All welding devices are made the same. Everywhere a circuit is used where powerful field-effect transistors act as switches. You can find a wide range of these devices in stores. However, their cost is often very high. Therefore, many people decide to make a welding inverter with their own hands. For work at home, in the garage and in the countryside, it is quite possible to get by with electric arc welding. It is done using a transformer or inverter device.
Transformer type is reliable and durable. It can operate at any current. But it has two big disadvantages: when the voltage drops below two hundred volts, it automatically turns off. And it also has a lot of weight.
The inverter device was invented recently. This article will talk about this type of welding equipment.
Advantages and disadvantages of an inverter device
The advantages are the following parameters:
- Weight - no more than five kilograms. This is an undeniable advantage, because it makes it possible to easily transport it or simply move it within the workshop.
- It is able to continue to work even when the voltage drops, without turning off, like a transformer device.
- The device operates with direct and alternating current.
Conditional disadvantages can be called:
- High cost of the device.
- It must be periodically cleaned of dust.
But due to the fact that the device will be made by hand, the first disadvantage is not so relevant. Periodic maintenance is necessary for any device, so cleaning will guarantee its smooth operation.
Also, for the operation of the device, you must acquire special skills and be careful when operating it.
What is needed for production?
A transformer from a regular microwave oven is perfect for making a simple welding inverter with your own hands. It consists of coils, iron, enamel and copper wire.
The coils are used as primary and secondary windings, and enamelled copper wire is wound around an iron core.
Each coil has its own number of turns. The primary winding is necessary for the operation of the electrical network, and in the secondary, due to induction, current is generated.
The current can reach one hundred and thirty amperes, but there will be only twenty amperes on the primary winding. For a good welding connection, electrodes no larger than three millimeters in diameter are required. Such a machine can perform welding with reverse polarity.
Reducing the number of turns
In order for a welding inverter, created with your own hands, to work normally, you need to reduce the voltage (since the microwave transformer produces over two thousand volts) and increase the current value.
For this purpose, the secondary winding is rewound with another wire, which is coated with enamel. To do this, carefully cut and remove the old winding. The number of turns and cross-section of the new wire depend on the transformer used. But it won’t be difficult to calculate it. Any physics textbook can help with this. Another option is to use an online calculator. At the end of the work, the new winding is coated with a special current-insulating varnish.
DIY welding inverter circuits
The following diagrams will help you better understand the operating principle of the device. Study them carefully.


Assembly
In order for a homemade welding inverter, made with your own hands, to be easy to use and transportable, it will need a housing. This is where all the parts will be mounted.
The transformers are attached one after the other, and the current is reduced to fifty amperes. The primary windings are mounted in parallel, and the secondary windings are mounted in series. Thus, you get a device with a load of sixty amperes and thirty-eight volts at the output.
The parts are installed on the factory board. In this case, the power supply, drivers and board are fixed separately. The power part is separated from the board by a metal sheet attached to the housing. The control conductors are connected.
All power paths must be reinforced with copper wire.
A special radiator is attached to remove heat. The durability of the entire device depends on its quality.
The resistance for the power supply is selected so that there is a supply of twenty volts. Input rectifiers must have sufficiently powerful radiators.
A thermal sensor is inserted into the housing to record the maximum temperature.
The control unit is a PWM controller with one configuration channel. Its purpose is to ensure arc combustion and stability of operation. The built-in capacitor will affect the strength of the welding current.
Cooling system features
Two fans are mounted on both sides of the future welding inverter with your own hands. Thanks to them, air is drawn out. To obtain it, up to several dozen through holes are drilled from the bottom of the housing.

Purpose of the device
This type of welding inverter, made with your own hands, is much more convenient and easier to use than a transformer device. In addition, the quality of the seam is better. It is used in welding:
- Non-ferrous metal.
- Black metal.
- Thin steel sheets.
- Stainless steel.
Device parts
After the circuits of welding inverters created by yourself, the design and assembly have been studied and understood, proceed to purchasing parts for the device. They can be purchased in stores, but it is better to use the Internet, since there is a much larger selection on virtual platforms, and the cost of the parts is lower.
However, in the pursuit of cheapness, we must not forget about their proper quality, because not only good work, but also safety in general depends on this.
So, you need to purchase:
- power unit;
- power units;
- scotch.
- drivers.
You will also need to buy other accessories, such as a holder, cable, etc.
DIY welding inverter repair

The welding device must be used correctly and inspected periodically. If problems are found, the welding inverters need to be repaired (it’s quite possible to do this with your own hands).
To this end, if there is poor contact, all parts are separated, themselves and their surfaces are cleaned, and then connected again.
If there is a low network load, but the device consumes a large current, then the cause is a short circuit of the turns. To fix the problem, you need to rewind the coils and replace the insulation.
If the welding arc constantly disappears, then the reason for this is winding breakdown.
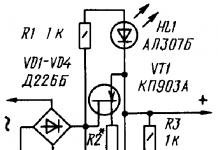
Semi-automatic welding inverter (made with your own hands) Pomelova V.N. Advantages

This device is suitable for accurate and fast spot welding. When welding in a carbon dioxide environment, a very small zone is subject to thermal influence; with a painted part, the paint will burn out only in a narrow strip, the melting of the electrode wire occurs very quickly, and even if the parts have different thicknesses, the weld will be of the same quality. In addition, carbon dioxide is easier to obtain than acetylene and oxygen, and welding is quite easy to master.
Design
The base of the device is transformer T1 for welding, which is connected to a network of two hundred and twenty volts (turned on by pressing the “Start” button, which is connected to the VT3 cascade).
A silicon diode VD14 is connected to the same VT4 switch, which can be attached as a temperature sensor during prolonged operation. But if the device does not overheat, then you can safely do without it.
IC DD1 155LAZ provides all phases of signals for output nodes. It is powered in the same way as VS1, VT1, VS2, VT2, VT3 and 4 with a voltage of five volts from the rectifier.
Powerful rectifier diodes can be D151-160, D160-200, V200-6, V2-200-9.
There should be no questions in the selection of other elements.
The welding transformer has a power of two and a half to three kilowatts with a copper wire of six by eight millimeters in the secondary winding, a core magnetic circuit for a voltage of twenty-one volts and a current of one hundred and twenty amperes.
One and the other windings are wound symmetrically, the end of one winding is necessarily connected to the beginning of the other. The wire used for this is two and a half millimeters in diameter.
The inductor L1 is wound onto the engine with a slot using a welding cable. Capacitor C1 has a capacity of four thousand microfarads.
The holder consists of a rubber hose with an approximate diameter of three centimeters. Carbon dioxide is supplied through it. On one side of the hose there is a connector with a fitting, contacts, a hole and a nut that secures the entire connector. On the other side there is a handle with a switch and a tube with an external thread where the tip is mounted.
Almost all components of the circuit are located in the housing. The rest are located as follows:

Making a welding inverter with your own hands is not at all difficult. All you need is desire and a little diligence to realize your plans.
It is difficult to imagine, in our time, any work with metal without the use of a welding machine. Using this device, you can easily connect or cut iron of various thicknesses or dimensions. Naturally, to perform high-quality work you will need certain skills, but first of all you need the welder itself. Nowadays, of course, you can buy it, as well as, in principle, hire a welder, but in this article we will talk about how to make a welding machine with your own hands. Moreover, with all the wealth of choice of models, reliable ones are quite expensive, and cheap ones do not shine with the quality of the work performed. But even if you decide to buy a welding machine, reading this article will help you choose the machine you need. There are several types of welders: direct current, alternating current, three-phase and inverter. In order to determine which option you need, we will consider the design and structure of the first two, which you can assemble with your own hands at home without any specific skills.
AC
This type of welding machine is one of the most common options, both in industry and in private households. It is easy to use and, compared to others, can be made quite easily at home, as evidenced by the photo below. To do this, you need to have a wire for the primary and secondary windings, as well as a transformer steel core for winding the welder. In simple words, an AC welding machine is a step-down transformer.
The optimal voltage when operating a welding machine assembled at home is 60V. The optimal current is 120-160A. Now it’s easy to calculate what cross-section the wire should have in order to make the primary winding of the transformer (the one that will be connected to the 220 V network). The minimum cross-sectional area of the copper wire should be 3-4 square meters. mm, the optimal is 7 sq. mm, because it is necessary to take into account voltage drops and possible additional load. We find that the optimal diameter of the copper core for the primary winding of a step-down transformer should be 3 mm. If you decide to take an aluminum wire in order to make a welding wire yourself, then the cross-section of the copper wire must be multiplied by a factor of 1.6. It is important that the wires are in a rag sheath; you cannot use conductors in PVC insulation - when the wires heat up, it will melt and this will happen. If you do not have a wire of the required diameter, you can use thinner wires by winding them in pairs. But then it should be taken into account that the thickness of the winding will increase, and, accordingly, the dimensions of the device itself. For the secondary winding, you can use a thick stranded copper wire - the same as the core on the holder.
The first step is to make a transformer core for a homemade welding machine. The best option would be a rod-type core as shown in Figure 1:

This core must be made from transformer steel plates. The thickness of the plates should be from 0.35 mm to 0.55 mm. Before assembling the core, it is necessary to calculate its dimensions, this is done as follows: firstly, the size of the window, i.e. dimensions c and d in Figure 1 must be chosen such as to accommodate all the windings of the transformer, secondly, the roll area, which calculated by the formula Skren=a*b, must be at least 35 square meters. cm. If there is more Slope, then the transformer will heat up less and, accordingly, work longer. It is better that the Skrena is equal to 50 square meters. see. Next, we proceed to assembling the plates of a homemade welding machine. It is necessary to take the L-shaped plates and fold them, as shown in Figure 2, until you can make a core of the required thickness. Then we fasten it with bolts at the corners. Finally, it is necessary to process the surface of the plates with a file and insulate them by wrapping them with rag insulation. 
Next, we proceed to winding the welding machine from the step-down transformer. First, we wind the primary winding, which will consist of 215 turns, as shown in Figure 3. 
It is advisable to make a branch from 165 and 190 turns. We attach a thick textolite plate to the top of the transformer. We fix the ends of the windings on it using a bolted connection, noting that the first bolt is a common wire, the second is a branch from the 165th turn, the 3rd is a branch from the 190th turn and the 4th is from the 215th. This will make it possible to subsequently regulate the current strength during welding; the greater the number of turns in the primary winding, the higher the current strength of your welding device will be. Then we proceed to winding 70 turns of the secondary winding, as shown in Figure 4. 
A smaller number of turns are wound on the other side of the core - where the primary winding is wound. The ratio of turns should be approximately 60% to 40%. This ensures that after you catch the arc and start welding, the eddy currents will partially turn off the work of the winding with a large number of turns, which will lead to an increase in the welding current, and accordingly improve the quality of the seam. We will also secure the ends of the winding with bolts to the textolite plate. Now your homemade welding machine is ready. Having connected the holder and ground to the secondary winding, it is necessary to connect the network to the common wire and the wire extending from the 215th turn of the primary winding. If you need to increase the current, you can make fewer turns of the primary winding by switching the second wire to a contact with fewer turns. The characteristics can be reduced using a resistance made from a piece of transformer steel bent in the form of a spring and connected to a holder. It is always necessary to ensure that the welding machine does not overheat.
This is how you can make a welding machine from a step-down transformer with your own hands. As you can see, the instructions are not too complicated and even an inexperienced electrician can assemble the device on their own.
DC
Some types of welding require a DC welder. This tool can be used to weld cast iron and stainless steel. You can make a DC welding machine with your own hands in no more than 15 minutes by converting a homemade product to AC. To do this, you need to connect a rectifier assembled with diodes to the secondary winding. As for the diodes, they must withstand a current of 200 A and have good cooling. D161 diodes are suitable for this. Capacitors C1 and C2 with the following characteristics of 15000 μF and a voltage of 50V will help us equalize the current. Next, we assemble the circuit shown in the drawing below. Inductor L1 is needed to regulate the current. Contacts x4 are for connecting the holder, and x5 are for supplying current to the part to be welded.

We present to your attention a diagram of a welding inverter that you can assemble with your own hands. Maximum current consumption is 32 amperes, 220 volts. The welding current is about 250 amperes, which allows you to easily weld with a 5-piece electrode, an arc length of 1 cm, which passes more than 1 cm into low-temperature plasma. The efficiency of the source is at the level of store-bought ones, and maybe better (meaning inverter ones).
Figure 1 shows a diagram of the power supply for welding.
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the power supply
The transformer is wound on ferrite Ш7х7 or 8х8
The primary has 100 turns of 0.3mm PEV wire
Secondary 2 has 15 turns of 1mm PEV wire
Secondary 3 has 15 turns of 0.2mm PEV
Secondary 4 and 5, 20 turns of PEV wire 0.35mm
All windings must be wound across the entire width of the frame; this gives a noticeably more stable voltage.

Fig.2 Schematic diagram of a welding inverter
Figure 2 shows a diagram of the welder. The frequency is 41 kHz, but you can try 55 kHz. The transformer at 55 kHz is then 9 turns by 3 turns, to increase the PV of the transformer.
41kHz transformer - two sets Ш20х28 2000nm, gap 0.05mm, newspaper gasket, 12vit x 4vit, 10kv mm x 30kv mm, copper tape (tin) in paper. The transformer windings are made of copper sheet 0.25 mm thick and 40 mm wide, wrapped in cash register paper for insulation. The secondary is made of three layers of tin (sandwich) separated from each other by fluoroplastic tape, for insulation between themselves, for better conductivity of high-frequency currents, the contact ends of the secondary at the output of the transformer are soldered together.
Inductor L2 is wound on a Ш20x28 core, ferrite 2000nm, 5 turns, 25 sq.mm, gap 0.15 - 0.5mm (two layers of paper from the printer). Current transformer - current sensor two rings K30x18x7 primary wire threaded through the ring, secondary 85 turns of wire 0.5 mm thick.

Welding assembly
Winding the transformer
Winding the transformer must be done using copper sheet 0.3mm thick and 40mm wide, it must be wrapped in thermal paper from a cash register 0.05mm thick, this paper is durable and does not tear as much as usual when winding a transformer.
You tell me, why not wind it with an ordinary thick wire, but it’s not possible because this transformer operates on high-frequency currents and these currents are displaced onto the surface of the conductor and the middle of the thick wire is not used, which leads to heating, this phenomenon is called the Skin effect!
And you have to fight it, you just need to make a conductor with a large surface, so thin copper sheet has this, it has a large surface along which current flows, and the secondary winding should consist of a sandwich of three copper tapes separated by fluoroplastic film, it is thinner and all these are wrapped layers in thermal paper. This paper has the property of darkening when heated, we don’t need this and it’s bad, it won’t do anything, let the main thing remain that it doesn’t tear.
You can wind the windings with PEV wire with a cross-section of 0.5...0.7 mm consisting of several dozen cores, but this is worse, since the wires are round and are connected to each other with air gaps, which slow down heat transfer and have a smaller total cross-sectional area of the wires combined compared to tin by 30 %, which can fit into the ferrite core window.
It is not the ferrite that heats up the transformer, but the winding, so you need to follow these recommendations.
The transformer and the entire structure must be blown inside the housing by a fan of 220 volts 0.13 amperes or more.
Design
To cool all powerful components, it is good to use radiators with fans from old Pentium 4 and Athlon 64 computers. I got these radiators from a computer store doing upgrades, for only $3...4 apiece.
The power oblique bridge must be made on two such radiators, the upper part of the bridge on one, the lower part on the other. Screw bridge diodes HFA30 and HFA25 onto these radiators through a mica spacer. IRG4PC50W must be screwed without mica through KTP8 heat-conducting paste.
The terminals of the diodes and transistors need to be screwed towards each other on both radiators, and between the terminals and the two radiators, insert a board connecting the 300-volt power circuit to the bridge parts.
The diagram does not indicate the need to solder 12...14 pieces of 0.15 micron 630 volt capacitors to this board into a 300V power supply. This is necessary so that the transformer emissions go into the power circuit, eliminating the resonant current surges of the power switches from the transformer.
The rest of the bridge is connected to each other by hanging installation of conductors of short length.
The diagram also shows snubbers, they have capacitors C15 C16, they should be brand K78-2 or SVV-81. You can’t put any garbage there, since snubbers play an important role:
first- they dampen the resonant emissions of the transformer
second- they significantly reduce IGBT losses when switching off since IGBTs open quickly, but are closing much slower and during closing, the capacitance C15 and C16 is charged through the VD32 VD31 diode longer than the closing time of the IGBT, that is, this snubber intercepts all the power onto itself, preventing heat from being released on the IGBT switch three times than it would be without it.
When IGBT is fast open, then through resistors R24 R25 the snubbers are smoothly discharged and the main power is released on these resistors.
Settings
Apply power to the 15-volt PWM and at least one fan to discharge capacitance C6, which controls the relay response time.
Relay K1 is needed to close resistor R11 after capacitors C9...12 are charged through resistor R11, which reduces the current surge when the welding machine is turned on to a 220-volt network.
Without direct resistor R11, when turned on, there would be a large BAC while charging a 3000 μm 400V capacitance, which is why this measure is needed.
Check the operation of the relay closing resistor R11 2...10 seconds after power is applied to the PWM board.
Check the PWM board for the presence of rectangular pulses going to the HCPL3120 optocouplers after both relays K1 and K2 are activated.
The width of the pulses should be relative to the zero pause 44% zero 66%
Check the drivers on optocouplers and amplifiers that drive a rectangular signal with an amplitude of 15 volts and make sure that the voltage on the IGBT gates does not exceed 16 volts.
Apply 15 Volt power to the bridge to check its operation and ensure that the bridge is manufactured correctly.
The current consumption should not exceed 100mA at idle.
Verify the correct phrasing of the windings of the power transformer and current transformer using a two-beam oscilloscope.
One beam of the oscilloscope is on the primary, the second on the secondary, so that the phases of the pulses are the same, the only difference is in the voltage of the windings.
Apply power to the bridge from power capacitors C9...C12 through a 220 volt 150..200 watt light bulb, having previously set the PWM frequency to 55 kHz, connect an oscilloscope to the collector-emitter of the lower IGBT transistor, look at the signal shape so that there are no voltage surges above 330 volts as usual.
Start lowering the PWM clock frequency until a small bend appears on the lower IGBT switch indicating oversaturation of the transformer, write down this frequency at which the bend occurred, divide it by 2 and add the result to the oversaturation frequency, for example, divide 30 kHz oversaturation by 2 = 15 and 30 + 15 = 45 , 45 this is the operating frequency of the transformer and PWM.
The current consumption of the bridge should be about 150 mA and the light bulb should barely glow; if it glows very brightly, this indicates a breakdown of the transformer windings or an incorrectly assembled bridge.
Connect a welding wire at least 2 meters long to the output to create additional output inductance.
Apply power to the bridge through a 2200-watt kettle, and set the current on the light bulb to PWM at least R3 closer to resistor R5, close the welding output, check the voltage on the lower switch of the bridge so that it is no more than 360 volts according to the oscilloscope, and there should be no noise from the transformer. If there is one, make sure that the transformer-current sensor is correctly phased, pass the wire in the opposite direction through the ring.
If the noise remains, then you need to place the PWM board and optocoupler drivers away from sources of interference, mainly the power transformer and inductor L2 and power conductors.
Even when assembling the bridge, the drivers must be installed next to the radiators of the bridge above the IGBT transistors and no closer to the resistors R24 R25 by 3 centimeters. The driver output and IGBT gate connections must be short. The conductors going from the PWM to the optocouplers should not pass near sources of interference and should be as short as possible.
All signal wires from the current transformer and going to the optocouplers from the PWM should be twisted to reduce noise and should be as short as possible.
Next, we begin to increase the welding current using resistor R3 closer to resistor R4, the welding output is closed on the lower IGBT switch, the pulse width increases slightly, which indicates PWM operation. More current means more width, less current means less width.
There shouldn't be any noise, otherwise it will fail.IGBT.
Add current and listen, watch the oscilloscope for excess voltage of the lower key, so that it does not exceed 500 volts, a maximum of 550 volts in the surge, but usually 340 volts.
Reach the current where the width suddenly becomes maximum, indicating that the kettle cannot provide maximum current.
That's it, now we go straight without a kettle from minimum to maximum, watch the oscilloscope and listen so that it is quiet. Reach the maximum current, the width should increase, emissions are normal, no more than 340 volts usually.
Start cooking for 10 seconds at the beginning. We check the radiators, then 20 seconds, also cold and 1 minute the transformer is warm, burn 2 long electrodes 4mm transformer is bitter
The radiators of the 150ebu02 diodes noticeably warmed up after three electrodes, it’s already difficult to cook, a person gets tired, although he cooks great, the transformer is hot, and no one cooks anyway. The fan, after 2 minutes, brings the transformer to a warm state and you can cook it again until it becomes puffy.
Below you can download printed circuit boards in LAY format and other files
Evgeny Rodikov (evgen100777 [dog] rambler.ru). If you have any questions when assembling the welder, write to E-Mail.
List of radioelements
| Designation | Type | Denomination | Quantity | Note | Shop | My notepad | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| power unit | |||||||
| Linear regulator | LM78L15 | 2 | To notepad | ||||
| AC/DC converter | TOP224Y | 1 | To notepad | ||||
| Voltage reference IC | TL431 | 1 | To notepad | ||||
| Rectifier diode | BYV26C | 1 | To notepad | ||||
| Rectifier diode | HER307 | 2 | To notepad | ||||
| Rectifier diode | 1N4148 | 1 | To notepad | ||||
| Schottky diode | MBR20100CT | 1 | To notepad | ||||
| Protection diode | P6KE200A | 1 | To notepad | ||||
| Diode bridge | KBPC3510 | 1 | To notepad | ||||
| Optocoupler | PC817 | 1 | To notepad | ||||
| C1, C2 | 10uF 450V | 2 | To notepad | ||||
| Electrolytic capacitor | 100uF 100V | 2 | To notepad | ||||
| Electrolytic capacitor | 470uF 400V | 6 | To notepad | ||||
| Electrolytic capacitor | 50uF 25V | 1 | To notepad | ||||
| C4, C6, C8 | Capacitor | 0.1uF | 3 | To notepad | |||
| C5 | Capacitor | 1nF 1000V | 1 | To notepad | |||
| C7 | Electrolytic capacitor | 1000uF 25V | 1 | To notepad | |||
| Capacitor | 510 pF | 2 | To notepad | ||||
| C13, C14 | Electrolytic capacitor | 10 µF | 2 | To notepad | |||
| VDS1 | Diode bridge | 600V 2A | 1 | To notepad | |||
| NTC1 | Thermistor | 10 ohm | 1 | To notepad | |||
| R1 | Resistor | 47 kOhm | 1 | To notepad | |||
| R2 | Resistor | 510 Ohm | 1 | To notepad | |||
| R3 | Resistor | 200 Ohm | 1 | To notepad | |||
| R4 | Resistor | 10 kOhm | 1 | To notepad | |||
| Resistor | 6.2 Ohm | 1 | To notepad | ||||
| Resistor | 30Ohm 5W | 2 | To notepad | ||||
| Welding inverter | |||||||
| PWM controller | UC3845 | 1 | To notepad | ||||
| VT1 | MOSFET transistor | IRF120 | 1 | To notepad | |||
| VD1 | Rectifier diode | 1N4148 | 1 | To notepad | |||
| VD2, VD3 | Schottky diode | 1N5819 | 2 | To notepad | |||
| VD4 | Zener diode | 1N4739A | 1 | 9V | To notepad | ||
| VD5-VD7 | Rectifier diode | 1N4007 | 3 | To reduce voltage | To notepad | ||
| VD8 | Diode bridge | KBPC3510 | 2 | To notepad | |||
| C1 | Capacitor | 22 nF | 1 | To notepad | |||
| C2, C4, C8 | Capacitor | 0.1 µF | 3 | To notepad | |||
| C3 | Capacitor | 4.7 nF | 1 | To notepad | |||
| C5 | Capacitor | 2.2 nF | 1 | To notepad | |||
| C6 | Electrolytic capacitor | 22 µF | 1 | To notepad | |||
| C7 | Electrolytic capacitor | 200 µF | 1 | To notepad | |||
| C9-C12 | Electrolytic capacitor | 3000uF 400V | 4 | To notepad | |||
| R1, R2 | Resistor | 33 kOhm | 2 | To notepad | |||
| R4 | Resistor | 510 Ohm | 1 | To notepad | |||
| R5 | Resistor | 1.3 kOhm | 1 | To notepad | |||
| R7 | Resistor | 150 Ohm | 1 | To notepad | |||
| R8 | Resistor | 1Ohm 1Watt | 1 | To notepad | |||
| R9 | Resistor | 2 MOhm | 1 | To notepad | |||
| R10 | Resistor | 1.5 kOhm | 1 | To notepad | |||
| R11 | Resistor | 25Ohm 40Watt | 1 | To notepad | |||
| R3 | Trimmer resistor | 2.2 kOhm | 1 | To notepad | |||
| Trimmer resistor | 10 kOhm | 1 | To notepad | ||||
| K1 | Relay | 12V 40A | 1 | To notepad | |||
| K2 | Relay | RES-49 | 1 | To notepad | |||
| Q6-Q11 | IGBT transistor | IRG4PC50W | 6 | ||||
Even a home craftsman who does not have deep knowledge of electrical processes can assemble a homemade inverter welding machine. The main requirement is compliance with installation technology, compliance with the diagram and understanding of the operating principle of the device. If you create an inverter with your own hands, then its parameters and performance will not differ significantly from factory models, but the savings can be decent.
A simple homemade inverter-type device will allow you to carry out high-quality welding operations. Even an inverter with a simple circuit allows you to work with an electrode from 3 to 5 mm and an arc up to 1 cm.
Characteristics
A similar welder for home use may have the following parameters:
- Voltage level – 220 volts.
- Input current - 32 amperes;
- Output current - 250 amperes.
An inverter that operates from a 220 V household power supply is suitable for domestic use. If necessary, it is possible to assemble a more powerful device operating from 380 V. It has higher productivity compared to a single-phase inverter welding machine.
Features of operation
First you need to understand how the inverter functions. Essentially, it is a computer power supply. In it you can observe the transformation of electricity in the following sequence:
- The input AC voltage is transformed into DC.
- The 50 Hz current consumption is converted to high frequency.
- The output voltage decreases.
- The output current is rectified, the required frequency is maintained.
Such transformations are necessary to reduce the weight of equipment and its dimensions.
Transformer welding machines have sensitive weight and dimensions. Due to the significant current strength, arc welding can be carried out in them. To increase the current and lower the voltage, the secondary winding involves the presence of fewer turns, and the cross-section of the wire increases. As a result, the transformer welder is heavy and bulky.
The inverter principle makes it possible to reduce these figures significantly. The circuitry of such a device involves increasing the frequency to 60-80 kHz, which helps reduce its size and weight. To implement such a conversion, power field-effect transistors are used. They communicate with each other precisely at this frequency. They are powered by direct current coming from a rectifying device, which is a diode bridge. The voltage value is equalized by capacitors.
After the transistors, the current is transferred to a step-down transformer. It is a small coil. The small dimensions of the inverter transformer coil are ensured by a frequency that is greatly increased by field-effect transistors. The result is characteristics similar to those of a transformer device, but with less weight and size.
What is needed for assembly
To create such a homemade product, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the circuit, i.e., consumed voltage and current. An output current of 250 amps is enough to create a durable seam. To implement the idea you will need the following details:
- Transformer.
- Primary winding (100 turns with wire ⌀ 0.3 mm).
- 3 windings. In the outer: 20 turns, ⌀ 0.35 mm. On average: 15 and ⌀ 0.2. In internal 15 and ⌀ 1 mm.
In addition, before starting to assemble the inverter, it is necessary to prepare tools and elements for developing electronic circuits. You will need:
- Screwdrivers;
- Soldering iron;
- Hacksaw for metal;
- Fasteners;
- Electronic elements;
- Copper wires;
- Thermal paper;
- Electrical steel;
- Fiberglass;
- Textolite;
- Mica.
Scheme
The electrical circuit diagram of an inverter is one of the most critical moments when designing or repairing an inverter apparatus. Therefore, we recommend that you first study the options in detail and then begin to implement them.


List of radioelements




Power section
The power supply plays one of the leading roles in the inverter apparatus. It is a transformer wound on ferrite. It provides a stable decrease in voltage and increase in current value. You need 2 cores Ш20х208 2000 nm.
Thermal paper is used to create thermal insulation between the inverter windings. To minimize the negative impact of constant voltage drops in the electrical network, the winding should be carried out across the entire width of the core.

For the winding of the transformer, experts recommend the use of copper sheet having a width of 40 mm and a thickness of 0.3 mm. It needs to be wrapped in 0.05 millimeter thermal paper (cash register tape). Experts explain this by the fact that during welding, high-frequency current is displaced onto the surface of thick wires, while the core is not used and a lot of heat is generated. Therefore, ordinary conductors are not suitable. This effect can be eliminated by using conductors with a significant surface area.
An analogue of copper sheet that can be used is PEV wire with a cross-section of 0.5-0.7 mm. It is multi-core with air gaps between the cores, which reduces heating.

After creating the primary layer, a shielding wire with fiberglass is wound in the same direction. This wire (of similar diameter) must completely cover the fiberglass. It is necessary to proceed in the same way with other windings of the transformer. They must be isolated from each other using the above insulators.
In order for the voltage from the transformer to the relay to be at the level of 20 - 25 volts, it is necessary to select the correct resistors. The main task of the inverter power supply is to change alternating current into direct current. This is implemented by a diode bridge circuit of the “oblique bridge” type.
During operation, the diodes of the inverter device will heat up. Therefore, they must be placed on the radiator. It is allowed to use radiators from computers. Fortunately, they are now widespread and inexpensive. You will need 2 radiators. The upper element of the bridge is fixed on one, and the lower element on the second. In this case, when installing the first one, it is necessary to use a mica gasket, and in the second case, thermal paste.
The output of the diode bridge is in the same direction as the output of the transistors. Use wires no longer than 15 cm. The basis of the inverter unit is transistors. The bridge must be separated from the power supply by a sheet of metal, which is subsequently attached to the case.

Installation of diodes on a radiator
Inverter unit
The main task of this inverter unit is to transform the rectified current into a high-frequency alternating component. Power transistors that open and close at high frequencies are designed to perform this function.
It is better to create a converting unit of an inverter apparatus not with one more powerful transistor, but with the use of several weaker ones. Due to this, the frequency of the current is stabilized and the noise effect during welding is minimized.

The inverter circuit must contain capacitors. Connected in a series circuit. Perform 2 main tasks:
- Minimize resonant emissions of the power supply.
- Reduce losses of the transistor unit that occur after switching on. This is explained by the fact that the transistor opens faster. The closing speed is noticeably slower. In this case, a loss of current occurs and the switches in the transistor unit heat up.
Cooling system
The power elements of the converter will heat up significantly during welding. This may cause a breakdown. To eliminate this, in addition to the radiators mentioned above, you should use a fan that eliminates overheating and ensures stable cooling.
One fan of sufficient power may be enough. However, when using elements of an old PC, you may need up to 6 pieces, 3 of which must be placed near the transformer.

To completely protect a homemade inverter from overheating, you can use a temperature sensor. It should be mounted on the hottest element with a radiator. The element will be able to turn off the power when a certain temperature is reached, and the indication will signal a critical level.
For efficient and stable operation of the inverter ventilation system, it is necessary to ensure constant correct air intake. To do this, the holes through which air will be taken in should not be blocked by anything. A sufficient number of holes should be provided in the inverter housing. In this case, they need to be placed on opposite surfaces of the body.
Control
When placing the electronic boards of the device, it is possible to use foil-coated PCB with a thickness of 0.5 - 1 millimeter.
To ensure automatic control of inverter welding, you should buy and install a PWM controller. It will stabilize the welding current and voltage level. For convenient control, all controls and connection points are located on the front part.
Frame
After creating the main elements of inverter welding, you can begin preparing the body parts. When planning, you need to take into account the width of the transformer, since it must be placed unobstructed in the housing. Based on this size, approximately 70% of the space should be added for the remaining parts. The protective casing can be made from sheet iron, 0.5-1 millimeters thick. The elements can be connected using welding or bolts. A more sophisticated option would be a one-piece design made from curved raw materials. Handles and belt mounts are required to carry the device.
When designing an inverter, consideration should be given to the possibility of easy disassembly to access internal components for easy repair. The front side must also contain:
- Current switch;
- A button that will turn the device on/off;
- Light indication elements;
- Connectors for connecting cables.
Factory inverters are powder coated. You can use regular paint at home. It is worth applying a coating to prevent the appearance of rust.
Connection
The assembled welding machine must be connected to the electrical network. When connecting to an outlet, be sure to have a fuse or circuit breaker. For protection, a 25 amp circuit breaker can be installed at the inverter input.
If the connection point is remote, you can use an extension cord.
The device is turned on according to the standard scheme - using the “on/off” button. The indication should light up, usually a green LED is used for this.
The connection to the network must be made with a wire having a cross-section of at least 1.5 mm 2 . However, the optimal cross-section will be a wire of 2.5 mm 2.
Before connecting the device to the electrical network, you should check that all high-voltage elements are insulated from the housing parts.

Functionality check
After all assembly and debugging work has been completed, it is necessary to check the functionality of the created inverter.
According to the recommendations of specialists, it is necessary to check the current and voltage of the device using an oscilloscope. The lower voltage loop should be up to 500 volts, not exceeding 550 V. If all design requirements are met, the voltage level will be 330 - 350 volts. But this method is not always available, because not every home has its own similar measuring device.
Often the inspection is carried out in action directly by the welder. To do this, a test seam is created with complete burnout of the electrode. At the end of the test welding, you need to check the temperature on the transformer. If it goes off scale, then there are some deficiencies in the circuit and everything should be double-checked.
If the temperature of the power unit is normal, then you can carry out another 2-3 test runs. After this, check the temperature of the radiators. They may also overheat. If after two to three minutes they return to normal, then you can safely continue working.
The assembly procedure of the device is not complicated. The most important step is setting up the inverter device. You may need to seek help from a specialist.
1. First you need to connect 15 volts to PWM while simultaneously connecting one convector. This way you can reduce heat and noise during operation.
2. To close the resistor you need to connect a relay. It is connected when the capacitors have finished charging. Due to this, you can significantly reduce voltage fluctuations when connecting to a 220 volt power supply. Without a resistor, an explosion is possible when connected directly.
3. Check the operation of the resistor closure relay a couple of seconds after current is supplied to the PWM board. Check for the presence of a rectangular pulse on the board after the relay has been tested.
4. Supply 15 volt power to the bridge to check its functionality and correct assembly. The current should be no higher than 100 mA at idle.
5. Checking the correct placement of phases. Use an oscilloscope. The bridge circuit is supplied with 200 volts from the capacitors through the lamp with a load of 200 W. The PWM frequency is set to 55 kHz. An oscilloscope is connected, the signal shape and voltage level are checked (no more than 350 volts).
To determine the frequency of the device, you should slowly lower the PWM frequency until a slight turn occurs on the IGBT switch. The resulting frequency value must be divided by 2 and the oversaturation frequency added. The result is an operating frequency oscillation of the transformer.
The transformer of the device should not make any noise. If they are present, the polarity must be checked. The diode bridge can be connected to power for the test through suitable household appliances. For example, a kettle with a power of 3000 W is suitable.
The conductors going to the PWM must be short. They need to be twisted and placed further from the source of interference.
6. The current is gradually increased using a resistor. In this case, you need to listen to the inverter and monitor the values on the oscilloscope. There should be no more than 500 volts on the lower key. The average value is 340. If noise is present, the IGBT may fail.
7. Start welding after 10 seconds. The radiators are checked, if they have not heated up, then extend the work for another 20 seconds. After re-checking, welding can last from one minute or longer.
Safety
All operations performed, with the exception of performance testing, must be carried out exclusively on de-energized equipment. It is recommended to check each element in advance so that after installation it does not fail due to overvoltage. Basic electrical safety rules are also mandatory.
Thus, almost anyone can do homemade inverter welding. The proposed description should help you understand all the nuances. If you study video tutorials and photo materials, then assembling the device will not be difficult.
Today, a widely demanded welding machine is the welding inverter. Its advantages are functionality and performance. You can make a mini welding machine with your own hands without any special financial investments (spending only on consumables), if you have an understanding of how the electronics are structured and work. Today, good inverters are expensive, and cheap ones can disappoint with poor welding quality. Before constructing such a tool yourself, you need to carefully study the diagram.
The first stage of assembly is winding the transformer
Copper sheet 4 cm wide and 0.3 mm thick is suitable for winding the transformer. Copper wire can operate under high heat. You can use cash register paper as a thermal layer. You can use photocopier paper, but it is less durable and may tear when winding.
Lacquered fabric is considered the best insulator. It is always desirable to have at least one layer of it for insulation. Textolite plates can be placed in the windings for the electrical safety of the device. The better the insulation between the windings, the higher the voltage. The length of the paper strips should be such as to cover the perimeter of the winding with a margin of 2-3 cm at the end.
You cannot use thick wire for winding, since the inverter operates on high-frequency currents. The core of a thick wire will not be used, which can lead to overheating of the transformer. It won't work even 5 minutes.
To avoid such a “skin” effect, you need to use a conductor with a larger area and minimal thickness. Such a surface conducts current well and does not overheat.
When re-winding, it is advisable to use 3 copper strips, which must be separated from each other by a fluoroplastic plate. Everything needs to be wrapped again with cash register tape as a thermal layer. This paper has a drawback - it darkens when heated. But despite all this, it does not break.
Instead of copper sheet, you can use PEV wire up to 0.7mm. It consists of many veins, which is its main advantage. However, this winding method is worse than copper, since such wires have large air gaps and do not fit well with each other. The total cross-sectional area decreases and heat transfer slows down. When working with PEV, the design of a homemade welding machine with your own hands can have 4 windings:
- primary, consisting of one hundred turns (PEV thickness 0.3 mm);
- three secondary windings: the first includes 15 turns, the second -15, the third -20.
The transformer and the entire mechanism must be equipped with a fan. A cooler from a system unit with a current of 220 volts 0.15A or more is suitable.
DIY welding inverter circuit: design features
You first need to think about ventilation of the inverter mechanism, which will protect the system from overheating. To do this, it is good to use radiators from Pentium 4 and Athlon 64 system units. Today they can be purchased quite cheaply.
After winding the transformer, it is connected to the base of the welding machine. To do this, you will need several staples, which can be made from wire (copper with a diameter of at least 3 mm).
To make boards you will need foil-coated PCB (about 1mm thick). You need to make small slots in each of the boards. They will help reduce the load on the diode terminals. They must be attached towards the terminals of the transistors. As a layer between the radiators and the terminals, place a board that will connect the bridge mechanism with the power lines. Each step of assembling the device can be checked using an approximate diagram of a homemade welding inverter:
Capacitors must be soldered onto the board. There can be about 14 of them. Thanks to them, transformer emissions will go into the power circuit.
To eliminate resonant current surges from the transformer, it is necessary to install snubbers, which will contain capacitors C15, C16. It is necessary to use only high-quality proven devices, since the function of snubbers is very significant in the inverter - they reduce the resonant emissions of the transformer and reduce IGBT losses during shutdown. The best models are SVV-81, K78-2. All power is transferred to the snubber, reducing heat generation several times.
 In the case when during the soldering process it is necessary to monitor and adjust the temperature or other parameters, the need arises not for a simple soldering iron, but for a more complex tool. To do this, you don’t have to go to the store; you can assemble a soldering station with your own hands at home.
In the case when during the soldering process it is necessary to monitor and adjust the temperature or other parameters, the need arises not for a simple soldering iron, but for a more complex tool. To do this, you don’t have to go to the store; you can assemble a soldering station with your own hands at home.
You can learn how to make the main tool of a soldering station—a soldering iron—on your own here.
All components of the device must be installed on the base. A getinax plate ½ cm thick is suitable for its production. In the center of the plate, cut a round hole for a fan, which will need to be protected with a grill.
There must be air space between the wires.
On the front part of the base you need to bring out LEDs, resistor and toggle switch handles, and cable clamps. This entire mechanism must be equipped with a “casing” on top, for the manufacture of which vinyl plastic or textolite (at least 4 mm thick) are suitable. A button is mounted on the electrode mount, which, together with the connected cable, must be well insulated.
 The assembly process itself is not that complicated. The most important stage is setting up the welding inverter. Sometimes this requires the help of a specialist.
The assembly process itself is not that complicated. The most important stage is setting up the welding inverter. Sometimes this requires the help of a specialist.
- First an inverter is needed connect 15V power to PWM. simultaneously connect one convector to the power supply to reduce the heating of the device and make its operation quieter.
In order to determine the frequency of the device, you need to gradually reduce the PWM frequency until a small turn appears on the lower IGBT switch. Record this indicator, divide it by two, and add the value of the oversaturation frequency to the resulting sum. The final sum will be the operating frequency oscillation of the transformer.
The bridge should consume current in the region of 150mA. The light from the light bulb should not be bright; very bright light may indicate a breakdown in the winding or errors in the bridge design.
The transformer should not produce any noise effects. If they are present, then it is worth checking the polarity. You can connect test power to the bridge through some household appliance. You can use a 2200 W kettle.
The conductors that come from the PWM should be short, twisted and placed away from sources of interference.
After using several electrodes, the transformer heats up. After 2 minutes the fan cools it down and you can start working again.
Assembling a homemade welding inverter with your own hands on video
DIY welding inverter: diagrams and assembly instructions
It is quite possible to make a welding inverter with your own hands, even without deep knowledge of electronics and electrical engineering; the main thing is to strictly adhere to the diagram and try to understand well the principle on which such a device works. If you make an inverter whose technical characteristics and efficiency differ little from those of serial models, you can save a decent amount.

Homemade welding inverter
You should not think that a homemade machine will not give you the opportunity to effectively carry out welding work. Such a device, even assembled according to a simple scheme, will allow you to weld with electrodes with a diameter of 3–5 mm and an arc length of 10 mm.
Characteristics of a homemade inverter and materials for its assembly
By assembling a welding inverter with your own hands using a fairly simple electrical circuit, you will get an effective device with the following technical characteristics:
- voltage consumption – 220 V;
- the current supplied to the input of the device is 32 A;
- The current generated at the device output is 250 A.
The diagram of an inverter-type welding machine with these characteristics includes the following elements:
- power unit;
- power switch drivers;
- power block.
Before you start assembling a homemade inverter, you need to prepare working tools and elements for creating electronic circuits. So, you will need:
- Screwdriver Set;
- soldering iron for connecting elements of electronic circuits;
- hacksaw for working on metal;
- threaded fasteners;
- thin sheet metal:
- elements from which electronic circuits will be formed;
- copper wires and strips - for winding transformers;
- thermal paper from a cash register;
- fiberglass;
- textolite;
- mica.
For home use, inverters are most often assembled that operate from a standard electrical network with a voltage of 220 V. However, if necessary, you can make a device that will operate from a three-phase electrical network with a voltage of 380 V. Such inverters have their advantages, the most important of which is a higher Efficiency compared to single-phase devices.
power unit
One of the most important elements of the welding inverter power supply is the transformer, which is wound on ferrite Ш7x7 or 8x8. This device, which provides a stable voltage supply, is formed from 4 windings:
- primary (100 turns of PEV wire with a diameter of 0.3 mm);
- first secondary (15 turns of PEV wire with a diameter of 1 mm);
- second secondary (15 turns of PEV wire with a diameter of 0.2 mm);
- third secondary (20 turns of PEV wire with a diameter of 0.3 mm).
To minimize the negative impact of voltage surges that regularly occur in the electrical network, the winding of the transformer windings should be carried out across the entire width of the frame.

Power transformer winding process
After completing the primary winding and insulating its surface with fiberglass, a layer of shielding wire is wound onto it, the turns of which should completely cover it. The turns of the shielding wire (it must have the same diameter as the primary winding wire) are made in the same direction. This rule is also relevant for all other windings formed on the transformer frame. The surfaces of all windings wound on the transformer frame are also insulated from each other using fiberglass or ordinary masking tape.
To ensure that the voltage supplied from the power supply to the relay is within 20–25 V, it is necessary to select resistors for the electronic circuit. The main function of the welding inverter power supply is to convert alternating current into direct current. For these purposes, the power supply uses diodes assembled using an “oblique bridge” circuit.

Inverter power supply diagram (click to enlarge)
During operation, the diodes of such a bridge become very hot, so they must be mounted on radiators, which can be used as cooling elements from old computers. To install a diode bridge, you need to use two radiators: the upper part of the bridge is attached to one radiator through a mica spacer, and the lower part is attached to the second through a layer of thermal paste.
The terminals of the diodes from which the bridge is formed must be directed in the same direction as the terminals of the transistors, with the help of which direct current will be converted into high-frequency alternating current. The wires connecting these terminals should be no longer than 15 cm. Between the power supply and the inverter unit, the basis of which is the transistors, there is a sheet of metal attached to the body of the device by welding.

Attaching diodes to the radiator
Power block
The basis of the power unit of the welding inverter is a transformer, due to which the voltage of the high-frequency current is reduced and its strength is increased. In order to make a transformer for such a block, it is necessary to select two Ш20x208 2000 nm cores. You can use newsprint to provide a gap between them.
The windings of such a transformer are made not of wire, but of copper strip 0.25 mm thick and 40 mm wide.
To ensure thermal insulation, each layer is wrapped with cash register tape, which demonstrates good wear resistance. The secondary winding of the transformer is formed from three layers of copper strips, which are insulated with each other using fluoroplastic tape. The characteristics of the transformer windings must correspond to the following parameters: 12 turns x 4 turns, 10 sq. mm x 30 sq. mm.
Many people try to make the windings of a step-down transformer from thick copper wire, but this is the wrong solution. Such a transformer operates on high-frequency currents, which are forced onto the surface of the conductor without heating its interior. That is why the best option for forming windings is a conductor with a large surface area, that is, a wide copper strip.

Homemade inverter output choke
Plain paper can also be used as a thermal insulation material, but it is less wear-resistant than cash register tape. This tape will darken due to elevated temperatures, but its wear resistance will not be affected by this.
The transformer of the power unit will become very hot during its operation, so to force it to cool, it is necessary to use a cooler, which can be a device previously used in the computer system unit.
Inverter unit
Even a simple welding inverter must perform its main function - convert the direct current generated by the rectifier of such a device into high-frequency alternating current. To solve this problem, power transistors are used that open and close at high frequencies.

Schematic diagram of the inverter unit (click to enlarge)
It is better to assemble the inverter unit of the device, which is responsible for converting direct current into high-frequency alternating current, using not one powerful transistor, but several less powerful ones. This design solution will stabilize the current frequency and also minimize noise effects when performing welding work.
The electronic circuit of the welding inverter also contains capacitors connected in series. They are necessary to solve two main problems:
- minimizing resonant emissions of the transformer;
- reducing losses in the transistor unit that occur when it is turned off and due to the fact that the transistors open much faster than they close (at this moment current losses may occur, accompanied by heating of the switches of the transistor unit).

Assembled electronic part of the inverter
Cooling system
The power elements of the homemade welding inverter circuit become very hot during operation, which can lead to their failure. To prevent this from happening, in addition to the radiators on which the hottest units are mounted, it is necessary to use fans responsible for cooling.
If you have a powerful fan, you can get by with just one, directing the air flow from it to a step-down power transformer. If you use low-power fans from old computers, you will need about six of them. At the same time, three such fans should be installed next to the power transformer, directing the air flow from them to it.

A powerful fan will ensure good cooling of the device elements
To prevent overheating of a homemade welding inverter, you should also use a temperature sensor by installing it on the hottest radiator. Such a sensor, if the radiator reaches a critical temperature, will cut off the flow of electric current to it.
For the inverter ventilation system to work effectively, its housing must have properly designed air intakes. The grilles of such intakes, through which air flows will flow into the device, should not be blocked by anything.
DIY inverter assembly
For a homemade inverter device, you need to choose a reliable housing or make it yourself, using sheet metal with a thickness of at least 4 mm. As a base on which the welding inverter transformer will be mounted, you can use a getinax sheet with a thickness of at least 0.5 cm. The transformer itself is mounted on such a base using brackets that you can make yourself from copper wire with a diameter of 3 mm.

Factory made sliding housing
To create electronic circuit boards for the device, you can use foil PCB with a thickness of 0.5–1 mm. When installing magnetic cores that will heat up during operation, it is necessary to provide gaps between them necessary for free air circulation.
To automatically control the operation of the welding inverter, you will need to purchase and install a PWM controller in it, which will be responsible for stabilizing the welding current and voltage. To make it convenient for you to work with your homemade device, you need to install controls in the front part of its body. These elements include a toggle switch for turning on the device, a variable resistor knob with which the welding current is regulated, as well as cable clamps and signal LEDs.

Example of inverter front panel layout
Diagnostics of a homemade inverter and its preparation for operation
Making an inverter welding machine is half the battle. An equally important task is its preparation for work, during which the correct functioning of all elements is checked, as well as their settings.
The first thing you need to do when checking a homemade welding inverter is to apply a voltage of 15 V to the PWM controller and one of the cooling fans. This will allow you to simultaneously check the functionality of the controller and avoid overheating during such a test.

Checking the output voltage with a tester
After the capacitors of the device are charged, a relay is connected to the electrical supply, which is responsible for closing the resistor. If you apply voltage directly to the resistor, bypassing the relay, an explosion may occur. After the relay operates, which should happen within 2-10 seconds after voltage is applied to the PWM controller, you need to check whether the resistor has shorted.
When the relays of the electronic circuit operate, rectangular pulses should be generated on the PWM board and supplied to the optocouplers. This can be checked using an oscilloscope. The correct assembly of the diode bridge of the device also needs to be checked; for this, a voltage of 15 V is applied to it (the current should not exceed 100 mA).
The transformer phases may have been incorrectly connected when assembling the device, which can lead to incorrect operation of the inverter and the generation of strong noise. To prevent this from happening, the correct phase connection must be checked using a dual-beam oscilloscope. One beam of the device is connected to the primary winding, the second to the secondary. The phases of the pulses, if the windings are connected correctly, should be the same.

Using an oscilloscope to diagnose an inverter
The correct manufacturing and connection of the transformer is checked using an oscilloscope and connecting electrical devices with different resistances to the diode bridge. Based on the noise of the transformer and the readings of the oscilloscope, they conclude that it is necessary to improve the electronic circuit of the homemade inverter apparatus.
To check how long you can continuously work on a homemade inverter, you need to start testing it from 10 seconds. If the device’s radiators do not heat up during operation for such a duration, you can increase the period to 20 seconds. If such a time period does not negatively affect the condition of the inverter, you can increase the operating time of the welding machine to 1 minute.
Maintenance of a homemade welding inverter
In order for the inverter device to serve for a long time, it must be properly maintained.
If your inverter stops working, you need to open its cover and blow out the insides with a vacuum cleaner. Those places where dust remains can be thoroughly cleaned with a brush and a dry cloth.
The first thing you need to do when diagnosing a welding inverter is to check the voltage supply to its input. If there is no voltage, you should check the functionality of the power supply. The problem in this situation may also be that the fuses of the welding machine have blown. Another weak link of the inverter is the temperature sensor, which, in the event of a breakdown, must not be repaired, but replaced.

A temperature sensor that often fails, usually located on a diode block or inductor
When performing diagnostics, it is necessary to pay attention to the quality of connections of the electronic components of the device. You can identify poorly made connections visually or using a tester. If such connections are identified, they must be corrected in order to avoid future overheating and failure of the welding inverter.
Only if you pay due attention to the maintenance of the inverter device can you count on it to serve you for a long time and enable you to perform welding work as efficiently and efficiently as possible.
Do-it-yourself welding inverter - save on the purchase of expensive equipment
Welding machines have become part of the everyday life of home craftsmen. Traditional transformers are inexpensive, easy to repair, and this design can be made by hand.
However, they have a drawback - to weld metal thicker than a car body, high currents are required. This gives a load on the side of the primary winding of 220 volts, about 3-5 W.
It will not be possible to weld a pipe in an apartment; according to technical conditions, the input of the meter is limited to a power of 3.5-5 W. And in a private house, power loss is guaranteed.
For work in domestic conditions, it is better to use a welding inverter. This device has less power, compact dimensions and light weight. 
The cost of such a machine is higher than that of a conventional transformer machine. Therefore, many home “Kulibins” make a welding inverter with their own hands.
Unlike a transformer, in the manufacture of which you struggle with the large weight and thickness of the secondary winding, the inverter offers a solution to other problems.
The circuit of a welding inverter can shock even an experienced radio amateur, not to mention a home handyman whose knowledge is limited to replacing a fuse. 
Don't be afraid. Following the assembly instructions, any radio amateur who knows how to hold a soldering iron in his hands will assemble this unit in a few free evenings.
Important! During operation, the welding inverter uses high-frequency currents, so some elements become very hot.
Any inverter. even low power requires forced cooling. To this we add the correct arrangement of components inside the case.
Of course, the housing itself must be equipped with flow holes for ventilation. Otherwise, the thermal protection (a necessary piece of equipment) will constantly be triggered.
We offer for consideration options on how to make a welding machine yourself.
Resonant inverter in a factory case
As a shell, you can use a familiar computer power supply. The older the age, the better. 20 years ago, they did not spare metal on the walls, and the dimensions of AT format power supplies were larger.
All you need from the power supply itself is a fan (if it is in good condition) and cooling radiators. Therefore, we are not interested in the serviceability of the donor's electrical components. It will be cheaper to buy it this way.
The inverter is built on used components from old monitors and TVs. If you don’t have access to such “reserves,” buying radioelements on the market won’t put much of a burden on your wallet.
Detailed story on how to make a welding inverter with your own hands - video
Important! Currents of up to 25A flow through these paths; the thin copper of the printed circuit board will burn out from the high temperature.
Important! Failure to comply with safety requirements when installing power electronics will result in equipment damage and, in worst cases, personal injury.
We set for ourselves the parameters of the future welding machine:
- Output load current: 5 – 120A
- Open circuit voltage 90V
- Load duration for 2 mm electrodes – 100%, for 3 mm electrodes – 80%. (at high air temperatures, cooling time increases by 20% -50%)
- Input current consumption: no more than 10A
- Weight without power cables 2 kg
- Current regulator
- The current-voltage characteristic is falling. Therefore, you can work in semi-automatic mode with CO2.
This is a fairly simple welding inverter, despite the fact that the circuit is saturated: 
All values of the element base are indicated on the diagram; it makes no sense to duplicate them in a separate list. The heart of the master oscillator is assembled on the popular SG3524 chip.
It is used in power supplies for computer uninterruptible power supplies. You can remove a part from a burnt UPS.
A special feature of the inverter is its extremely low power consumption (by the standards of a welder, of course) - no more than 2.5 W. This allows you to use it not only in the garage, but also in an apartment with a 16A input circuit breaker.
The power transformer is assembled using E42 cores. Vertical installation, otherwise it will not fit into the case. Such cores are present in abundance in old lamp monitors, and in principle they are not in short supply. To make one transformer, you will need to “gut” 6 monitors.
From the same parts (which will remain from the disassembled transformers) we make a choke. The cores for the remaining components are made from standard 2000 NM ferrite. 
The basis of the power unit is powerful diodes and transistors that need heat dissipation. They can be installed on radiators from the power supply (in which the inverter is assembled), or collected from the same old computer monitors. 
Before turning on the voltage booster, the idle speed is maintained at 35V. Due to such a low voltage, the power section is not overloaded. The length of the grasped arc is 3-4 mm. This is a comfortable value that allows even novice welders to work confidently.
The rectified voltage has a sine shape (this is a feature of resonant inverters). For final smoothing of half-waves, it is necessary to lay the output cables in ferrite tubes with an inductance of 3-4mkH. You can use filter rings from the same computer power supply, and lay the wire in 2 turns. 
The additional winding of the transformer adds voltage, so when work begins, the arc ignites instantly, regardless of atmospheric conditions. The main thing is high-quality coating of the electrodes.
Current transformers are connected in the secondary winding. This is a design feature of the circuit - in the primary winding, the maximum current is possible only during the formation of resonance.
Inverter protection
Electrode sticking is prevented by the IRF510 field effect transistor. The diagram clearly shows this area. It also ensures a smooth start. Note that such a device adds comfort for an inexperienced welder.
On the SG3524 chip, the shutdown input is interrupted in three cases:
- Thermal sensor triggered
- Blocking by transistor circuit in case of short circuit
- Switch off with a toggle switch.
Important! A homemade welding inverter does not have a factory safety certificate. Therefore, operator protection is the responsibility of the device creator.
The design includes key safety considerations and should not be excluded from the design. The housing should not have extra holes (except for ventilation) and open cavities. Power output terminals are installed on heat-resistant durable insulators. 
Result:
It is possible to assemble an inverter with your own hands. Don't be intimidated by the many details in the circuit - this is the developer's concern. There is no need to adjust the finished product; the welder is immediately ready for use. Provided that you solder everything correctly and arrange the modules in the case.
Step-by-step assembly of inverter welding
Do-it-yourself inverter welding is very simple
Inverter welding is a modern device that is widely popular due to the light weight of the device and its dimensions. The inverter mechanism is based on the use of field-effect transistors and power switches. To become the owner of a welding machine, you can visit any tool store and acquire such a useful thing. But there is a much more economical way, which is due to the creation of inverter welding with your own hands. It is the second method that we will pay attention to in this material and consider how to do welding at home, what is needed for this and what the diagrams look like.
Features of the inverter operation
An inverter-type welding machine is nothing more than a power supply, the one that is now used in modern computers. What is the operation of the inverter based on? The following picture of electrical energy conversion is observed in the inverter:
2) Current with a constant sinusoid is converted into alternating current with a high frequency.
3) The voltage value decreases.
4) The current is rectified while maintaining the required frequency.
A list of such electrical circuit transformations is necessary in order to be able to reduce the weight of the device and its overall dimensions. After all, as you know, old welding machines, the principle of which is based on reducing the voltage and increasing the current on the secondary winding of the transformer. As a result, due to the high current value, the possibility of arc welding of metals is observed. In order for the current to increase and the voltage to decrease, the number of turns on the secondary winding decreases, but the cross-section of the conductor increases. As a result, you can notice that a transformer-type welding machine not only has significant dimensions, but also a decent weight.
To solve the problem, an option was proposed for implementing a welding machine using an inverter circuit. The principle of the inverter is based on increasing the frequency of the current to 60 or even 80 kHz, thereby reducing the weight and dimensions of the device itself. All that was required to implement an inverter welding machine was to increase the frequency thousands of times, which became possible thanks to the use of field-effect transistors.
Transistors provide communication with each other at a frequency of about 60-80 kHz. The transistor power supply circuit receives a constant current value, which is ensured by the use of a rectifier. A diode bridge is used as a rectifier, and capacitors provide voltage equalization.
Alternating current that is transferred after passing through transistors to a step-down transformer. But at the same time, a coil that is hundreds of times smaller is used as a transformer. Why a coil is used, because the frequency of the current that is supplied to the transformer is already increased 1000 times thanks to field-effect transistors. As a result, we obtain similar data as with transformer welding, only with a large difference in weight and dimensions.
What is needed to assemble an inverter
To assemble inverter welding yourself, you need to know that the circuit is designed, first of all, for a consuming voltage of 220 Volts and a current of 32 Amps. After energy conversion, the output current will increase almost 8 times and reach 250 Amperes. This current is sufficient to create a strong seam with an electrode at a distance of up to 1 cm. To implement an inverter-type power supply, you will need to use the following components:
1) A transformer consisting of a ferrite core.
2) Winding of the primary transformer with 100 turns of wire with a diameter of 0.3 mm.
3) Three secondary windings:
— internal: 15 turns and wire diameter 1 mm;
- medium: 15 turns and diameter 0.2 mm;
— external: 20 turns and diameter 0.35 mm.
In addition, to assemble the transformer, you will need the following elements:
- copper wires;
— electrical steel;
- cotton material.
What does an inverter welding circuit look like?
In order to understand what an inverter welding machine is, it is necessary to consider the diagram presented below.

Electrical circuit of inverter welding
All these components must be combined and thereby obtain a welding machine, which will be an indispensable assistant when performing plumbing work. Below is a schematic diagram of inverter welding.

Inverter welding power supply diagram
The board on which the device's power supply is located is mounted separately from the power section. The separator between the power part and the power supply is a metal sheet connected electrically to the unit body.
To control the gates, conductors are used, which must be soldered close to the transistors. These conductors are connected to each other in pairs, and the cross-section of these conductors does not play a special role. The only thing that is important to consider is the length of the conductors, which should not exceed 15 cm.
For a person who is not familiar with the basics of electronics, reading this kind of circuit is problematic, not to mention the purpose of each element. Therefore, if you do not have skills in working with electronics, then it is better to ask a familiar specialist to help you figure it out. For example, below is a diagram of the power part of an inverter welding machine.

Diagram of the power part of inverter welding
How to assemble inverter welding: step-by-step description + (Video)
To assemble an inverter welding machine, you must complete the following work steps:
1) Frame. It is recommended to use an old computer system unit as a housing for welding. It is best suited as it has the required number of holes for ventilation. You can use an old 10-liter canister in which you can cut holes and place the cooler. To increase the strength of the structure, it is necessary to place metal corners from the system housing, which are secured using bolted connections.
2) Assembling the power supply. An important element of the power supply is the transformer. It is recommended to use 7x7 or 8x8 ferrite as the base of the transformer. For the primary winding of the transformer, it is necessary to wind the wire across the entire width of the core. This important feature entails improved operation of the device when voltage surges occur. It is imperative to use PEV-2 copper wires as wire, and if there is no busbar, the wires are connected into one bundle. Fiberglass is used to insulate the primary winding. On top, after the layer of fiberglass, it is necessary to wind turns of shielding wires.

Transformer with primary and secondary windings for creating inverter welding
3) Power section. A step-down transformer acts as a power unit. Two types of cores are used as a core for a step-down transformer: Ш20х208 2000 nm. It is important to provide a gap between both elements, which is solved by placing newsprint. The secondary winding of a transformer is characterized by winding turns in several layers. It is necessary to lay three layers of wires on the secondary winding of the transformer, and fluoroplastic gaskets are installed between them. It is important to place a reinforced insulating layer between the windings, which will avoid voltage breakdown on the secondary winding. It is necessary to install a capacitor with a voltage of at least 1000 Volts.

Transformers for the secondary winding from old TVs
To ensure air circulation between the windings, it is necessary to leave an air gap. A current transformer is assembled on a ferrite core, which is connected to the circuit to the positive line. The core must be wrapped with thermal paper, so it is best to use cash register tape as this paper. Rectifier diodes are attached to the aluminum radiator plate. The outputs of these diodes should be connected with bare wires with a cross-section of 4 mm.
3) Inverter unit. The main purpose of an inverter system is to convert direct current into high-frequency alternating current. To ensure an increase in frequency, special field-effect transistors are used. After all, it is the transistors that work to open and close at high frequencies.
It is recommended to use more than one powerful transistor, but it is best to implement a circuit based on 2 less powerful ones. This is necessary in order to be able to stabilize the current frequency. The circuit cannot do without capacitors, which are connected in series and make it possible to solve the following problems:

Aluminum plate inverter
4) Cooling system. Cooling fans should be installed on the case wall, and for this you can use computer coolers. They are necessary to ensure cooling of the working elements. The more fans you use, the better. In particular, it is imperative to install two fans to blow over the secondary transformer. One cooler will blow on the radiator, thereby preventing overheating of the working elements - rectifier diodes. The diodes are mounted on the radiator as follows, as shown in the photo below.

Rectifier bridge on the cooling radiator

It is recommended to install it on the heating element itself. This sensor will be triggered when the critical heating temperature of the working element is reached. When it is triggered, the power to the inverter device will be turned off.

Powerful fan for cooling the inverter device
During operation, inverter welding heats up very quickly, so the presence of two powerful coolers is a prerequisite. These coolers or fans are located on the device body so that they work to extract air.
Fresh air will enter the system thanks to the holes in the device body. The system unit already has these holes, and if you use any other material, do not forget to provide a flow of fresh air.
5) Soldering the board is a key factor since the board is what the entire circuit is based on. It is important to install diodes and transistors on the board in opposite directions to each other. The board is mounted directly between the cooling radiators, with the help of which the entire circuit of electrical appliances is connected. The supply circuit is designed for a voltage of 300 V. The additional arrangement of capacitors with a capacity of 0.15 μF makes it possible to dump excess power back into the circuit. At the output of the transformer there are capacitors and snubbers, with the help of which the overvoltages at the output of the secondary winding are suppressed.
6) Setting up and debugging work. After the inverter welding has been assembled, several more procedures will need to be carried out, in particular, setting up the operation of the unit. To do this, connect a voltage of 15 volts to the PWM (pulse width modulator) and power the cooler. Additionally connected to the relay circuit through resistor R11. The relay is included in the circuit in order to avoid voltage surges in the 220 V network. It is imperative to monitor the relay’s activation, and then apply power to the PWM. As a result, a picture should be observed in which rectangular areas in the PWM diagram should disappear.

The device of a homemade inverter with a description of the elements
You can judge whether the circuit is connected correctly if the relay outputs 150 mA during setup. If a weak signal is observed, this indicates that the board connection is incorrect. There may be a breakdown in one of the windings, so to eliminate interference you will need to shorten all power supply wires.

Inverter welding in a computer system case
Checking the device's functionality
After all the assembly and debugging work has been completed, all that remains is to check the functionality of the resulting welding machine. To do this, the device is powered from a 220 V power supply, then high current values are set and the readings are verified using an oscilloscope. In the lower loop, the voltage should be within 500 V, but not more than 550 V. If everything is done correctly with a strict selection of electronics, then the voltage indicator will not exceed 350 V.
So, now you can check the welding in action, for which we use the necessary electrodes and cut the seam until the electrode burns out completely. After this, it is important to monitor the temperature of the transformer. If the transformer simply boils, then the circuit has its shortcomings and it is better not to continue the work process.
After cutting 2-3 seams, the radiators will heat up to a high temperature, so after this it is important to allow them to cool down. To do this, a 2-3 minute pause is enough, as a result of which the temperature will drop to the optimal value.

Checking the welding machine
How to use a homemade device
After connecting a homemade device to the circuit, the controller will automatically set a certain current strength. If the wire voltage is less than 100 Volts, this indicates a malfunction of the device. You will have to disassemble the device and recheck the correct assembly again.
Using this type of welding machine, you can solder not only ferrous, but also non-ferrous metals. In order to assemble a welding machine, you will need not only knowledge of the basics of electrical engineering, but also free time to implement the idea.
(1 ratings, average: 5,00 out of 5)
Scheme of a simple welding inverter
Good day, gentlemen, radio amateurs. Every radio amateur, and not only in his own practice, is faced with the problem of joining metal, and of such thickness that a soldering iron is no longer needed. I had the same problem, so I’ll tell you how I assembled the welding inverter. But I warn you right away, the device is not lightweight. If you have never worked with converters, you should not take on such a complex circuit.
Inverter circuit for welding work

I started working on power electronics a long time ago, from car inverters to 160-amp welding machines! Since he is a student himself and doesn’t have much money, he chose a scheme with good repeatability and a small number of parts!

I took the power capacitors from the robot, I also took a couple of fans from coolers there, they are well suited because they are high-speed and provide good air flow, one fan I took was large, but not so high-speed, it blows out warm air.

The master oscillator chip is UC3842, you can also use UC3843. UC3845, to boost the power transistor I used a complementary pair KT972-KT973, the power switch irg4pf50w burned one, but nothing, there are a lot of them on the radio market :)

The power paths were reinforced with copper wire. I didn’t photograph the process of winding the transformer, I’ll just say that the primary is 32 turns of 1.5 mm wire, the secondary is a loop from a kinescope, it fits just right! Read about transformers on ferrite rings here.

The aparatik will turn out to be small, in general, just what is needed for country work. I'm very pleased with the result. Best regards, Columnist.