipes. Coupled with compliance with the rules of agricultural technology, you will forever forget that growing raspberries may be accompanied by any problems.
If you do not monitor the condition of your raspberry bushes, then various pathogenic bacteria (fungi) and pests will certainly settle on them, which will reduce the yield, and some plants may even die. Therefore, you need to regularly carry out preventive measures and spraying of raspberries.
In this article you will find information about how to treat raspberries in the spring against diseases and pests, about the features and timing of the procedure.
Obviously, any treatment is carried out to protect the plant (berry crop), so that it is healthy, and therefore produces a bountiful harvest.

Pests

- Raspberry-strawberry weevil- destroys flower buds during oviposition, which occurs during the period from the budding of strawberries to the appearance of ovaries on raspberries.
Perhaps this is one of the most common and harmful pests of raspberries.

- Raspberry beetle- damages buds and flowers (eats huge wide holes in them). Berries developing from flowers damaged by beetles have an ugly shape, in other words, their quantitative (weight) and quality characteristics are reduced, moreover, they are susceptible to rotting, especially in damp, humid weather

- Raspberry or raspberry stem fly- lays eggs during raspberry flowering on the apical leaves (tips of young shoots). Next, the hatched larvae gnaw through the top of these shoots, as a result the tops of the shoots turn black, wither and dry out.


Video: why raspberry shoots wither - raspberry fly
- Raspberry glass(more often called currant) - the caterpillars bite into the core of the shoots, as a result, the damaged branches stop growing, wither and dry out;
Damaged shoots should be cut back to healthy wood, and infected parts should be burned.
 glass butterfly
glass butterfly
- Raspberry bud moth;
- Stem and shoot gall midges;
- Mite;
Diseases

- Anthracnose- one of the most harmful diseases for this crop. Infection of raspberries with this fungus leads to the death of the ends of the shoots and fruit branches even before the berries ripen. As a result, they become mummified and the leaves fall off ahead of schedule.

- Septoria (white spot)- appears as white spots on the leaves and trunk.

- Raspberry purple spot (didimella) - is characterized by the formation of purple girdling spots on the raspberry trunk closer to its base, which affect the buds, subsequently the shoot completely blackens and dries out.


- Gray rot(botrytis) - the berry becomes covered with gray mold and literally rots.
As a rule, gray rot especially affects remontant raspberry varieties in August-September if the weather is humid (rainy).

Video: treatment of raspberries for diseases - anthracnose, septoria, didimella (purple spot), gray rot.
Note! For remontant varieties, fungal diseases pose almost no danger (except perhaps gray rot), but for ordinary varieties - even so...
- Rust.


- Powdery mildew.

- Viral mosaic.

- Stem and root cancer.
Preventive measures to protect raspberries
Agrotechnical measures to control and protect raspberries from diseases and pests:
- Digging up the soil (shallow loosening) and plowing between rows is an excellent measure to combat pests that overwinter in the soil (raspberry beetles, weevils, flies, glass beetles).
Along with loosening, it is also necessary to destroy weeds.
- Mulching- one of the ways by which you can close the main source from which all diseases and pests come (come out), namely the soil. You can mulch with humus or rotted sawdust.
- Maintaining normal plant density, because Fungal diseases develop especially strongly when plantings are thickened. Accordingly, you need to get rid of the thickening excess growth.
- And of course, you can plant the most raspberry varieties resistant to diseases and pests.
- Regular pruning of fruit-bearing and diseased (infected) shoots. Wherein raspberry pruning they do exactly that, but it is also possible.
In general, if you notice damaged or infected shoots, they need to be removed in a timely manner (cut out completely or to healthy wood) and burned.
In addition, you can use mechanical method of struggle. Namely, shake off the beetles from the bushes into special gauze nets, linen or gauze shields and then destroy them.
Biological control with pests is planting strong-smelling plants, for example, calendula, which with its strong smell will repel insect pests (the same weevils).
Unfortunately, the use of strong-smelling herbs, as a rule, does not give much effect...
How to properly process raspberries in spring
- Use individual protection means when preparing solutions and carrying out direct processing.
- Spraying must be carried out in dry and windless weather.
- Attentively read the instructions for the drug, including at what temperature the processing should be carried out.
Note! It is useless to work with colloidal sulfur in cool weather, as well as with the sulfur-containing drug Tiovit Jet: the optimal temperature is +25-30 degrees, only then will the sulfur evaporate and act.
- You need to spray not only the bushes themselves (leaves), But And soil between bushes or mulch(if your bushes are mulched), since pathogens of diseases and pests (fungal spores and pest eggs) overwinter in the soil.
Important! If raspberries last season or this season was very heavily affected by diseases and pests, then it is recommended remove all old mulch, and then carry out processing.
- You can cook tank mixture(from 2 selected products), having previously dissolved each drug separately in water (according to the instructions). Then pour the resulting solutions into a common container (sprayer) and carry out a comprehensive treatment against diseases and pests.
Question! How to check drug compatibility?
If no sediment forms after mixing the preparations, they can be used in a tank mixture.
- At each stage of spraying, preparations with different active ingredients should be used so that the pests do not develop resistance (they do not develop addiction). However, as an option, you can alternate them, including every season.
Are chemicals dangerous? Is it better to use biological products?
Preparations for treating raspberries against diseases and pests can be of either biological or chemical origin.
Of course, it is believed that it is safest to spray with biological products or use folk remedies, because they are absolutely harmless to human health. However, it is in the spring (before fruiting) that chemical preparations can be used without any consequences, especially if the affected area is quite extensive. The point is that after the waiting period, all harmful substances(pesticides) are displayed long before the berries ripen and are picked.
When to process raspberries:schedule and scheme of treatments
After you have done this, it’s time to treat the remaining shoots from diseases and pests.
Thus, as a rule, the following scheme for processing raspberries in spring is used:
- early spring (before or at the beginning of bud break);
- before flowering (during the period of bud development) - the most important;
- after flowering and the formation of the first ovaries;
- after harvest (summer-autumn).
At the same time, at each stage it is worth spraying the bushes both against pests and diseases.

Early spring (before or at the beginning of bud break)
It is recommended to carry out the first treatment of raspberries against diseases (wintering fungal infections) on bare trunks, and it is advisable to spray them before they bloom, but it is also possible at the beginning of their bloom.
Also required cut out stems affected by stem gall midge and spend loosening to disturb the wintering sites of raspberry flies, shoot gall midges and other pests.
During the period of bud development (before flowering)
2-3 weeks after the previous treatment, you need to spray again. In this case, the treatment should be done before flowering!
The fact is that processing raspberries before flowering is considered the most important.
During the period of bud protrusion (before flowering), it is necessary to carry out treatment against such a dangerous pest like raspberry weevil. For example, you can use one of the following chemical preparations (insecticides): Iskra M, Fufanon-Nova (Expert), Taran, Alatar, Actellik.
Treatment with the above drugs will also be directed against:
- raspberry glass;
- raspberry fly;
You can also trim the shoots below the location of the raspberry fly larva and then burn them.
- raspberry beetle;
In particular, the raspberry beetle can simply be shaken off the bush early in the morning and then destroyed.
- raspberry bud moth;
- ticks.
By the way! It is against ticks that Vertimek is most effective, but Masai and Actellik can also be used.
Against ticks (as well as aphids), you can also try using biological insectoacaricides - Fitoverm or Actofit, Bitoxibacillin, Biokill.
You also need to carry out treatment of raspberries against fungal diseases (various spots)— purple spot (didimella), anthracnose, septoria, rust, etc. For this, you can use special preparations, for example, Agromedicine or Chistoflor (analogs).
However! Against pests who are planning to spend the winter in your raspberry patch, it is more effective to use one of the following chemical insecto-acaricides - Iskra M, Fufanon-Nova, Fufanon Expert or Karbofos (all preparations with the same active ingredient, i.e. analogues).
Against diseases (wintering fungi) - Agromedicine or Chistoflor.
How to treat raspberries in spring: preparations for diseases and pests
To protect your raspberry plant from diseases and pests, there are quite a large number of different products, so you need to familiarize yourself with their list in advance and choose the ones that are right for you (including cost). You also need to decide when, how and in what quantity you will use them.
Important! The instructions for each drug always indicate when (in what time frame) and how many times they can and should be processed.
So, all means for spring processing of raspberries are divided into 3 groups:
- fungicides (drugs to combat diseases);
By the way! In this case, fungicides are divided into preparations protective (preventive) and curative action, and protective and healing (complex).
Of course, it is optimal to use complex drugs that have protective and therapeutic effects.
Accordingly, if you noticed signs of illness, then no preventive (protective) means will help you, only healing (or protective-healing).
- insecticides (pest control products);
There are also acaricides- means to combat ticks. They are more often called insectoacaricides, because they also destroy other pests.
- insectofungicides (complex preparations that act simultaneously against pests and diseases).
By origin, these products (fungicides and insecticides) can be:
- chemical (the same “chemicals”);
- biological (biological products).
Of course, there are folk remedies, for example, various solutions and infusions based on herbs, but their effectiveness is very, very limited.
Biological agents against diseases and pests
Biological products insecticidal action(against pests):
Aversectin S, enteric-contact insectoacaricide against ticks, aphids and other pests)
Aktofit and Fitoverm are complete analogues.
- Bitoxibacillin ( Bacillus thuringiensis var. thuringiensis, intestinal insectoacaricide against weevils, mites, leaf gall midges and other pests).
- Biokill ( Abamectin, enteric-contact insectoacaricide against ticks and aphids).
Unfortunately, in the fight against fungal diseases of raspberries, biological products (biofungicides), as practice shows, do not show decent results. However, you can try the same.
Or one of the preparations based on mushrooms of the genus Trichoderma(Trichocin, Trichoplant and Trichoderma veride), as well as Planriz or Rizoplan.
Chemical fungicides (disease control agents)
For spring spraying of raspberries against diseases, you can use the following: fungicides:
Important! For one treatment you only have to choose one drug (fungicide), and then use a new one (preferably with a different active ingredient) or alternate.
- . Active ingredients - copper sulfate + calcium hydroxide = lime, a protective contact fungicide (a 3% solution of Bordeaux mixture is applied before buds open and 1% after they open) against spots and other fungal diseases.
- . Active substance - copper sulfate, a protective contact fungicide (3% solution before buds open and 1% after buds open) against various spots and other fungal diseases.
- Abiga Peak. Active substance - copper oxychloride, a contact fungicide with protective action against anthracnose and septoria (white spot), as well as against ticks.
Abiga-Peak = Hom = Copper oxychloride.
- Colloidal sulfur- contact fungicide with protective action against anthracnose and septoria (white spot), as well as against ticks.
- Thiovit Jet. Active substance - sulfur, a contact fungicide and acaricide against powdery mildew and mites.
- Topaz. Active substance - Penconazole (Topaz) , a systemic protective fungicide against purple spot (didimella) and gray mold.
- Agromedicine. Active substance - Propiconazole
- Clean flor. Active substance - Propiconazole, a systemic fungicide with protective and curative action against purple spot (didimella), anthracnose, septoria, rust.
Agrolekar and Chistoflor are complete analogues, as is Propi Plus.
Chemical insecticides (pest control agents)
To treat raspberries against pests, you can use the following: insecticides:
- Actellik. Active substance - Pirimiphos-methyl (Actellic), a systemic insectoacaricide of contact-intestinal action against beetles, aphids, mites and other pests.
- Ram. Active substance - Zeta-cypermethrin, enteric-contact insectoacaricide against strawberry-raspberry weevil, raspberry beetle.
- Iskra M. Active ingredient: Malathion (Karbofos),
- Fufanon-Nova. Active substance - Malathion (Karbofos), enteric-contact insecticide against raspberry beetle, raspberry-strawberry weevil, mites, raspberry bud moth, aphids, gall midges.
Iskra M = Fufanon Expert = Fufanon-Nova = Karbofos.
- Alatar. Active ingredients - Malathion and cypermethrin, enteric-contact insectoacaricide, against raspberry beetle, raspberry-strawberry weevil, mites, raspberry bud moth, aphids, gall midges.
- Vertimek. Active substance - Abamectin, insectoacaricide of intestinal contact action against ticks, aphids and other pests.
- Masai. Active substance - Tebufenpyrad, an acaricide of enteric contact action against ticks (has a strong ovicidal effect against summer oviposition).
Insecticides against gastropod pests of raspberries - slugs and snails:
- Slug Eater ( Metaldehyde, enteric insecticide against slugs and snails);
- Storm ( Metaldehyde, enteric insecticide against slugs and snails).
Slime Eater and Thunderstorm are complete analogues.
Folk remedies
You can try to use against pests:
- Infusion of wormwood or marigold.
- A solution of birch tar with liquid soap (10-15 g of tar and 40 g of soap per 10 liters of water).
- Dust the tree trunks of raspberry bushes with tobacco dust or wood ash.
Video: folk methods of pest control on raspberries without chemicals
Thus, now you know when and what to spray raspberries in the spring to protect your bushes from diseases and pests. May your raspberry bushes be healthy and your harvest rich. Good luck!
In contact with
Proper care of raspberries in the spring is the key to their further growth and a bountiful harvest.
Improper pruning, lack of fertilizing, lack of treatment against pests and diseases will further affect the harvest of this tasty, healthy berry.
Do you want to grow such beautiful raspberries?
What to do with raspberries in spring
The list of spring work that needs to be done in the raspberry garden in the spring includes:
- pruning after winter;
- feeding;
- treatment of shrubs from pests.
The raspberry leaves have already blossomed
Caring for raspberries in spring begins in early or mid-March. It depends on the region where the berries are grown.
To begin work, the air temperature must be at least +5 degrees.
Trimming
The first step is to prune the raspberries. It must be done as early as possible in order to have time to carry out all the work before active sap flow begins.
In spring, it is better to prune raspberry bushes before sap flows.
Spring pruning is carried out in two stages.
First, shoots that are affected by stem gall midge are removed.
You can detect traces of the vital activity of this pest with the naked eye, especially while there are no leaves on the bushes. Swellings are visible at the bottom of the shoots and stems. If you cut them, you will find gall midge larvae. Remove damaged, heavily frozen, weak shoots.
Regardless of the form of planting, raspberries are thinned. Thickening of plantings affects productivity. With the tape form of cultivation, up to 25 stems are left per linear meter, with the bush form - from 8 to 12.
At the second stage, the raspberries are pruned again when they begin to grow. The top trimmings are shortened to the first overwintered bud.
Fertilizing raspberries in spring
Urea is a popular fertilizer for raspberries.
The most important fertilizers for raspberries are nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus, but she also loves organic ones. In spring, raspberries are fed with nitrogen. Lack of nitrogen leads to slower growth of shoots, shredding of leaves and a sharp decrease in yield.
Do not forget about phosphorus and potassium fertilizers. A lack of phosphorus is manifested by weakening of shoots, and a deficiency of potassium not only has a bad effect on yield, but also greatly reduces winter hardiness.
Scheme for fertilizing raspberries in spring
- After the snow melts, even before loosening the soil, nitrogen fertilizers are applied (10-15 g of ammonium nitrate or 10 g of urea per 1 sq.m.). Along with nitrogen fertilizers, it is also good to add a glass of ash under each bush. Before applying fertilizing, the plants must be watered well.
- After loosening the soil, apply organic fertilizers as mulch. This can be humus, peat compost, straw manure, etc.
- In May, raspberries are fed with mullein, diluted at the rate of 500 ml per bucket of water.
Treatment of raspberries from pests and diseases in spring
In the spring, it is important to take measures to protect bushes from pests and diseases.From the raspberry beetle
The photo shows a dangerous pest for raspberries
Raspberries are treated against beetles immediately after the snow melts and the shoots are tied, generously spraying the bushes and ground with Nitrafen solution.
Before flowering, treatment is carried out with a mixture of infusions of marigolds and wormwood.
Two-time treatment of raspberries with biological preparations Fitoverm and Agravertin also shows good results.
From raspberry gall midge
Traces of raspberry gall midge on the bushes
To combat gall midges, you need to inspect the raspberries as carefully as possible after wintering, and if growths are detected, cut out and burn the affected shoots.
At the stage of bud appearance, raspberries are again sprayed with Fufanon or Actellik.
From raspberry fly
Common pest for raspberry bushes
Prevention consists of spring mulching of tree trunk circles. This makes it difficult for insects to leave their wintering areas. In early May, before flowering, you can treat raspberries with Actellik, Fitoverm or Agravertin.
For diseases (anthracosis and gray rot), raspberries are treated with Nitrafen solution in early spring, with Bordeaux mixture at the stage of bud break, and at any time with Fitosporin.
With the first warm days of spring, not only necessary and useful plants and living creatures awaken from winter sleep. Insects begin preparing for the season, causing damage to the future harvest. How to properly treat raspberries in the spring against pests, what preparations or folk remedies to use so that the healthy berry remains intact is a question that concerns most summer residents.What needs to be done before the buds open?
Until the buds burst, the tender young raspberry leaves are practically invulnerable. This period should be used to carry out a number of measures to protect the bushes from pest attacks.
The first step is to cut out raspberry branches that did not survive the winter well (broken or frozen), remove plant debris that has accumulated over the winter - they will not only interfere with the normal development of overwintered shoots, but will also serve as a medium where pests - weevils, gall midges - will begin to multiply.
Raspberry waste is not put into compost, as fermentation will not prevent the proliferation of pests. Dry residues are burned, and the ash is used for fertilizer.
- in the second half of March - in the south of the country;
- in mid-April - in the Middle Zone, in the Central Black Earth Region;
- in May - in the Urals, in Siberia.
Raspberry fields are sprayed with solutions of biological products “Agravertin” or “Fitoverm”. “Poliversum VR” received good reviews, at the same time protecting plants from pathogenic microorganisms - pathogens. These drugs provide a wide spectrum of action and help get rid of various types of pests. Treatment is carried out in the early evening hours, since these products quickly decompose in the light.
It is useful to spill boiling water on the soil under the bushes. The procedure promotes disinfection and destroys some of the pests and their larvae hiding in the ground. It is carried out when the ground warms up a little.
Raspberry pests and ways to combat them
Although broad-spectrum insecticides are effective and easy to use, the beautiful raspberry attracts “atypical” pests. They have to be dealt with using special-purpose drugs. An attentive summer resident always knows which insects threaten his farm and prepares the necessary remedies in advance.
The presence of its colonies is determined by swellings on the shoots, especially young ones. Gall midges weaken stems, make them brittle, prone to freezing, and contribute to the development and spread of fungal infections.
In early spring, the raspberry bush is carefully examined, shoots with characteristic growths are cut out and burned. Then the treatment is carried out in 2 stages.
- At the first stage, in the spring, the soil is loosened to a depth of 15 cm, sprayed with Fufanon solution at the rate of 20 ml of product per bucket of water.
- The second treatment is carried out when the buds begin to form. The bushes are sprayed with “Fufanon” (10 ml per 10 l of water) or “Aktellik” (15 ml per 10 l). Consumption rates for solutions are 200 ml per bush.
There are no traditional methods of combating gall midges.
Aphid
Colonies populate the apical parts of young shoots, focusing on the underside of the leaves.
Treatment against aphids is carried out before bud break with Actillicom, Karbofos or folk remedies.
A pest that causes damage only to raspberries. Its larvae feed on the tender greenery of young and apical shoots, while simultaneously spreading viral and fungal infections.
Stem fly larvae overwinter in the soil under raspberry bushes, so prevention begins with removing debris and pouring boiling water on the soil. Then the plantings are mulched to make it difficult for the pest to reach the surface.
Treatment with chemical or biological preparations is carried out before flowering begins. “Fitoverm”, “Agravertin”, “Aktellik” are effective against stem flies.
Folk remedies only repel the pest, but are ineffective in the fight.
Massive attacks begin during flowering. The pest devours buds, flowers, young leaves, ovaries, and is capable of destroying all hopes for a harvest in a short time.
Preventive measures are carried out simultaneously with the first. Immediately after tying the stems, the bushes and soil are treated with a Nitrafen solution at the rate of 200 g of the drug per 10-liter bucket of water. You need to spray generously, not sparing the solution.
The second treatment is carried out immediately before flowering. Use Actellik or Fitoverm spraying. After 20-30 days, the procedure is repeated.
Folk remedies work against the raspberry beetle. Solutions for spraying are prepared:
- 200 g of crushed dried marigolds are poured into 10 liters of hot water, left for two days;
- 200 g of dried wormwood herb are infused for 2 hours in 10 liters of hot water.
The prepared solutions are mixed, then filtered, and the raspberries are generously irrigated.
Weevil
The voracious beetle not only feeds on young leaves, weakening the shoots - the female lays eggs in the buds, the larvae quickly eat the delicate tissues and pupate. By mid-summer, the second generation of the pest continues its dirty work, and in the fall it retires to the ground for the winter.
To combat the weevil, prepare a solution of the drug “Iskra-M” at the rate of 1 ml per 1 liter of water. Spray the bushes at the budding stage.
Spraying the pest 2-3 times in the spring with pine concentrate, sold at the pharmacy, repels the pest from the raspberry tree. For 10 liters of water take two tablespoons of the product.
Bud moth
The pest larvae settle in the raspberry buds and live in them, feeding on the juices of the plant, preventing the shoots from developing. In the first days of spring, before the buds open, it is useful to treat the bushes with Bordeaux mixture or the preparations “Iskra” and “Decis”.
Female pests lay eggs on raspberry shoots. The larvae eat young shoots, causing the bush to dry out. The presence of the pest is recognized by elongated growths on the branches, similar to growths from gall midges.
Affected shoots discovered during inspection of the bush in the spring are cut out and sprayed with a solution of Karbofos or Actellik.
Raspberries and garden blackberries have almost all common pests. When processing raspberries in the spring, you should not forget about their relatives.
Wormy raspberries - what to do
It's a shame when a beautiful, fragrant berry contains an unpleasant addition - one or more worms. This “stuffing” is inhabited by two pests, the raspberry beetle and the grape budworm.
What to do to get rid of the raspberry beetle is described above. Let's figure out how to get rid of bunchworm worms in berries.
The leaf roller settles not only on raspberries, but also on currants, grapes, hawthorn, and buckthorn. If these plants grow on the site, the treatment is carried out comprehensively.
The leaf roller butterfly flies out early, when the air warms up to 12-15°. Eggs are laid in newly formed buds. The caterpillar (worm) appears in the second week after laying. It feeds on buds, then on the ovary. Within a month, the worm matures, pupates and soon turns into a butterfly. The insect lays eggs, but only in berries that have begun to ripen. The third generation eats already ripe berries - the summer resident gets wormy raspberries. Leaf roller caterpillars not only hopelessly spoil the crop, but also infect the raspberry tree and adjacent plantings with brown rot.
To properly process raspberries, keep an eye on the butterflies. As soon as the intensity of their summer has decreased, on the 4th or 5th day they begin spraying. Solutions are prepared on the basis of chemical preparations “BI-58”, “Intra-Vir”, “Actellik” or “Lepidotsid”, “Bitoxibacillin” (these are biological agents), following the attached instructions.
Remontant raspberries are treated for pests according to the same rules and within the same time frame. However, it should be noted that pesticides and infusions of poisonous herbs (for example, hellebore against bunch budworm) are not used from the moment flowering begins until the end of harvest.
Folk remedies against raspberry pests
In addition to the above-mentioned infusions of marigolds and wormwood, other folk remedies help cope with pests:
- Spraying with ammonia in the spring not only charges the bush with nitrogen, but also helps get rid of early-waking pests. The treatment is carried out when the average daily temperature is +10 °C, with a solution of 2 tbsp. l. product, a bucket of water and a small amount of green or tar soap - for adhesion.
- Garlic infusions help in the fight against aphids and weevils.
- The bush can be sprayed with tansy infusion against the raspberry beetle.
Many ornamental flowering plants have the ability to repel pests. Planting them next to raspberries will be a good help.
- Marigolds repel aphids, weevils, and nematodes.
- Wormwood protects against leaf rollers.
- Yarrow is planted to prevent aphids and spider mites from bothering them.
- Dwarf chrysanthemums repel weevils.
- Melissa and mint are also useful - the aroma of their leaves is intolerable to ants, and accordingly, the number of aphids decreases.
Summer residents who are experienced in pest control plant next to raspberries, pyrethrum (Caucasian chamomile), and garlic. This proximity makes it possible to completely abandon the use of pesticides.
The volume and quality of the raspberry harvest depends on the timely prevention of the appearance and reproduction of pests. All measures here are good, but the approach must be comprehensive - the treatment of raspberries is carried out in conjunction with the treatment of other plants on the site, since most of the enemies threaten other crops.