|
Boardpieces per cube |
barpieces per cube |
||
|
25x100x6000 |
66 |
100x100x6000 |
16 |
|
25x130x6000 |
51 |
100x150x6000 |
11 |
|
25x150x6000 |
44 |
100x200x6000 |
|
|
25x200x6000 |
33 |
150x150x6000 |
|
|
40x100x6000 |
41 |
150x200x6000 |
|
|
40x125x6000 |
33 |
200x200x6000 |
|
|
40x150x6000 |
27 |
25x50x3000 |
266 |
|
40x200x6000 |
20 |
40 x40 x3000 |
208 |
|
50x100x6000 |
33 |
40 x50 x3000 |
166 |
|
50x150x6000 |
22 |
50 x50 x3000 |
133 |
|
50x200x6000 |
16 |
50 x70 x3000 |
95 |
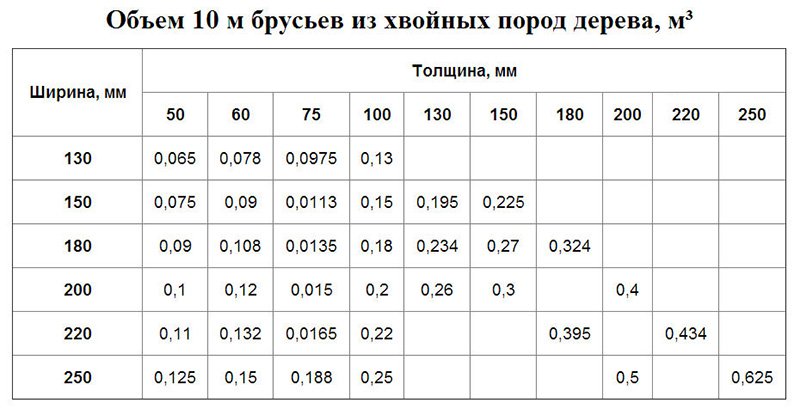
How to determine the cubic capacity (volume) of the material? It is very simple if the material, as in our case, has right angles. You need to multiply the width by the thickness by the length. And to find out how much of this material is in a cube, you need to divide the result by cubic / meter. Here is an example of how to determine how many 50x150x6000mm boards are in a cube. We will decide in centimeters.
(Thickness) 5cm x (Width) 15cm x (Length) 600cm = 45000cc/cm
The cube is = 100cm x 100cm x 100cm = 1,000,000 cc/cm
(Cube/meter) 1000000: (Board) 45000 = There are 22.22 boards in a cube.
If you want to know how much in a cube square meters lumber, you need to divide the thickness of the board in centimeters by 100 centimeters. Let's say you buy a lining 12.5mm x 90mm and you know that its square meter costs 120 rubles. The solution will be like this.
Lining thickness 1.25 cm 100: 1.25 = 80
From this it follows that this lining in a cube will be 80 square meters. And that the cube of this lining will cost 80x120 = 9600r
During construction frame house the main material is a wooden beam. It is needed not only to create the frame of the house, but also for the construction of the roof, during the installation of log crowns, the arrangement of internal partitions and other house structures. Due to the wide range of uses of wood, this construction material has tens and hundreds of positions that regulate the size of the product. Knowing the exact dimensions of one unit, it is possible, without going into complex calculations, using simple formulas to calculate how many pieces of a 6-meter beam fit in 1 m 3 - to make an estimate and optimize logistics operations for the delivery and storage of lumber at the construction site.
Features of lumber calculations in different units
The volume of any physical rectangular object is the result of multiplying the length, width and height of the rectangle, in our case, a wooden beam. Volume V \u003d a x b x c, where the designations: a is the length, b is the width, and c is the height of the beam. For example, a product 6 meters long, 10 cm wide and 10 cm high will have a volume of 0.06 m 3. But this is an ideal mathematical formula, and in practice products in one batch can have different sizes, which is allowed by the standards, but complicates the calculation of the volume of lumber .
Edged or profiled timber is much more expensive than regular timber, so the accuracy of the calculations is crucial - you will have to pay from your wallet. The traditional system of measurements when buying lumber is a cubic meter, but for beams for rafters, wall frames, floor beams and wood for flooring, it is more convenient to use linear meters. Also, the features of production in the woodworking industry allow for some variation in size, in particular, length, which can vary between 3-6 meters in increments of 50 cm.

Different units of measurement and different approaches in calculating the required amount of timber can cause errors and inaccuracies, as well as cause a general misunderstanding of the situation - how to convert the given units to others.
- For example, a product with a section of 100 x 50 mm is required, and the total length of the batch is known - 100 p / m (linear meters). To find out the volume of a beam, it is necessary to calculate the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bone unit, and for this mm convert to m 2, then multiply the cross-sectional area "S S" and the length "a": 0.1 x 0.05 x 100 \u003d 0.50 m 3 . It is easier to calculate the cost of a batch - you need to multiply the volume of the batch by the price per 1 m 3.
- Or how to find out how many units of timber will be obtained in a certain volume of lumber? To do this, you need to know both the cross section and the length of one unit. For example, if there is data on the total length of the batch - 100 p / m, and a product with a length of 4 m is required, then how many pieces will there be in this batch? First, the volume of one product is calculated: 0.1 x 0.05 x 4 \u003d 0.02 m 3. When purchasing 0.5 m 3 of timber, 25 units are obtained, or 50 pieces per 1 m 3.
In individual construction, every ruble counts, so ordering, for example, 4 m 3 of edged or profiled timber, if you need 3.8 m 3, is uneconomical.
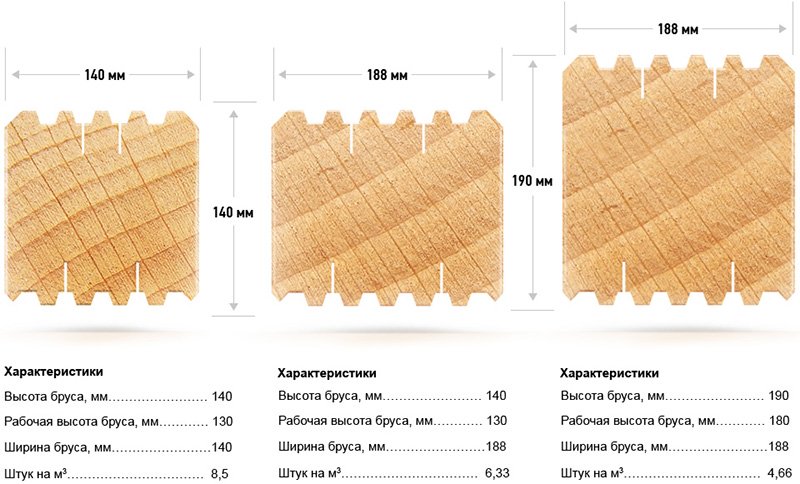
Example: when buying 52 p / m lumber with a section of 100 x 180 mm and a length of 6 meters, the total volume of the beam will be: 52 x 0.1 x 0.18 \u003d 0.936 m 3. You can find out the number of pieces in this volume as follows: divide the total volume by the volume of one unit. We find out the volume of one product: 0.1 x 0.18 x 6 m / n \u003d 0.108 m 3. Last calculation: 0.936 / 0.108 = 8.666 units. Since no one will cut the lumber in the store, it is easier to pay this small difference for one unit than to buy the entire lot with the difference in price multiplied by the number of pieces in the lot.
Profiled timber, although of a more complex shape, is calculated using the same formulas. That is, to calculate the cross-sectional area of the profiled product, the height "c" must be multiplied by the width "b". The height of the profiled beam is defined as the distance from the bottom surface with the groove to the top of the tenon. 
When calculating the number of units of lumber in 1 m 3, already when buying it, you need to measure the real section of any product with a tape measure to make sure that you do not have to overpay. A difference of even 0.5 cm is a rather significant blow to the family budget.
There is such a production concept as a technological deviation in length. This error can reach 4-6 cm for one unit, since the logs do not end when sawing. Therefore, the seller should be reminded of this so that he does not add payment for a non-existent length of material when calculating the total amount. If during the construction of a frame house you need to know how much 150x150 timber in a cube, the table below will help you make quick and accurate calculations.
The number of units of profiled and edged timber in 1 cubic meter:
| Width, height, length in m | Volume 1 pc. in m 3 | Units in 1m 3 |
| 0.10 x 0.10 x 6 | 0,06 | 16 |
| 0.10 x -0.15 x 6 | 0,09 | 11 |
| 0.15 x 0.15 x 6 | 0,135 | 7 |
| 0.1 x 0.18 x 6 | 0,108 | 9 |
| 0.15 x 0.18 x 6 | 0,162 | 6 |
| 0.18 x 0.18 x 6 | 0,1944 | 5 |
| 0.10 x 0.20 x 6 | 0,12 | 8 |
| 0.15 x 0.20 x 6 | 0,18 | 5 |
| 0.18 x 0.20 x 6 | 0,216 | 4 |
| 0.20 x 0.20 x 6 | 0,24 | 4 |
| 0.25 x 0.20 x 6 | 0,3 | 3 |
| 0.25 x 0.25 x 6 | 0,375 | 2 |
| 0.25 x 0.30 x 6 | 0,45 | 2 |
| 0.30 x 0.30 x 6 | 0,54 | 1 |
To find out how much timber is in a cube, the table is presented below:
| Width, height, length in m | The volume of one unit |
| 0.10 x 0.10 x 6 | 0,06 |
| 0.10 x -0.15 x 6 | 0,09 |
| 0.15 x 0.15 x 6 | 0,135 |
| 0.1 x 0.18 x 6 | 0,108 |
| 0.15 x 0.18 x 6 | 0,162 |
| 0.18 x 0.18 x 6 | 0,1944 |
| 0.10 x 0.20 x 6 | 0,12 |
| 0.15 x 0.20 x 6 | 0,18 |
| 0.18 x 0.20 x 6 | 0,216 |
| 0.20 x 0.20 x 6 | 0,24 |
| 0.25 x 0.20 x 6 | 0,3 |
| 0.25 x 0.25 x 6 | 0,375 |
| 0.25 x 0.30 x 6 | 0,45 |
| 0.30 x 0.30 x 6 | 0,54 |
Simplified formulas for calculating lumber 0.15 x 0.15 x 6 m:
- Volume 1 piece: 0.15 x 0.15 x 6 - = 0.135 m 3.
- Pieces in 1 m 3: 1 / 0.135 = 7 pcs.
The final and correct calculation implies that 12-15% is added to the result.
Necessary primary knowledge for calculations
A few simple formulas will help the developer do without intermediaries in calculating the amount and volume of wood for building a house:
- The area of the product S is the result of multiplying the length (a) and width (b) of the wood product;
- The volume V is the result of multiplying the area S and the height c, or multiplying a the length, b the width, and c the height;
Calculation features:
- The calculation for wood products with grooves, spikes and other complex geometric surfaces is carried out on the working plane;
- When purchasing a certain amount of wood, control the rounding that the seller makes when calculating the cost of the purchase. So, at a cost of 1 m 3 within 10,000 rubles, such an “insignificant miscalculation” as 0.005 m 3 will increase your costs by 30-50 rubles. Naturally, no one takes into account such small errors, but larger values will lead to higher costs.
- When buying wood, it is recommended to have the data of the above tables with you in order to exclude even unintentional cases of incorrect calculation and overpayment.
How many timber in a cube table updated: August 1, 2017 by: crunch0
To simplify the calculation, we have prepared a summary table for you. The tables below show data on the volume of one beam and how many pieces of beams of different sizes are in the 1st cube. To make you feel comfortable.
How many pieces of edged and profiled timber in 1 cube table
| Dimensions , mm | The volume of boards in 1 m 3 | Number of boards in m 3 |
| 100x100x6000 | 0.06 m 3 | 16 pcs. |
| 100x150x6000 | 0.09 m 3 | 11 pcs. |
| 150x150x6000 | 0.135 m 3 | 7 pcs. |
| 100x180x6000 | 0.108 m 3 | 9 pcs. |
| 150x180x6000 | 0.162 m 3 | 6 pcs. |
| 180x180x6000 | 0.1944 m 3 | 5 pieces. |
| 100x200x6000 | 0.12 m 3 | 8 pcs. |
| 150x200x6000 | 0.18 m 3 | 5 pieces. |
| 180x200x6000 | 0.216 m 3 | 4 things. |
| 200x200x6000 | 0.24 m 3 | 4 things. |
| 250x200x6000 | 0.3 m 3 | 3 pcs. |
| 250x250x6000 | 0.375 m 3 | 2 pcs. |
| 250x300x6000 | 0.45 m 3 | 2 pcs. |
| 300x300x6000 | 0.54 m 3 | 1 PC. |
How to calculate how much timber in 1 cube?
We offer a simple calculation so that you do not get lost with the question of how to find out how much timber is in a cube. These calculation options are suitable if you know the dimensions of the timber. For example, let's take a bar 260 x 260 x 6,000 mm (6 meters). The same can be done for a beam measuring 3 meters, 4 meters, 5 meters.
The formula for calculating the volume of a beam:
100mm 100mm 6000mm = 0.1m 0.1m 6m = 0.06m3
The formula for calculating the beam in pieces:
Bar length - 6 meters
1m 3 / 0.06m 3 \u003d 16 pcs / m 3
Difficult? It seems to be no! But if the calculation causes you difficulties, just use our table. The table contains a calculation for all known sizes of timber, which are given in GOST 8486-86.
The page contains answers to simple questions people have:
- How much timber
- How many cubes of timber
- Cube of timber how many pieces
- How much timber do you need
- How many in one cube
- How many pieces in a cube
- How many bars are in a cube
- How to calculate how much timber in 1 cube
Why do you need to know how much timber is in 1 cube?
There are two reasons for this:
- You can immediately calculate the total price of the volume of timber you need. To do this, you need to know the volume of 1 piece of timber, the price for 1 cube and how many pieces will be needed to implement your plans.
- You can calculate the total number of timber units needed to complete the project. And you can do this by knowing how many cubes are required for work, and by calculating the number of pieces of timber in 1 cube.
When building a house, craftsmen have to perform various tasks, such as preparing an estimate for materials and directly erecting an object and decorating the premises. Prices for edged boards in Moscow are at an average level. When buying a material, its correct calculation is very important, which will save and reduce unnecessary costs. Calculating the number of boards in a cube can be difficult for an inexperienced person. For this you need to know general information how the calculations are done.
Before starting the calculations, it is necessary to determine what the concept of "1 cube" means, and highlight the main types of lumber available on the construction markets.
Ungrooved lumber is edged and unedged boards. Grooved includes lining, floorboard, block house and imitation of timber. You can buy a dry planed board in Moscow in almost any hardware store. When buying, you should take into account that when calculating the cubic capacity, the working width of the board is taken into account - the spike is not taken into account.
Calculation method
The first step is to find the product of three quantities - the width, length and height of the material. It is most convenient to convert all parameters to meters when calculating. For example, the cubic capacity of one board with a cross section of 150x25 mm with a length of 6 meters is calculated as follows: 0.15 x 0.025 x 6 = 0.0225 m3. Getting the price of a board, knowing the volume, is even easier: 0.0025 is multiplied by the cost of one cubic meter. For example, if a board cube costs 6,500 rubles, the price of one will be 146 rubles and 25 kopecks.
As a rule, the cubic capacity is rounded up to 0.023 - this means that in fact the board will cost the buyer 149.50 rubles. Some unscrupulous sellers round the cubic capacity of lumber with dimensions of 150x50 mm to 0.05 m3, with the correct calculation it is 0.045 m3. This rounding causes the cost of the board (the price per cube is 6,500 rubles) to be 325 rubles, and not 292.50 rubles. In addition, you should be aware that for materials with a length of 6 meters, the actual length is several centimeters longer, which should not be taken into account when selling.
In order to find out how many boards of one or another length and width are contained in one cube, there are special tables that indicate the cubic capacity of the most popular types of materials.
|
Quantity in 1 m 3 |
Volume of 1 piece (m 3) |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Board 150x25 mm |
||
|
Board 150x40 mm |
||
|
Board 150x50 mm |
||
|
Board 100x25 mm |
||
|
Board 100x40 mm |
||
|
Board 100x50 mm |
||
|
Beam 100x100 mm |
||
|
Beam 150x100 mm |
||
|
Beam 150x150 mm |
||
|
Beam 200x200 mm |
Knowing how to calculate the number of boards in a cubic meter, you can easily calculate the amount of lumber needed and the amount that the purchase will cost.




















