Building materials for walls largely determine the cost of building a house, its strength, durability and appearance. There are no ideal building materials for the walls of a house. Each building material has its own advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we will consider in more detail the main ones.
Building materials for the walls of the house - selection criteria
When choosing building materials for walls, the following main factors should be considered:
- building material cost. On average, the cost of wall materials is about 15-20% of the cost of building a house box. Choosing the cheaper one construction material walls can save money. Or, using lightweight materials (aerated concrete, "sandwich" panels, fixed formwork) you can save on the foundation, as they allow you to choose a cheaper design, for example, a columnar foundation.
- Wall thermal protection– must be at least standard for the region of construction. To do this, it is necessary to build walls of warm material or insulate them.
- Labor intensity. Using large blocks instead of bricks or small-piece stones, you can reduce labor intensity and increase the speed of building walls by 3-4 times.
- New materials- thanks to smooth surfaces, they reduce the time and cost of finishing the walls.
Below are the main characteristics of the most common building materials for wall construction.
Wood (timber) as a building material
Wood -
 traditional natural building material used to build walls wooden houses, installation of ceilings and roofs, manufacturing of wooden floors, stairs, doors, windows, etc. Wood has a unique structure - inside it at the cellular level there is a constant air exchange.
traditional natural building material used to build walls wooden houses, installation of ceilings and roofs, manufacturing of wooden floors, stairs, doors, windows, etc. Wood has a unique structure - inside it at the cellular level there is a constant air exchange.
The tree interacts with the environment in a special way: it disinfects the air without letting in harmful substances. Humidity and oxygen balance are maintained in a wooden house at an optimal level.
The most commonly used building material is pine.
Pine wood light, resinous, with frequent knots, strong and easy to work. It is light in color but darkens over time.
spruce wood softer than pine, gets off worse but more moisture resistant, has few knots and a beautiful, almost white color.
birch wood homogeneous, the texture is weakly expressed, the strength is medium, it is easily processed and finished, but has a low moisture resistance.
Larch- durable, resistant to decay, not afraid of moisture, has a beautiful pink wood.
Cedar wood(Russian) - durable, with a beautiful texture and bactericidal odor.
Oak has a very strong wood, viscous and moisture resistant, it is well processed and has a large beautiful texture and a lot of tannins.
Larch, oak and cedar wood is more expensive than pine, spruce and birch wood.
For the construction of the walls of the house, the following types of wood materials can be used:
- Logs processed manually or rounded in industrial conditions;
- Timber, which can be sawn, planed, profiled or glued;
- Boards.
Advantages of wood as a building material:
- environmental safety (if the wood is from an ecologically clean area);
- relatively low cost;
- low thermal conductivity;
- aesthetic appearance;
- relatively small specific gravity;
- simplicity and ease of processing.
Flaws:
- hygroscopicity - the ability to absorb moisture and get wet, as a result of which it can rot or become infected with a fungus, to prevent which it becomes necessary to treat it with antiseptics and protect it with hydro- and vapor barrier materials;
- combustibility of the material - to reduce this ability, it is necessary to treat it with flame retardants (anipyrenes);
- shrinkage of fresh wood - its decrease in volume upon drying;
- protection against wood pests is required.
Brick is a traditional building material for walls.
- ceramic (clay) brick;
- clinker brick;
- refractory fireclay bricks;
- special types of bricks for cladding (" broken stone" and etc.)
ceramic brick

Ceramic (red) brick is made of clay. Such a brick is full and hollow.
Solid brick, as a building material, is usually used for laying load-bearing walls, constructing columns and vaults, as well as for plinths, foundations and basements.
Hollow bricks are used in the construction of external walls with increased thermal insulation capacity. The more voids inside the brick, the warmer the wall will be from it. The voids in the brick are both through and closed on one side. The shape of the holes can be square, rectangular, round and oval, and their location is horizontal or vertical.
By purpose, bricks are distinguished ordinary, facing and special(for special operating conditions).
As building materials for walls, all these types of bricks are used.
Internal and external walls are erected from ordinary bricks, which are subsequently plastered or lined.
The front brick is divided into textured and shaped(for finishing cornices, window openings and other parts of the facade of the house). It is made with a brand not lower than M125. Facing or facing bricks, as a building material, are used for the outer surfaces of the walls of buildings. It should be with a flat and smooth surface and regular geometric shapes, as well as have increased heat and moisture resistance.
Clinker brick
Clinker brick is a building material for wall cladding, but with increased strength, frost and water resistance. It is used not only for cladding, but also for paving, as it has a high wear resistance.
Refractory fireclay brick
Fireclay bricks are made with the addition of fireclay - fired refractory clay. It is able to withstand temperature drops of the order of 1000 ° C, so it is practically not used as a building material for walls, but is used for interior decoration of fireplaces and stoves.
silicate brick
Silicate (white) brick is one of the traditional building materials for walls and partitions. It consists of sand, lime and additives. Silicate brick, like ceramic  it can be hollow and full-bodied, facial and private. Such a building material is usually used for laying load-bearing walls and various partitions. Silicate brick has increased soundproofing properties, which is very important for interior partitions. Silicate facing brick is used for facing buildings.
it can be hollow and full-bodied, facial and private. Such a building material is usually used for laying load-bearing walls and various partitions. Silicate brick has increased soundproofing properties, which is very important for interior partitions. Silicate facing brick is used for facing buildings.
Brick sizes
Bricks are distinguished by size:
- single - 250x120x65 mm;
- one and a half - 250x120x88 mm;
- double - 250x120x138 mm.
Double and large bricks are also called building stones (blocks). They reduce laying time and mortar consumption, but a single brick is a more convenient building material for walls.
Strength and frost resistance of bricks
An important indicator for a brick is its strength. The brand of brick, which is denoted by the letter M with a numerical value, indicates what load in kg per 1 cm 2 it can withstand.
In addition to strength, bricks are divided according to the degree of frost resistance of the brand: F25, F35, F50, F100, etc. Frost resistance grade means that the brick withstands a certain number of freezing cycles without signs of destruction (splits, peeling), indicated by numbers after the letter F.
Advantages of brick as a building material for walls:
- aesthetic appearance;
- environmentally friendly material;
- long service life;
- not affected by corrosion, pests and fungi;
- the ability to implement projects of varying complexity;
- high fire safety;
- low thermal conductivity;
- good soundproofing.
Flaws:
- high price;
- great weight;
- high labor intensity of masonry;
- high qualification of masons is required;
- the need for strong foundations;
- the need for additional thermal insulation.
Ceramic blocks
This building material for walls combines the advantages of ceramic bricks, excellent  thermal insulation properties and environmental safety.
thermal insulation properties and environmental safety.
The ceramic block is a multi-slit hollow stone with corrugated side faces and a microporous structure. It is several times larger than an ordinary brick in size and has a small weight, which reduces the time spent on building a wall.
Besides, ceramic block - porous ceramics, natural material. The manufacturing technology of this building material for walls includes only natural ingredients: clay, water and small wood chips, which are added to the mix to turn ordinary ceramics into porous ones. Firing, the temperature of which reaches 1000 ° C, burns out the chips, creating micropores that increase the thermal insulation properties of ceramic blocks.
The internal structure of the ceramic block is a multi-slot structure, the total void volume of which (together with micropores) is equal to 50% of the total volume of the block.
Ceramic blocks are a very convenient building material for laying walls. They have a tongue-and-groove vertical docking system.
Keramoblocks have a multiple height brickwork. The block width is usually 230,240 and 250mm. The length can be different: 80, 100, 110, 250, 300, 380, 440, 500 and 510 mm.
Half and corner blocks are also made for right angles and angles of 135 o.
The weight of the ceramic block does not exceed 25 kg.
Advantages of ceramic block as a building material for walls:
- high heat and sound insulation;
- stability of thermal parameters throughout the entire service life;
- environmental Safety;
- speed and convenience of masonry;
- light weight;
- solution saving;
- high mechanical strength;
- fire resistance;
- frost resistance.
Flaws:
- high price;
- fragility during transportation;
- not all masons are able to work with ceramic blocks.
On the Internet, you can sometimes find very negative reviews about ceramic blocks. Therefore, we note that all of the above applies to high-quality ceramic blocks, serious manufacturers, made from high-quality raw materials and in compliance with the necessary technology. Even an ordinary full-bodied clay brick made from poor-quality clay or loam or with violations of the firing technology will be fragile and crumble at the first blow.
Cellular concrete (light concrete blocks)
Cellular concretes, as building materials for the walls of houses, are of several types:
- - concrete on porous aggregates;
- - foam concrete.
Concrete on porous aggregates easy to distinguish by structure: balls and spheres are visible in it, which are connected by concrete.
Aerated concrete and foam concrete differ in manufacturing technology. As the main binder component for aerated concrete, lime, and for foam concrete – cement.
Cellular concretes are produced by autoclave and non-autoclave methods. In the autoclave method, the hardening of the material occurs when high temperature and under pressure, thus forming a more durable and homogeneous material. In the non-autoclave method, the mixture is left to harden under normal conditions.
Aerated concrete or cellular autoclaved concrete (gas blocks)
 Aerated concrete, as a building material for walls, has a low density (300-500 kg / m3), which makes it possible to produce blocks of increased sizes with a mass of 15-30 kg. A standard block with dimensions of 200x250x600 mm weighs about 18 kg and can replace up to 15-20 bricks in a wall. Due to the air contained in the pores, the level of thermal insulation of aerated concrete is almost three times greater than that of a brick.
Aerated concrete, as a building material for walls, has a low density (300-500 kg / m3), which makes it possible to produce blocks of increased sizes with a mass of 15-30 kg. A standard block with dimensions of 200x250x600 mm weighs about 18 kg and can replace up to 15-20 bricks in a wall. Due to the air contained in the pores, the level of thermal insulation of aerated concrete is almost three times greater than that of a brick.
Advantages of aerated concrete as a building material for walls:
- light weight;
- high strength;
- exact geometry;
- low thermal conductivity;
- speed of construction;
- low labor intensity of masonry;
- smooth and even walls;
- easily cut with a hacksaw;
- incombustible;
- frost-resistant;
- high vapor permeability.
Disadvantages of aerated concrete (gas blocks):
- low bending strength;
- cracking ability;
- the need to use only special mixtures for masonry;
- during storage needs protection from atmospheric precipitation;
- not moisture resistant enough, if it gets wet, it is very difficult to dry it.
Foam concrete as a building material for walls
It looks similar to aerated concrete, but differs from it in composition (it does not contain lime), manufacturing technology and scope. The shrinkage of foam concrete is much greater than that of aerated concrete. Foam concrete, as a building material for walls, is also distinguished by the quality of the surface - its edges are smooth (for aerated concrete, the edges are porous). At finishing work plaster on foam concrete does not fit well, therefore, reinforcing mesh or various primers are used. But, unlike aerated concrete, foam blocks are more moisture resistant, since they contain not lime, but cement.
Expanded polystyrene thermoblocks - a new building material for walls
 Expanded polystyrene thermoblocks are a relatively new building material for walls, which is simultaneously a fixed formwork, enclosing structure and insulation.
Expanded polystyrene thermoblocks are a relatively new building material for walls, which is simultaneously a fixed formwork, enclosing structure and insulation.
They are ordinary, angular and wall-mounted. The most common blocks are 1000x250x250 mm in size, but sizes may vary from manufacturer to manufacturer.
Thermoblocks have a tongue-and-groove joint system and cavities for pouring concrete and laying reinforcement. A thermal house built from such blocks is actually a thermos.
Advantages of expanded polystyrene thermoblocks as a building material for walls:
- high rates of thermal insulation;
- high installation speed;
- durability;
- ease.
Disadvantages of thermoblocks:
- destruction upon contact with gasoline, oil or organic solvents;
- at temperatures above 90 ° C, the structure of expanded polystyrene is destroyed with the release of harmful substances;
- permissible load on a dowel driven into a wall of such blocks is 70 kg;
- compulsory ventilation of the premises and automatic control of heating.
Limestone-shell rock - sawn and recrystallized as a building material
 Limestone-shell rock(sometimes they say: "shell rock") is natural,
for real ecologicaly clean building material, which is a porous carbonate rock from compressed shells.
Limestone-shell rock(sometimes they say: "shell rock") is natural,
for real ecologicaly clean building material, which is a porous carbonate rock from compressed shells.
Sometimes the concepts of limestone and shell rock are separated, implying different kinds building materials. But this is wrong. Any shell rock is limestone. It's just that there are different types of limestone, both in density and in the form and shape of shells, which are its basis. Such types of limestone can vary greatly both in strength and in appearance and other characteristics.
In construction, porous saw limestone-shell rock is most often used as a building material, from which blocks and recrystallized limestone are cut - very dense, often layered.
Shells are easily visible in the saw limestone massif - shell rock (this is where its name comes from). Although in different fields they can be different in size, shape and color. For example, oolitic limestone-shell rock has inconspicuous shells 1-2 mm in size, almost round, and detrital limestone has shells 1-4 cm in size. Sometimes voids in a shell rock of one type are filled with shells of another - smaller ones.
Blocks are rarely sawn out of recrystallized limestone, as this is a very expensive pleasure due to its density. Most often it is used as rubble stone. In quarries, it is most often mined using blasting. Unlike saw limestone, recrystallized limestone is characterized by very little water absorption and has a crystalline structure, which gives it strength, but it is also more "cold". If you look closely, you can also see shells of various shapes and sizes in it, but they are recrystallized under the influence of temperature and pressure (metamorphism) and almost all the voids of such limestone are filled with a dense carbonate mass.
If there is a desire to build a foundation or basement from limestone, then dense recrystallized limestone is suitable for this. The porous saw shell rock is of little use for this.
Depending on the shape and color of shells, sawn limestone-shell rock from different deposits can differ in color (from white to brown), structure, texture and strength over a fairly wide range.
The strength of saw limestone-shell rock characterizes its grade - usually from M15 to M 50, where the number indicates the value of the compressive strength in kg / cm 2.
For the construction of buildings, limestone-shell rock is cut in the form of blocks with dimensions: 490x240x188, 390x190x188 or 390x190x288 mm.
True, due to the fact that blocks of limestone-shell rock are sawn out, and not stamped or molded, their sizes usually deviate from the standard depending on the mechanisms used for sawing and adhering to standards in a particular quarry, which can be inconvenient when masonry, especially combined (block + brick). This must be taken into account when buying a shell rock as a building material for the walls of your house and be sure to check their dimensions. If the laying of the walls will be carried out only from shell rock, then the main thing is that the blocks are at least approximately the same size.
Advantages of limestone-shell rock as a building material:
- -environmental Safety. It is difficult to find a more environmentally friendly building material than shell rock. Even a tree, growing in modern conditions, can accumulate harmful compounds from the air or soil in its wood. In addition, wood, in modern construction, is impregnated with various compounds from decay and fire. Shell limestone, on the other hand, was formed millions of years ago and was preserved under a layer of alluvial rocks, and its radioactivity is usually even below the sensitivity limit of modern instruments;
- -speed of construction, as the blocks are quite large;
- -increased thermal insulation, compared with solid brick or concrete, which, however, depends on its porosity and density;
- - relatively small cost, if you do not take into account the cost of delivery.
Disadvantages of this material:
- block sizes often deviate from the standard;
- higher water absorption compared to brick, especially blocks of low grades or highly porous;
- thermal conductivity is greater than that of hollow bricks, ceramic blocks, aerated concrete, foam blocks or wood;
- sometimes - the heterogeneity of the material (blocks from different batches, and even from one), in terms of strength and porosity.
 Expanded clay concrete blocks are made from a mixture of expanded clay, sand, cement and water by pressing. Due to the presence of expanded clay in their composition, they have quite good thermal insulation properties, and the presence of cement as a binder provides them with sufficient strength to construct both load-bearing external walls and internal partitions from them.
Expanded clay concrete blocks are made from a mixture of expanded clay, sand, cement and water by pressing. Due to the presence of expanded clay in their composition, they have quite good thermal insulation properties, and the presence of cement as a binder provides them with sufficient strength to construct both load-bearing external walls and internal partitions from them.
Such blocks can be made both solid and hollow - with the presence of internal voids of various shapes and volumes. Hollow expanded clay concrete blocks can be with voids of cylindrical, rectangular, slit-like and small-slotted, located both along the block and across it, which during laying can be filled with insulation.
Blocks of expanded clay concrete are produced in different sizes and shapes. Most often they are rectangular in shape with dimensions: for laying exterior walls - 300x390x188 and 190x390x188 mm, for interior walls and partitions - 190x390x90 mm.
The laying of expanded clay concrete blocks requires reinforcement with reinforcement or mesh every 3-4 rows.
Adobe
 It is one of the most ancient building materials for walls. It was also used in Ancient Egypt and even in more distant times. This is an affordable, environmentally friendly, rather "warm" but also labor-intensive material. Nowadays, you can’t buy it in a store, you can only make it yourself. Fortunately, it is not very difficult, although it requires a lot of effort and time.
It is one of the most ancient building materials for walls. It was also used in Ancient Egypt and even in more distant times. This is an affordable, environmentally friendly, rather "warm" but also labor-intensive material. Nowadays, you can’t buy it in a store, you can only make it yourself. Fortunately, it is not very difficult, although it requires a lot of effort and time.
Cob is a block of naturally dried mixture of clay or ordinary soil with straw. Such blocks can be formed using molds made from boards according to the size of future blocks. First, clay is mixed with water (or any loose soil, you can even black soil) with the gradual addition of straw, which should result in 30-50%. The more straw, the "warmer" the adobe will be. On the other hand, the mixture must be sufficiently viscous to be easily formed into blocks. The prepared mixture is placed with a rammer into molds, after which it is taken out and left to dry in the sun or under a canopy (depending on the weather). The laying of ready-made adobe blocks, after they have dried, can be carried out on a clay-sand mortar. Walls made of such material are quite durable, and outside and inside they can be finished with any modern materials.
Building materials for the walls of the house (types of bricks) - video
Below you can watch a video about the types of bricks and their features.
Dlet's look at what building materials to choose for building a house. Start with the foundation, continue with the walls and floors, and finish with the roof . Everyone who has ever thought about building a house has wondered " what house to build?»,« what to build? and “which ones can be used?”. Let's deal with this issue once and for all. To get started, you need to know that…
… on the modern market there are a million offers that will satisfy both the most fastidious and the most economical builder.
building material- building material for the construction of any structures.
I want to immediately emphasize that in this article we will not talk about finishing materials. If you want to know which is better to use, then this is in another article.
Foundation.
What is the foundation made of?
 H
u, there is no need for special wisdom, although some factors still influence. To decide on the type of foundation (and this is a tape, columnar, solid monolith, glass-type foundation, etc.), you better read this article - do-it-yourself foundation, as well as this one - types of foundations. To find out which foundation suits you best - study the soil map Russian Federation with the determination of freezing depths and the selection of the type of foundations in the article soil map of the Russian Federation
H
u, there is no need for special wisdom, although some factors still influence. To decide on the type of foundation (and this is a tape, columnar, solid monolith, glass-type foundation, etc.), you better read this article - do-it-yourself foundation, as well as this one - types of foundations. To find out which foundation suits you best - study the soil map Russian Federation with the determination of freezing depths and the selection of the type of foundations in the article soil map of the Russian Federation
Walls.
Construction materials
building materialfor walls. First you need to know the main thing about building walls.
Walls occupy from 30% of all Money spent on construction. Walls are the second foundation (after the foundation) of your home. How to choose the right building material for building walls? Many factors need to be taken into account, such as:
climatic conditions of the region;
number of storeys of the building;
financial component;
Now let's go over the materials for the walls.
Wooden walls - wooden walls. The building material for such buildings is wood.
An example is an article on the construction of a frame house, where the frame is mounted from wood. Also, the frame can be metal, and even reinforced concrete.
 D
wooden houses made of timber or a log house are very warm, but are more suitable for dry climates, such as Siberia, middle lane Russia, etc. In the south of the country, such houses used to be made from railway sleepers, since they are very hard, I don’t know for sure, but they say that they were even treated with creosote so that rodents and insects would not rot and start ( for reference - creosote has a sharp specific smell, reminiscent of either diesel fuel or kerosene.) Also in the Kuban, turluch construction was often practiced earlier. The building material for such construction was a wooden picket fence, from which shields were placed for assembling walls and clay, with which these shields were upholstered on both sides. Very cheap and warm, but not very pretty and durable. Moreover, it is difficult to pick up such walls.
D
wooden houses made of timber or a log house are very warm, but are more suitable for dry climates, such as Siberia, middle lane Russia, etc. In the south of the country, such houses used to be made from railway sleepers, since they are very hard, I don’t know for sure, but they say that they were even treated with creosote so that rodents and insects would not rot and start ( for reference - creosote has a sharp specific smell, reminiscent of either diesel fuel or kerosene.) Also in the Kuban, turluch construction was often practiced earlier. The building material for such construction was a wooden picket fence, from which shields were placed for assembling walls and clay, with which these shields were upholstered on both sides. Very cheap and warm, but not very pretty and durable. Moreover, it is difficult to pick up such walls.
Tobrick walls. .
 What house to build? Brick of course...
What house to build? Brick of course...
So, probably, 70% of the population will answer. But this is not always prudent.
Materials for building a brick house can be silicate, hollow, dense ceramic bricks. Do not forget also the frequent use of decorative facing bricks.
In our article - A private brick house, you can learn about all the pros and cons of brick construction and the use of brick as a building material in general.
 And
the use of lightweight concrete building material in the construction of houses has become used quite often now. Gas silicate, expanded clay concrete, slag concrete, sawdust concrete and foam concrete blocks are used. .The advantage of these building materials is frost resistance, ease of installation and affordable price. Block masonry.
And
the use of lightweight concrete building material in the construction of houses has become used quite often now. Gas silicate, expanded clay concrete, slag concrete, sawdust concrete and foam concrete blocks are used. .The advantage of these building materials is frost resistance, ease of installation and affordable price. Block masonry.
 D
heavy concrete ohms - Reinforced concrete slabs, poured monolithic walls, panels, etc.
D
heavy concrete ohms - Reinforced concrete slabs, poured monolithic walls, panels, etc.
Such houses are very heavy and are mainly used in industrial construction, but if we talk about some features, then such methods are still applicable in private housing construction. For example, you can build a house from flood walls, using expanded clay and concrete as a building material, or sawdust concrete, or, alternatively, slag concrete. This method will be practical, since the house will be built very quickly, and the walls will be strong and warm.
FROMaman house. Adobe is mainly used in villages, villages and villages, although in our time housing is already being built there from more modern building material.
Saman can be classified as: cheapest building materials, since it contains only clay, sand, straw, sometimes lime, and sometimes manure (dung in the common people).
Floors. Building material for floors
So, we continue the topic "materials for building a house with your own hands"
Wooden floors, concrete screed, parquet, tiles - These are the four main types of floors.
 D
wooden floor - usually such floors are made in houses where there is an underground. The underground is the space between the floor slab and the zero point (under the floor). The wooden floor is made of boards that are nailed to a wooden crate mounted on a plinth or pillars. Such a floor is usually chipped and then painted. Also, the wooden floor can be covered with sheets of fiberboard, chipboard or plywood (all about plywood).
D
wooden floor - usually such floors are made in houses where there is an underground. The underground is the space between the floor slab and the zero point (under the floor). The wooden floor is made of boards that are nailed to a wooden crate mounted on a plinth or pillars. Such a floor is usually chipped and then painted. Also, the wooden floor can be covered with sheets of fiberboard, chipboard or plywood (all about plywood). B
concrete screed - The easiest and cheapest option. Such floors are poured with a monolithic concrete slab with reinforcement. The materials used - rebar, sand, sometimes crushed stone, cement, water - agree,
B
concrete screed - The easiest and cheapest option. Such floors are poured with a monolithic concrete slab with reinforcement. The materials used - rebar, sand, sometimes crushed stone, cement, water - agree,
 P
arket. Parquet, like laminate and tile, can be considered a finishing material. Parquet is laid on a concrete screed, laminate on any surface, and tiles, like parquet, on concrete. How to level and pour a concrete floor with your own hands.
P
arket. Parquet, like laminate and tile, can be considered a finishing material. Parquet is laid on a concrete screed, laminate on any surface, and tiles, like parquet, on concrete. How to level and pour a concrete floor with your own hands.
Roof
building material for the roof.
Gthe main thing is a roof over your head. With a roof, everything is more complicated. Choosing for a roof is a responsible matter. Construction materials roofs are divided into many categories: hard, soft, metal, plastic, etc. etc. Let's talk about the main options:
· Slate;
· Decking;
· Tiling;
· Composite tiles;
· flexible roof;
· wood flooring

Hwhat can I say, the roof - it is also the roof in Africa. When choosing the type of roof, be guided mainly by the financial component. The more money spent, the more beautiful and durable the roof will be. The most for the roof will, perhaps, be wood and slate. The tree is practically no longer used, and slate has already proven itself well. Slate - asbestos cement
 wave sheet can be both ordinary and dyed in different shades. To tell the truth - the current quality of slate manufacturing leaves much to be desired in comparison with Soviet quality.
wave sheet can be both ordinary and dyed in different shades. To tell the truth - the current quality of slate manufacturing leaves much to be desired in comparison with Soviet quality.
 P
corrugated board - profiled metal, sometimes painted and galvanized. Roof decking has become very popular, has a wide range of color options, is mounted on a wooden crate using a vapor barrier.
P
corrugated board - profiled metal, sometimes painted and galvanized. Roof decking has become very popular, has a wide range of color options, is mounted on a wooden crate using a vapor barrier.
 H
tile is a very reliable, as well as expensive material for roofing. A roof made of tiles looks very beautiful, and besides, such a roof is very easy to repair, replacing only individual elements.
H
tile is a very reliable, as well as expensive material for roofing. A roof made of tiles looks very beautiful, and besides, such a roof is very easy to repair, replacing only individual elements.
 M
metal tile - in fact the same corrugated board, only in structure resembling a tile.
M
metal tile - in fact the same corrugated board, only in structure resembling a tile.
Tocomposite tile - profiled metal sheet with

coated with crumbs of natural stone.
Results.
So what kind of house to build? Is it possible to use cheap building materials? The answer is simple, build the house you like, you just need to take into account the type of soil and the depth of freezing. Cheap building materials are sometimes the best option.
formwork
ceramics
Comparison of various materials and their combinations in terms of thermal conductivity:
What to build a house from?
Before starting construction, you need to decide what a country house is for. Conventionally, country houses can be divided into two broad categories.
Seasonal houses. They are designed mainly for the summer period of residence and for an ambient temperature of 0 ... -5 ° С. The walls of such houses are made in a frame design, from a bar with a thickness of 100 - 150 mm, from rounded logs of small (up to 220 mm) diameters. Due to the low level of protection of the walls of such a house from heat loss, the cost of construction is low.
Some typical wall options for such houses:

Houses for permanent residence. The name speaks for itself and implies constant heating in the winter. They are designed for outdoor temperatures down to -30°C. Such houses can be both wooden and stone.
The walls of wooden houses for year-round use are made of profiled or sawn timber from 200 mm and above, with or without insulation, from rounded or chopped logs 240 - 280 mm.
Stone houses of permanent residence are also built according to different technologies: monolithic houses in fixed formwork, stone houses made of gas blocks (gas silicate blocks), bricks, warm ceramics, expanded clay concrete blocks.
Typical wall designs for permanent residences:
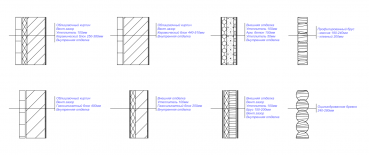
You can read more about the energy efficiency of various building materials in the article. Thermal characteristics of wall materials.
Choosing a building material
Wooden house usually chosen by people who prioritize the environmental friendliness of the building. In such a house, it is most pleasant to take a break from a hard working week, get enough sleep, get psychological relaxation. Wooden walls maintain a very comfortable atmosphere for a person - the optimal level of humidity and air exchange. Stone house, first of all, a practical choice. Minimal operating costs, low heat loss and long service life are the factors that make you think about building such a home. Combined house- a house that allows you to combine the practicality of a stone house with the light atmosphere of a wooden one. The stone first floor provides space for practical solutions and design experiments, and in the bedrooms of the wooden second floor, sleep will be strong and pleasant. General comparative characteristics of materials are summarized in two tables. The tables contain general information, and not technical coefficients and parameters, which, in case of interest, are not difficult to find. Table 1.|
Material |
+ |
- |
|
Light weight (600 - 900 kg / m3) allows the use of a light, shallow foundation. The material is environmentally friendly, acts as a natural filter in the room. The ability to leave the inner and outer surface of the walls without additional finishing. Possibility of year-round construction, wide architectural possibilities, attractive appearance. Price. |
Fire hazard, biological attack, wood shrinkage, cracking, lower durability compared to stone houses, lower heat transfer resistance of the wall. |
|
|
Warm ceramics |
High degree of protection against fire, low exposure to weathering, no biological attack, high structural strength, durability, good vapor permeability. |
The desirability of using foundations poured to the depth of soil freezing. Internal wall decoration is required, restrictions on the construction of walls in the winter. The complexity of attaching heavy hinged structures to hollow walls. Sufficiently large wall thickness - 51cm (without insulation). High price. |
|
Monolithic houses |
Short construction time. Savings in the construction of foundations. Cost Savings wall materials. High thermal performance of the walls. |
Not a natural eco-friendly material. Wall decoration required. For plaster, special expensive materials are used - "wet plaster". |
| gas silicate blocks (gas blocks) |
Good vapor permeability, high heat capacity. Does not emit any harmful substances into the atmosphere. Good frost resistance and durability. |
Requires more complex foundations compared to monolithic houses. Difficulty of attaching heavy hinged structures to fragile walls made of gas blocks. Inability to work in winter. |
Table 2.
| materials | Thermal conductivity | Reliability | Environmental friendliness | Exploitation | Foundation cost | Fire safety | Vapor-air-permeability |
| Beam and log | * | ** | *** | * | *** | * | *** |
| gas silicate block | ** | ** | ** | *** | ** | *** | ** |
| Foam block | * | * | ** | ** | ** | *** | ** |
| Monolith in fixed formwork | *** | *** | ** | *** | ** | ** | * |
| Warm ceramics (porous brick) | ** | ** | *** | *** | * | *** | ** |
Some additions.
To maintain normal heat and humidity conditions in brick house, it must be constantly heated. If the house has not been used in winter, then in the spring it will have to be thoroughly heated before it warms up and the rooms become dry. A house made of wood or a monolithic house built using fixed formwork technology does not require heating during the winter.
The construction of a heavy foundation and thick brick walls is significantly more expensive compared to building a wooden cottage or building a monolithic house.
AT wooden house more intensive exchange and purification of air. Up to 30% of the air per day can change through a log or timber indoors, and the unique properties of these materials allow in dry weather to release accumulated moisture, and in wet weather, on the contrary, to absorb its excess from the living space. That is why wooden houses are distinguished by a special microclimate and high level comfort. Wood is a very living material. Even after the log house, it continues to breathe, radiate heat energy, exude the aroma of resin. Wooden houses give people bioenergetic nourishment, heal them, have a positive effect on the human nervous system.
Construction of a monolithic house with fixed formwork gives creative scope to the most daring architectural ideas. In this material, you can bring to life any architectural forms - from a warm garage for an iron pet, to the floating lines of a small country residence. And the heating of the building can be proud of the neighbors - it is so economical.
A house made of warm ceramics is a combination of durability, reliability and environmental friendliness. The walls of such a house will stand for more than one hundred years, paying off their rather high cost. A house made of such blocks does not need additional insulation (with a wall thickness of 51 cm). The use of natural clay as a basis for ceramic blocks guarantees the absence of any chemical impurities in the air. Such a house is a long-term investment in which more than one generation of descendants will live.
So decide!! If your choice is in favor of cozy wooden house or you are attracted by the reliability and durability of stone - contact our construction company, we will help you choose a project from the catalog, or we will develop a new one for your needs.
WOODEN HOUSING
Which tree is best?
Many developers are faced with the question of what kind of wood to build a house from. During the construction of a wooden house from time immemorial, preference was given to coniferous trees - larch, pine and spruce. Not without reason there was a saying among the people: “The hut of the spruce, but the heart is great!”
The best-known material for timber construction is pine. It has a hard, resin-impregnated core and a looser
upper part. Of all conifers, pine is most often used in construction. It is distinguished by the greatest straightness of the trunk, the minimum number of knots and good technical properties. Pine has a high resistance to decay, but often (especially in July-August) with high humidity it tends to "turn blue". Blue in itself does not change the physical and mechanical properties of wood, but spoils the appearance. Pine is the main material for the construction of wooden houses, both in our country and in Europe (in particular, in Finland).
No less popular building material is spruce. The physical characteristics of these rocks are very close. Spruce has a stronger outer skin but a softer core. When dry, spruce wood is as strong as pine wood. Spruce is more prone to decay, but turns blue much less. On the world market, spruce is valued higher than pine.
Another building material (almost perfect) is larch, which has a unique, only inherent pattern. Larch is stronger, denser and practically unaffected by moisture, but it is more difficult to process than pine and splits easily. Therefore, larch is ideal as a wall material, but is not used for structural material (beams, valleys, rafters, puffs, etc.). However, this material is relatively expensive and not available to everyone.
What are the walls made of?
Our construction company offers a wide range of building materials for your home or bath. Let's look at their main types.
Technological material that requires a minimum of manual labor when  building a house, as the house is assembled according to the principle of a constructor. All necessary operations with rounded logs are performed at the place of production, in particular, the choice of mounting cups and landing channel in rounded logs.
building a house, as the house is assembled according to the principle of a constructor. All necessary operations with rounded logs are performed at the place of production, in particular, the choice of mounting cups and landing channel in rounded logs.
The advantage of a rounded log is its even, rounded shape, which makes it possible to achieve a dense connection of logs. The diameter of rounded logs ranges from 160 to 320 mm. And due to the same diameter and high quality surface treatment rounded logs do not require wall finishing.
Advantages of building houses and baths from logs:
Accuracy in the production of rounded logs and their marking speeds up the assembly of buildings and reduces construction costs;
The beautiful appearance of rounded logs due to the high quality and cleanliness of the surface treatment makes it possible to do without additional wall decoration inside and outside;
The tightness of the crown and corner joints of the logs is ensured by the technological accuracy of the groove and "cups";
Aesthetic appeal of buildings built using logs.
2. Hand-hewn logs up to 40 cm in diameter
For manual cutting, environmentally friendly, high-quality wood (spruce, pine, larch) is used, not infected with woodworm and fungus, with a moisture content of 45-60%. It is quite easy to process and deforms less when  natural drying in assembled form. Logs undergo manual processing: removal of bark, proteza, selection of cups and grooves, processing with a planer. With this treatment, the upper solid protective layer logs ("sapwood"). Hand-hewn logs are less deformed during the aging process. Corner joints of logs between themselves are made in a "bowl" or in a "paw", the crowns are fastened with wooden spikes (nagel) after 1000 - 1500 mm, all logs are treated with an antiseptic. Such houses are warmer than those assembled from rounded logs, their walls are less prone to cracking. And with high-quality processing of logs, the appearance of such houses is not much inferior to houses made of logs.
natural drying in assembled form. Logs undergo manual processing: removal of bark, proteza, selection of cups and grooves, processing with a planer. With this treatment, the upper solid protective layer logs ("sapwood"). Hand-hewn logs are less deformed during the aging process. Corner joints of logs between themselves are made in a "bowl" or in a "paw", the crowns are fastened with wooden spikes (nagel) after 1000 - 1500 mm, all logs are treated with an antiseptic. Such houses are warmer than those assembled from rounded logs, their walls are less prone to cracking. And with high-quality processing of logs, the appearance of such houses is not much inferior to houses made of logs.
If you like the old Russian or Finnish style of houses - this is your material!
 A house made of profiled timber is an island of comfort and coziness in the world of concrete jungle. A wooden house will delight its owner with a very comfortable indoor atmosphere - after all wood is an excellent natural conditioner ,
maintaining air exchange and humidity at a very comfortable level for a person.
A house made of profiled timber is an island of comfort and coziness in the world of concrete jungle. A wooden house will delight its owner with a very comfortable indoor atmosphere - after all wood is an excellent natural conditioner ,
maintaining air exchange and humidity at a very comfortable level for a person.
In the manufacture of profiled timber, a high purity of the treated surface is achieved, so the wood becomes almost polished, which makes it possible not to use Additional materials for the interior decoration of a wooden house, and therefore avoid unnecessary costs. Unlike log walls, the walls in a cottage made of profiled timber are even,  o facilitates possible finishing, arrangement of furniture, use of wall cabinets.
o facilitates possible finishing, arrangement of furniture, use of wall cabinets.
Currently, many prefer this particular material. The ratio "price-quality" is optimal here. Cottages made of profiled timber are very modern, look great, keep temperature fluctuations well, which is very important for the regions of central Russia.
The construction of houses and cottages from profiled timber is a technological process that includes the processing of material on a machine tool, the preparation of a “cup” with a double lock. Pre-assembly at home in the workshop is possible, which ensures particularly high assembly accuracy. The final assembly includes the erection of a log house at the construction site, drilling and fixing the timber with dowels.
During the construction of cottages and country houses from profiled timber, our company uses material manufactured by one of the company's departments.
4. Ordinary sawn (unplaned) timber
This is the cheapest building material made of wood. The sawn timber used for the construction of the well of a wooden house is made of an equilateral section (150x150mm, 200x200mm), or a versatile section (from 150x100 mm). In construction, either simply sawn timber is used, or planed (on one or two sides).  Basically, an ordinary bar with a section of 150x150, 200x150, 200x200 mm is used for construction country houses(optimal ratio: price / quality), and bigger size- for the construction of cottages with subsequent insulation and finishing with other facing materials.
Basically, an ordinary bar with a section of 150x150, 200x150, 200x200 mm is used for construction country houses(optimal ratio: price / quality), and bigger size- for the construction of cottages with subsequent insulation and finishing with other facing materials.
However, we must not forget that a simple bar does not have a thermal lock. Because of this, it is difficult to insulate it, because. the blowing coefficient will be several times higher than that of a wall made of a properly made log or profiled beam. In any case, after 1 - 1.5 years (after the shrinkage of the log house), it is necessary to carefully caulk the seams between the beams and sheathe the walls with finishing materials both inside and outside (lining, saiting, etc.). All these activities absorb the savings obtained by purchasing the timber itself. The benefit here is one thing - such a house can be built (and, therefore, invested in it) in stages, with a stretch over time.
Naturally, with any option for building a wooden house, antiseptic treatment of the walls with special compounds and paints should be implied, protecting the wood from turning blue, putrefactive disease, mold and woodworm beetles.
TECHNOLOGIES OF THE XXI CENTURY: Monolithic houses in fixed formwork
AT modern world, where prices for  building materials, as well as electricity, gas and fuel are growing rapidly, the question of the cost-effectiveness of building cottages is quite seriously raised, and in the process of operation - savings on heating and air conditioning houses.
building materials, as well as electricity, gas and fuel are growing rapidly, the question of the cost-effectiveness of building cottages is quite seriously raised, and in the process of operation - savings on heating and air conditioning houses.
For this reason, we propose technology of monolithic housing construction "Izodom" (using non-removable formwork made of expanded polystyrene). This technology for thermal protection, sound insulation, comfort, simplicity and speed of construction, as well as  durability refers to the advanced technologies in the field of construction and is designed for the rapid construction of warm, reliable and inexpensive homes.
durability refers to the advanced technologies in the field of construction and is designed for the rapid construction of warm, reliable and inexpensive homes.
This technology has been tested for many years in the USA, Canada and Western Europe, confirming the cost-effectiveness and durability of this system, and in last years begins to be popular in Russia. The sphere of application of Izodom technology is the construction of cottages, rural houses and summer cottages; construction of shops, cafes; multi-storey residential buildings; warm individual pools, garages and much more.
What gives developers the Izodom technology (monolithic houses)?
Reduced construction time. When using traditional materials (such as brick), building a house stretches for a long time. If you build using the Izodom technology, the same wall area is built several times faster.
savings when constructing foundations, since Izodom walls create a much lower specific load on the foundation. For such a house, it is recommended to install a shallow foundation.
Savings on the cost of wall materials. Price square meter Izodom walls are significantly lower than the cost of a brick wall, similar in terms of heat saving.
Benefit from obtaining additional usable area, since the thickness of the walls of "IZODOM" is much less than the thickness of walls made of other building materials, similar in terms of heat-saving capacity.
High thermal performance of walls- this is a way to avoid high costs for the purchase of expensive heating equipment, transportation of fuel, time and labor costs for its operation. The cost of heating the IZODOM building will be 3-4 times less compared to a brick building.
How cottages are built from monolithic concrete.
Modules of the Izodom system are hollow polystyrene blocks with a density of 25-27 kg / m3, which are joined together like parts children's constructor. Fixed formwork modules have cavities that are reinforced and filled with concrete during the construction process, and a special  the design of the locks allows you to quickly and accurately connect the blocks. Thus, a monolithic wall is constructed, framed on the inside and outside with a heat and sound insulating shell of expanded polystyrene. Thanks to this wall construction, houses built using fixed formwork are strong, light and very warm. The thickness of the wall is selected depending on
the design of the locks allows you to quickly and accurately connect the blocks. Thus, a monolithic wall is constructed, framed on the inside and outside with a heat and sound insulating shell of expanded polystyrene. Thanks to this wall construction, houses built using fixed formwork are strong, light and very warm. The thickness of the wall is selected depending on  the purpose of the building, as well as the temperature parameters of the construction region.
the purpose of the building, as well as the temperature parameters of the construction region.
The internal partitions of the house can be made from the same blocks, as well as from any other traditional materials. During the construction of buildings, you can use any type of floors - monolithic floors, concrete slabs or classic wooden floor structures.
For exterior finish walls can be plaster, siding, facing brick or stone. Interior decoration can  carried out using plaster or plasterboard. The undoubted advantage of a house built using this technology is that the walls, both internal and external, have a very even surface, therefore, an economical thin layer of plaster is needed to finish the walls. In addition, it is very easy to lay electrical wiring in such walls.
carried out using plaster or plasterboard. The undoubted advantage of a house built using this technology is that the walls, both internal and external, have a very even surface, therefore, an economical thin layer of plaster is needed to finish the walls. In addition, it is very easy to lay electrical wiring in such walls.
Expanded polystyrene is environmentally friendly (97% air and 3%  material) and is even used for packaging food products. It does not contain substances that feed microorganisms, i.e. not subject to the destructive effects of rodents, mold and bacteria. In addition, it does not burn if there is no prolonged exposure to the flame (more than 2.5 hours).
material) and is even used for packaging food products. It does not contain substances that feed microorganisms, i.e. not subject to the destructive effects of rodents, mold and bacteria. In addition, it does not burn if there is no prolonged exposure to the flame (more than 2.5 hours).
Technical parameters of the walls.
Wall thickness - 25, 30 or 35 cm, where 15 cm is concrete, the rest (respectively - 10, 15 or 20 cm) is polystyrene foam.
The weight of walls without finishing is 400 kg/m2.
Concrete consumption - about 125 liters per square meter of wall.
Thermal conductivity coefficient - L0=0.036 W/mK, excluding exterior and interior finishes.
The fire resistance limit of the wall is 2.5 hours.
Vapor permeability - 0.032 mg / (m.ch. Pa).
Water absorption in 24 hours, by volume - 0.1%.
Acoustic isolation - 46 dB.
Fire safety:
The fire hazard class of the load-bearing wall is K0 (the fire spread limit is 0)
The fire resistance limit of the load-bearing wall is at least 155 min.**
* According to the conclusion of the State Unitary Enterprise "NIIMosstroy"
** According to the tests of the center of the Federal State Institution VNIIPO EMERCOM of Russia
Whatever material you choose to build your house - we will be happy to help the future homeowner decide on a project or develop an individual one, discuss materials and finishes, and build STRONG HOUSE according to your wishes, tastes and possibilities.
Brick, usually considered a traditional building material for building the walls of a house.
But today, on the construction market of materials for building walls of a house, there are also materials that are much lighter, have good thermal insulation properties and, most importantly, are cheaper, such materials for building walls of a house include cellular concrete.
Gas-silicate, gas-concrete, foam-silicate materials for the construction of house walls belong to one class of building materials - cellular building materials.
Cellular concrete, which seems to have appeared on the construction market not so long ago, is rapidly gaining popularity. Cellular concretes differ from one another in the materials used for their manufacture and in the method of production, cellular concretes belong to the group of light building materials for the construction of house walls.

Foam concrete is a simple solution of cement, to which special surface-active components are added, which cause it to foam, which is performed mechanically. Due to foaming, the mass of concrete is saturated with air bubbles and a cellular structure appears. These foam concrete cells are completely airtight and saturated with air. A huge number of such cells create excellent sound-heat insulating properties and lightness for foam concrete. It is possible to produce foam concrete of different densities by changing the composition of the mixture for the manufacture of foam concrete - from 400 to 1800 kg / m3. In this case, it is possible to increase the strength of foam concrete, but at the same time, the heat transfer resistance will decrease.
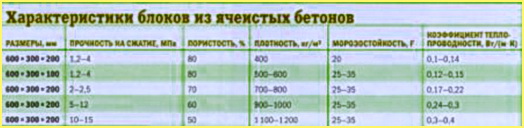
In appearance, foam concrete from the inside resembles foam concrete - porous chocolate, outwardly similar to a simple gray stone. Foam concrete blocks are made in sizes: 600 x 300 x 250 mm and 600 (length) x 300 (height) x 200 (width) mm. There are foam concrete blocks for the construction of partitions inside the house, with a width of 50 to 600 mm.
According to the type of application, building materials from cellular concrete can be divided into the following types: structural and heat-insulating, heat-insulating and structural. For the construction of load-bearing structures of buildings, blocks of cellular concrete with a density of at least D 500 are used, and for inlays with a density of D 400.
Cellular concrete won its popularity mainly due to its physical properties. Aerated concrete for the construction of house walls has the same thermal insulation properties as wood - from 0.12 to 0.4 W / (m K), it can be compared, pine has thermal insulation properties of 0.14 W / (m-K). Building foam concrete materials are light - this indicator significantly reduces the foundation.
Foam concrete can be easily processed, it perfectly resists high temperatures, is resistant to temperature extremes, frost-resistant, durable, environmentally friendly, has vapor permeability, and has good adhesion. The walls of a house built of cellular concrete will have many times more thermal insulation than, for example, brick ones.

Aerated concrete building materials are resistant to fire, are not subject to rotting and corrosion, are easy to work with (they are easy to process, easy to mill, drill, chisel). It has even edges, a smooth surface. Aerated concrete building materials have such quality properties as good thermal conductivity, which is higher than that of building materials such as silicate and ceramic materials, excellent water absorption and vapor permeability. 2 times more reliable, with the same density. For the construction of the walls of the house, one single aerated concrete block having a thickness of 37.5 cm is enough.
Construction of houses using cellular concrete
Aerated concrete has unique properties that make it possible to build houses throughout the year. It is a pleasure to build a house using this building material, not expensive, easy and quite fast, because one block of cellular concrete replaces a whole bunch of standard bricks (a block with dimensions of 60 x 30 x 20 cm is equal to 16 bricks). This type building material for the construction of walls are easy to process, with a simple hacksaw they can be given any desired shape,
Such products are easy to process using a simple hacksaw, this building material can be given any shape, so you can build a building of any complexity and shape, create arches and rounded surfaces, and when installing windows and doors in openings, it is easy to choose a quarter. For the construction of houses, cellular concrete with a density of 400-500 kg / m3 is used, at which cellular concrete is perfectly combined.

In order to prevent the appearance of cold bridges, it is advisable to lay cellular concrete on a special glue, and not on a cement-sand mortar. When a cement-sand mortar is used for masonry walls, water goes into the block and the seam becomes insufficiently reliable due to lack of moisture. To increase the strength of the masonry, it is possible to moisten the blocks with water before erecting the wall, and perform the masonry itself on a thick layer cement-sand mixture, the wall will turn out to be strong, but with this option of laying the walls, cold bridges are formed. When using glue, a ready-made dry mix, to which are added special preparations which retain water. When using glue, the laying of cellular concrete is obtained - thermally more homogeneous, and the seam is thinner. To complete the laying of the walls of a house of 1 m3, it will take about 40 kg of glue. The cost of twenty kilograms of glue fluctuates within twenty US dollars.
Construction of the walls of the house - monolithic construction
There is another method of building a house using cellular concrete, non-autoclaved (foam concrete), using a monolithic removable formwork, building a house in this way will require less finance, and will cost 1.5-2 times cheaper. Building a house with this method can only be done at a temperature not lower than +10 ° C and for construction a special installation is needed to make foam, it mixes the foam with a cement solution and transports the resulting mass through a hose to the construction site of the house.
To build the walls of the shape we need, fiberboards (fibreboards) are used for removable formwork, but fixed formwork, which is made of fiberboard and brick, can also be used to build walls and partitions, but for the construction of the walls of the house, using fixed formwork, you will need more money. Formwork can be made by construction, from two sides brick walls and pour concrete mixture between them. Another formwork construction method, you can build a brick wall only from the outside, and from inside, fix drywall or fiberboard boards. Fiberboard or GKL, leaving a foam concrete surface inside, can then be dismantled. In the future, you can proceed to finish the walls by gluing tiles, painting ...

When building the walls of a brick house, they breathe, as natural materials are used to make bricks. Brick has excellent sound and heat insulation properties, it is a durable and resistant to biological and weathering building material. In terms of environmental properties, brick is ahead of only wood, it is easy to work with brick, it is perfectly combined with building materials made of metal, concrete, stone, glass. When building the walls of a house from solid ceramic bricks, it takes a lot of time and labor, you need to make thermal insulation of the walls, a large amount of cement mortar is used. Well, as for the traditional silicate brick, which mainly consists of water, lime and sand, it is not very environmentally friendly, absorbs moisture and is a rather heavy building material.
To eliminate all of the above disadvantages, when building the walls of a house, you can use porous ceramic blocks, which are a little more expensive than bricks, but much better. The parameters of a brick determine its technologically correct use.
Ceramic bricks are available in size: in the form of blocks with dimensions of 25 x 12 x 25 cm and more, single 25x12x6.5 cm, one and a half - 25 x 12 x 8.8 mm., Double - 25 x 12 x 25 cm. The brand of ceramic brick is indicated by the letter M (M 100, M 125), which this letter means the strength of the brick. The number after the letter indicates the pressure that 1 cm2 of the surface of the material can withstand without collapsing. The weight of a brick depends on the brand, the higher the brand, the heavier the brick.
As a percentage, the water-absorbing ability of a brick is characterized, to absorb moisture. For the construction of the outer walls of the house, it is desirable to use a brick with low water-absorbing properties. The frost resistance of a brick is indicated by the letter F (F 25, F 50). The thermal conductivity coefficient of a brick depends on the structure and density. The thermal conductivity coefficient for facing ceramic bricks should be -0.36-0.5 W / (m K), porous ceramic blocks - 0.09-0.18 W / (m-K), clinker bricks 0.8 W / ( m-K). The thickness of the wall depends on the value, the higher it is, the thicker the wall of the house should be to preserve heat.
What material to choose
Choosing today a building material for erecting the walls of a house, between brick and cellular concrete, you need to carefully consider their aesthetic, energy-saving and economic properties. Today, thanks to the development of technology, the aesthetic and operational qualities of bricks have greatly increased. It is possible to build brick walls using the lightweight and solid masonry method. To build a wall using the continuous masonry method, in order to save heat, the wall must be insulated or have a thickness of at least 1.9 m. be no more than 400-500 mm. By building the walls of the house using cellular concrete, you will save 30-40% on heating without spending money on heat-insulating materials. When building the walls of the house from cellular concrete, you will also save not only money, but also time.
Construction of house walls - microclimate
The microclimate in a house built of cellular concrete is very similar to the microclimate in a wooden house. In a house built of cellular concrete, fungus and mold do not appear, because this building material has a higher vapor permeability than brick and can regulate the humidity in the room. Cellular concrete and bricks have a capillary structure, these building materials absorb water from the air and soil, but since the walls of houses built from these materials are subject to finishing that protects them from external atmospheric influences, they do not have high water absorption requirements.
It is not advisable to finish the walls of a house built of cellular concrete with clinker or facing bricks for facades, these building materials have a high density and low vapor permeability. The fact is that between brick and bearing wall, there must be a gap. Finishing the facade of the house, which is made closely, does not allow steam to leave the premises of the house, as a result, dampness forms on the walls inside the house.
Construction of the walls of the house from cellular concrete - foundation
When building a foundation for a house built of cellular concrete, you need Special attention draw on strength. Aerated concrete is not very durable. For example, if small foundation movements are allowed for houses built of brick or wood, then with such movements, a house built of cellular concrete will crack.
The growth of individual construction has led to the appearance on the market of various materials, including those that no one had heard of before. The range is so large that even experienced people are often lost, not knowing what is better to choose. Let's try to figure out what modern materials attractive not only in terms of cost, but also the feasibility of using it in the construction of private houses.
As a rule, individual developers are guided by the following indicators:
- the price of materials (including facing);
- the ability to perform all operations with your own hands to the maximum;
- the total weight of the structure, since the type of foundation and the cost of its installation largely depend on this;
- the cost of finishing work;
- durability;
- frequency of current (major) repairs.
Considering some types of new materials, we will focus only on their specific features.
Firstly, exhaustive information on each sample is not a topic for this article. Those who are interested in the details will be able to get acquainted with all the “pluses” and “minuses” on their own on our website in the “Building materials” section, where almost all popular ones are described in detail.
Secondly, many shortcomings are very relative, since the manifestation of defects is often caused not by product quality, but by violations of the work technology and ignorance of elementary things (on waterproofing, thermal expansion, compatibility, and so on). So let's start the review:
Wood
Glued timber
 Of all the materials in the "wood" category, professionals recommend giving preference to this particular product.
Of all the materials in the "wood" category, professionals recommend giving preference to this particular product.
- Strict geometry greatly simplifies installation and caulking.
- Finishing is practically not needed.
- Great looking home.
- Good microclimate.
Experts note the main drawback of glued laminated timber - additional insulation will be required, otherwise heating costs will be significant. Details about the beam.
rounded log
Possessing the above advantages, this material will require somewhat higher construction costs. Most likely, it will be necessary to involve specialists, at least at the stage of building a log house. Read about round log construction at.

artificial stone
aerated concrete
In every way good stuff. But it absorbs moisture quite intensively. Therefore, when using it, you will need high-quality waterproofing. And this entails the need to produce plastering, which limits the choice of type of cladding.

foam concrete
The specificity of its use is that this artificial stone is quite fragile. And this causes difficulties when attaching attachments and furnishings (lockers, shelves, and so on). You can’t drive a nail into it just like that and you can’t install a self-tapping screw (with a sleeve) - they won’t hold on. Only anchor bolts, and this is not convenient everywhere.
Foam concrete can be built in 1, maximum 2 floors, and then, with reinforcement of the structure. Comparison - perhaps you did not know this yet.
Polystyrene concrete
Of all artificial stones considered the best. In terms of its properties (vapor permeability, environmental safety), it is in many ways reminiscent of wood. Its main advantage is almost zero thermal conductivity. This material itself is an excellent insulation, and additional work in this regard will not have to be carried out.
Another difference from analogues is that fungus or mold will never start in polystyrene concrete. And given the low cost of production (about 1,000 rubles / m³), this stone can be recommended as one of the best building materials. By the way, "bricks" can be made on the spot, without spending money on renting a vehicle to deliver the blocks to the site.
Frame technology
Building with sandwich panels is beneficial in many ways. It is always cozy in such a house, and heating costs will be small (about 26,500 rubles a year). But the service life of products does not exceed 20 years (and this is the maximum). And the repair of such a structure can cost a pretty penny. With many advantages, such a house does not differ in durability. This is rather a variant of a quick solution to the housing problem, but it is not necessary to say that many generations will live in it. In fact, they talk about it




















