The design of the construction plan is carried out taking into account certain provisions.
Near the building they show all the assembly mechanisms, lifts with their size reference to the axes of the object under construction; crane runways, temporary assembly roads; parking, working and dangerous areas of cranes.
The placement of on-site warehouses should be carried out taking into account the location of lifting mechanisms and the routing of underground utilities. All warehouses must be at least 0.5 m from the edge of the road. The width of the warehouse is set depending on the parameters of the loading and unloading machines, the length of the warehouse depends on the size of the unloading front.
When placed on the construction plan, the internal construction roads have a width: for one-way traffic - 3.5 m, for two-way traffic - 6 m, the minimum radius of curvature is 12 m. less than 3.5 m and a length of 12 - 19 m, similar sites are arranged near on-site warehouses. When designing temporary works, minimum distances must be observed, m:
between the road and the storage area 0.5 ... 1.0;
temporary fence 1.5.
It is unacceptable to place temporary roads above underground networks and in close proximity to the laid and to be laid underground communications.
When tracing roads, the minimum distances must be observed, m:
between the road and the storage area - 0.5 ... 1.0;
between the road and the crane runways - 6.5 ... 12.5 (this distance is taken based on the size of the crane boom and the rational mutual placement of the crane - warehouse - road);
between the road and the fence enclosing the construction site, at least 1.5.
Temporary buildings and structures are placed in areas that are not subject to development by the main facilities, in compliance with fire safety rules and safety regulations, outside the dangerous zones of operation of mechanisms. The foreman's or foreman's office should be located closer to the object under construction, and the household premises near the entrance to the construction site. The room for heating workers should be located at a distance of no more than 150 m from the workplace. Food points should be located at least 25 m and not more than 600 m from workplaces from toilets and garbage bins, a first-aid post should be located in the same block in the same block with amenity premises and no further than 800 m from workplaces. The distance from toilets to the most remote places inside the building should not exceed 100 m, to workplaces outside the building - 200 m. The construction site should provide a place for workers to rest and smoke, and there should also be shields with fire fighting equipment.
The distributing network of temporary water and power supply is designed after all their consumers are placed on the building plan. The fire (permanent) water supply network must be looped, and fire hydrants are located on it no further than 100 m from one another. The distance from the hydrants to the building should be at least 5 m and not more than 50 m, and from the edge of the road - no more than 2 m. Temporary transformer substations should be located in the center of electrical loads and no further than 250 m from the consumer. To illuminate the premises and the construction site, a temporary electrical network independent of the power supply should be provided.
When designing a construction plan, it is necessary to provide for measures to protect the environment: the preservation of the soil layer, compliance with the requirements for dust and gas contamination of the air, the treatment of domestic and industrial wastewater, and others.
Modern requirements for the development of a construction plan prescribe: to equip exits from construction sites with points for cleaning or washing vehicle wheels; to close the facades of buildings and structures overlooking the streets, highways and squares with a hinged decorative mesh fence; release the construction site from foreign buildings, structures and structures (in accordance with the construction organization project).
On-site warehouses are organized for temporary storage of materials, semi-finished products, structures, products and equipment. The volume of storage facilities depends on the type, scale and methods of construction. The optimal method can be considered the organization of work, in which the volume of stored materials and the time of their stay in the warehouse is reduced to a minimum necessary for the smooth conduct of work.
Warehousing organization includes:
development of a general scheme and places of warehousing, acceptance, issue and accounting of materials;
selection of the most rational type of warehouse and methods of storage of materials and structures;
determination of the areas of warehouses, their sizes and unloading front.
Basic requirements for warehousing:
security;
mechanization of loading and unloading operations;
safe working conditions.
The type and size of warehouses are determined by the amount of minimum stock required building materials, structures and parts, type of vehicles, storage standards per 1 m2 of warehouse area and the size of the construction site.
The stock of materials should be minimal, but sufficient for the uninterrupted performance of construction and installation work.
The difference between warehouses by storage method:
open;
under a canopy;
closed.
The storage area is determined based on the average daily need for materials, products and structures on the most material-intensive day, taking into account the stock that ensures uninterrupted operation at the facility (according to the calendar plan).
The average daily need for materials of this type is determined by the formula:
Q day = Q/ t, where
Q is the amount of materials needed to complete a given amount of work,
t is the duration of the work according to the plan, days.
The estimated stock of materials is determined by the formula:
Q R = Qday*T n * k 1 * k 2 , where
k 1 - the coefficient of uneven receipt of materials at the warehouse (k 1 \u003d 1.3)
k 2 - coefficient of uneven consumption of materials (k 2 \u003d 1.2).
T n - standard time
The useful area of warehouses (without aisles and driveways) is determined by the formula:
S floor = Q R / q, where
q is the rate of storage of material per 1m 2 of the area of the warehouse.
The total estimated area of the warehouse is determined by the formula:
S calc = S floor / k 3 , where
k 3 - warehouse space utilization factor (depends on the type of warehouse).
|
Table 8 Calculation of warehouse areas |
|||||||||||
|
Materials and products stored in the warehouse |
Unit measurements |
Need for materials |
Coefficient of uneven consumption of resources, K1 |
coefficient of uneven receipt of resources, K2 |
stock of materials |
Storage rate per 1 m 2 warehouse area |
Useful area of the warehouse |
warehouse space utilization factor, K3 |
Estimated warehouse area |
||
|
average daily |
stock rate, days |
estimated margin |
|||||||||
|
crushed stone, gravel, sand | |||||||||||
|
formwork | |||||||||||
|
fittings | |||||||||||
|
foundation blocks (basement) | |||||||||||
|
floor slabs and coatings | |||||||||||
|
staircases and marches | |||||||||||
|
Wall panels | |||||||||||
|
slab insulation | |||||||||||
|
ruberoid | |||||||||||
|
window bindings | |||||||||||
|
door leafs | |||||||||||
|
ceramic tile | |||||||||||
Based on the established need for space, the type of warehouses is selected.
The accepted type of warehouses is entered in the table "Explication of warehouses".
|
Table 9 Explication of warehouses |
||||||
|
Warehouse type |
Warehouse area, m 2 |
Plan dimensions |
Storage method |
Used sample project |
||
|
Estimated |
Accepted |
|||||
|
crushed stone, gravel, sand |
open in stacks | |||||
|
formwork | ||||||
|
basement wall blocks | ||||||
|
Wall panels | ||||||
|
floor slabs and coatings | ||||||
|
staircases and marches | ||||||
|
fittings |
under a canopy in stacks | |||||
|
slab insulation | ||||||
|
ruberoid | ||||||
|
window bindings |
closed in stacks | |||||
|
door leafs | ||||||
|
ceramic tile | ||||||
The total storage area is 229.5 m 2 .
This type of lesson will tell you about how to count storage space. When designing a construction plan, a clear organization of on-site storage facilities plays a decisive role. For the storage of sand, gravel, precast concrete, lumber, I accept an open warehouse. For the storage of binders, finishing materials, glass, sanitary equipment, I accept a closed warehouse.
It stores structures, semi-finished products, products and equipment.
Open area planned, compacted and has a slope for the removal of atmospheric water. Thus, the stroygenplan is a set of warehouses, change houses, engineering networks, mechanisms and the object being built.
The amount of materials to be stored in the warehouse should ensure the uninterrupted supply of the construction of the building with all necessary materials, structures and products, the right amount. The figure below shows the location of various types of warehouses on the construction site. Please note that only the open warehouse is located in the crane's coverage area, the other two are located outside it.
We calculate warehouses in the following sequence:
2. We determine the stock of material. Q warehouse \u003d Qsk * t * K1 * K2 / Tc, where
Qsk. - the amount of material used;
n is the standard reserve in days, depending on the condition of the roads, the type of vehicles;
K1-coefficient of uneven consumption of materials K1=1.2, taking into account high labor productivity
K2-coefficient of uneven receipt of materials at the warehouse K2 = 1.1, depending on the remoteness of the factories supplying building materials, as well as the type of transport
We define warehouse area on the construction site for each material.
Fsk \u003d Qsk / q * Ksk, where
ksk- warehouse space utilization factor, taking into account aisles and driveways.
Qsk - amount of material to be stored in the warehouse
q -
normative amount of material placed on 1m2 of warehouse space.
We summarize the initial data and calculations for each material in a table
|
Statement of consumption of basic building materials |
|||||||||
|
name of materials |
meter |
working days |
days of stock |
stocking rate |
warehouse area |
warehouse type |
|||
|
foundation block |
open |
||||||||
|
floor slabs |
open |
||||||||
|
open |
|||||||||
|
open |
|||||||||
|
ceramic tile |
|||||||||
|
window and door blocks |
|||||||||
|
paints, varnishes |
closed |
||||||||
|
Warehouse type |
Estimated area |
Accepted area |
warehouse dimensions |
|
open warehouse |
|||
|
closed warehouse |
Thus we have found area of all types of warehouses, took their sizes, which will be sufficient for temporary storage of materials, taking into account their production and the receipt of new ones.
Electricity at the construction site is consumed to power the machines, i.e. for industrial needs, for outdoor and indoor lighting.
Power supply requirements: it is necessary to provide the construction site with electrical energy in the required quantity and quality (voltage, frequency), flexibility of the electrical circuit (the ability to supply consumers at all construction sites, reliability, uninterrupted operation, minimizing the cost of a temporary device, minimizing losses in the network.
When designing a PPR, the calculation of loads according to the installed capacity of electrical consumers-electricity consumers.
The estimated required power of the power supply source according to the installed power (P, kVA) was determined by the formula:
|
α = 1.1 - coefficient taking into account losses in the network depending on the length, section, etc.; |
||
|
V is the speed of water movement through pipes, m/s. |
||
|
k 1 c , k 2 c , k 3 c - demand coefficient, depending on the number of consumers; |
||
|
Р с - power of power consumers, kW; |
||
|
Р t - power for technological needs, kW; |
||
|
P o.v - power of internal lighting devices, kW; |
||
|
Р о.н - power of outdoor lighting devices, kW. |
||
Determination of power by types of consumers:
1.1 Power electricity
LIEBNER 118 H 8 .
Rammer IE-4502.
Various small mechanisms and tools.
1.2. Technological needs
AC welding equipment TDM-500
Plaster unit SO-57A
Puttying unit SO-150
Painting unit SO-47A
Parquet polishing machine SO-155 R = 2.2 kW.
1.3 Interior lighting
Workshops, offices, change houses with a total area
1.4. outdoor lighting
Site area lighting
Lighting installation S one floor
Outdoor warehouse lighting
Total required power:
We accept a complex transformer substation SKTP-750 with a capacity of 1000 kVA. The dimensions of the substation are 3.2x2.5 m. The structure is closed.
Spotlights are used to illuminate the construction site. The number of spotlights is calculated by the formula:
Taking into account the height of the building, we accept the installation height of the PZS-45 - 18m.
5.12.8 Calculation of temporary roads
Temporary roads to construction sites are intended for the implementation of uninterrupted transportation of structures, materials, equipment throughout the construction at any time of the year.
The road ensures the transport of materials to the area of the crane, the platform for unloading, pre-assembly, to the means of vertical transport, to workshops, storerooms, open warehouses, etc.
When routing roads, the distance between the road and:
storage area 1 m
fence fence 1.5 m
The intersection and junction of roads is carried out at an angle of 90-45 degrees, and with the railway 90-60.
Construction roads are looped, a circular detour is built around the object. The roads have a width of 6 m, the direction of movement is right-handed. In places of unloading structures, widenings are provided.
For the construction of a temporary construction road, a sand bed 10-25 cm thick is arranged, on top of which inventory reinforced concrete slabs are laid.
Slabs - reinforced concrete with non-directional reinforcement, 16-20 cm thick, 1-2-fold turnover.
Passages, passages, sidewalks have been built for the safe passage of workers to work sites, auxiliary buildings and residential buildings. We arrange, depending on the intensity of pedestrian traffic, a width of 2 m, a sidewalk that rises by 30-50 cm, has a transverse slope and a drainage system.
Temporary buildings and structures are erected at the construction site to ensure the production of construction and installation works, accommodation and consumer services for workers.
Temporary buildings and structures are called technological and social facilities that are equipped with a construction site in the process of organizational and technical preparation for construction.
Temporary buildings are constructed only for the period of construction. The cost of temporary buildings is one of the main cost items for the creation of a construction economy at the facility, and its reduction is an important task when designing a construction plan. Accurate calculation of needs, right choice types of buildings and their rational placement on the site predetermine the level of costs for temporary facilities.
Unlike permanent buildings, temporary facilities have their own characteristics related to their functional purpose, design solution and type of mobility, construction and operation methods.
According to their functional purpose, temporary buildings are divided into four groups, each of which is characterized by a certain range of buildings: production, storage, auxiliary (administrative and sanitary), residential and public.
According to the constructive solution, temporary buildings are non-inventory and inventory.
Non-inventory buildings include buildings erected for a single use. The construction of such buildings, despite the relatively low cost in relation to original cost inventory buildings, is economically unprofitable and is currently used extremely rarely, only as an exception, for example, when used for the needs of the construction of buildings from materials and structures of dismantled buildings, and also subject to sufficiently low costs.
Inventory temporary buildings are reusable buildings at various sites, usually prefabricated. Inventory buildings are more economical, meet the requirements of reliability and safety, the level of unification and standardization, sanitary hygiene, and fire safety.
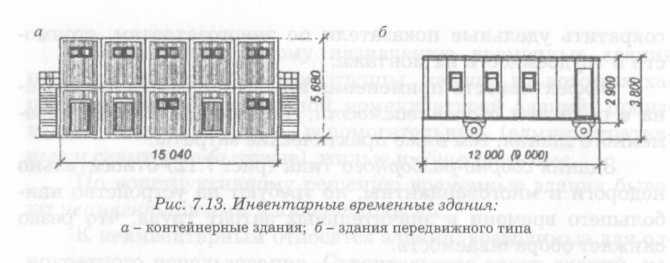
Inventory buildings according to the degree of mobility and constructive solution can be container, mobile and collapsible.
Depending on the duration of operation of inventory buildings, they are divided into three groups: temporary buildings with a service life of 6 months or less. (mobile); temporary buildings with a service life of 6 to 18 months. (container) and temporary buildings with a service life of more than 18 months. (collapsible).
Currently, two-story, two-row collapsible administrative and amenity buildings are of great interest. These buildings are designed to serve 320 builders. The layout and constructive solutions of two-story administrative buildings make it possible to reduce specific indicators in terms of energy consumption, cost and labor intensity of their installation.
The effectiveness of the use of inventory buildings is associated with the concept turnover: the more turnovers of the temporary building, the lower the practical costs.
Building collapsible type (Fig. 7.12) are relatively inexpensive and multivariate, but require the most time and significant labor costs for the device, which sharply reduces turnover.
Such buildings are, as a rule, of considerable size; in particular, they house manufacturing enterprises equipped with cranes. Bent and rolled profiles are widely used as load-bearing structures.
container buildings (Fig. 7.13, a) are a three-dimensional structure of a frame-panel type. The load-bearing frame of such buildings is most often made of rolled steel, the enclosing structures of the walls are made of wood or "sandwich" type panels with sheathing of steel profiled sheet, the roof is flat of steel sheet or rolled. Dimensions of containers are determined by the conditions of transportation by road or railways, most often within: length - 6.0 m, width 3.0 m, height - 2.7 m. Container buildings are assembled from various modifications of single containers - end and ordinary, connecting them with bolts.
The design of the construction processes required for servicing and the totality of temporary buildings and structures under construction is carried out in the following sequence:
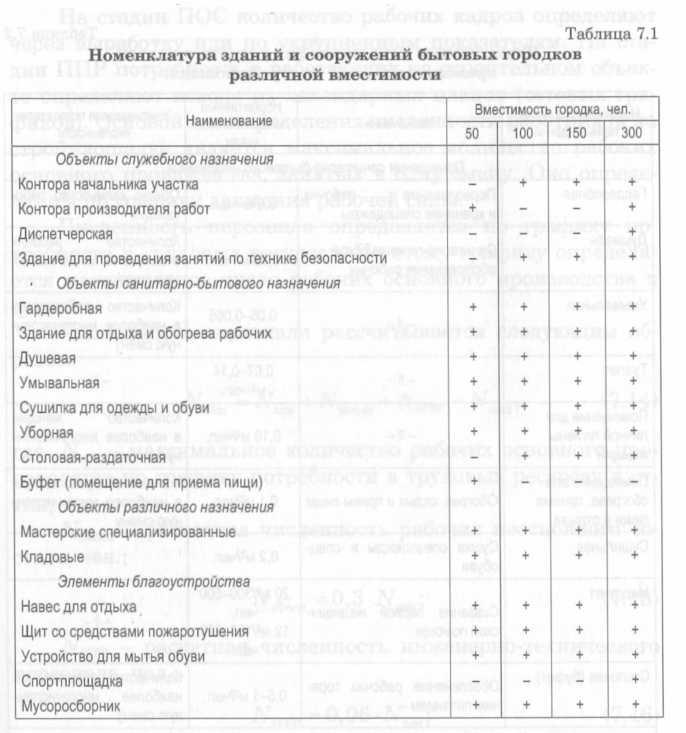
determined with a minimum range of temporary buildings (Table 7.1);
establish the general need for temporary buildings;
determine the type and number of inventory buildings;
draw up a layout of temporary buildings at the construction site;
make binding of temporary buildings at the construction site;
determine ways to connect temporary buildings to the necessary communications.
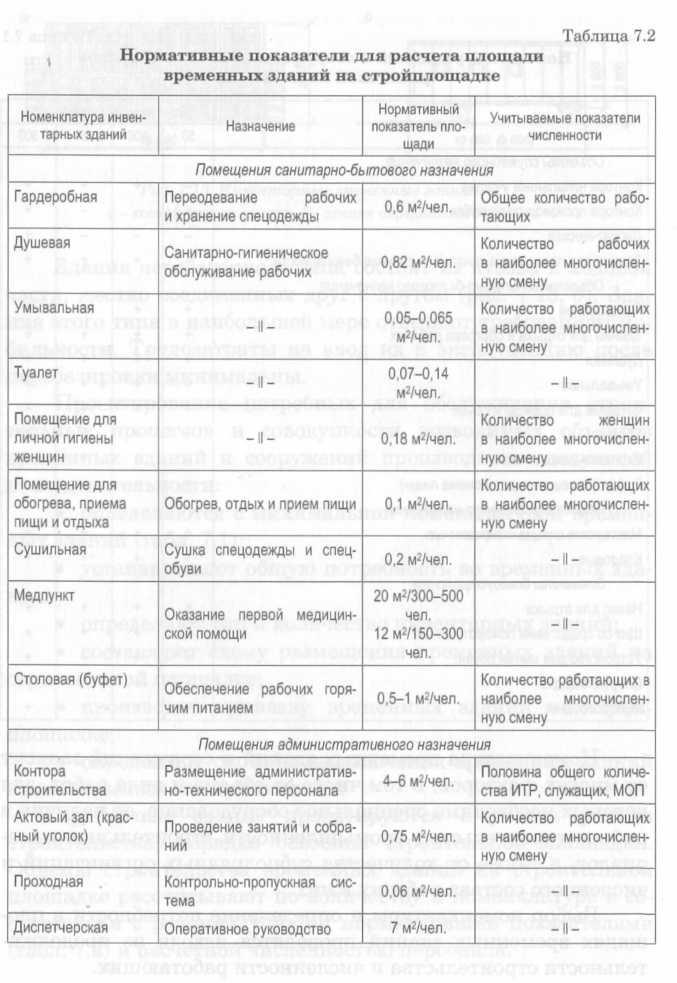
Temporary buildings are designed taking into account the area of construction, the order of development of the construction site. The volume of construction of temporary buildings at the construction site is calculated by the number and range in accordance with the recommended standard indicators (Table 7.2) and the estimated number of personnel.
The range of temporary buildings and structures depends on many factors, including the volume and type of work that requires special equipment, the presence of building materials industry in the construction area, as well as the number of subcontractors and the number of workers in them.
The choice of nomenclature and the determination of the need for areas of temporary buildings are carried out based on the duration of construction and the number of employees.
At the PIC stage, the number of workers is determined through output or by aggregated indicators. At the stage of PPR, the need for workers at a construction site is determined based on calendar plans (network schedules). The basis for determining the number of workers on a construction site is maximum amount workers of the main production, employed in one shift. It is determined by the schedule of movement of the labor force.
The number of personnel is determined according to the schedule of the need for labor resources. According to this schedule, the maximum number of workers in the main production per day is determined.
The headcount is calculated as follows:

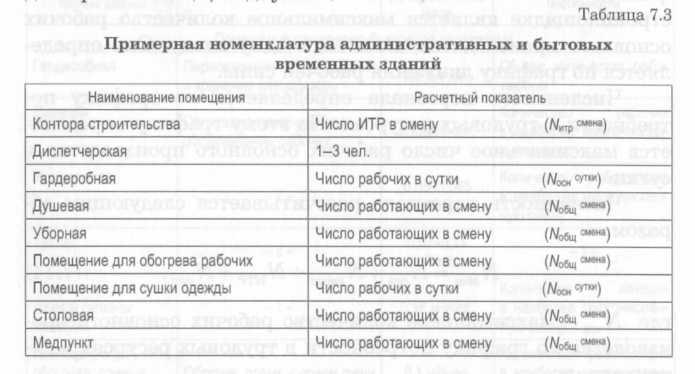
When designing temporary buildings, it is allowed to combine the following services: an office with amenity premises and a dining room; buffet office; office with a first-aid post; washrooms with wardrobe; washrooms with showers; dressing rooms with shower; a room for heating workers with a room for eating. At the same time, it is not allowed to combine a washroom, a dressing room, a room for drying clothes with rooms for heating workers, eating.
In accordance with the established number of personnel and the standards for the need for temporary buildings and structures for various purposes, the estimated area of buildings is established. The areas of temporary buildings are determined by the formula:
where S is the area of one temporary building; N - the number of personnel, taking into account the approximate range of temporary administrative and household buildings; m is a standard indicator for determining the need for this type temporary building.
Based on the calculated indicators, they proceed to the selection of projects for temporary buildings. At the same time, it should be borne in mind that the norms regulate the minimum need for space, and when moving from calculated indicators to the selection of specific projects for temporary premises, significant discrepancies may be found in the direction of overestimating the area, especially in single containers. In this case, the final decision is made in accordance with the passport data of real projects.
The next task to be solved in the design of the construction plan is the placement of temporary buildings and structures on the site and their binding to construction sites. In doing so, the following recommendations should be followed.
Administrative buildings - offices, control rooms are located at the entrance to the construction site. Buildings for sanitary purposes - dressing rooms, showers, rooms for drying clothes and shoes are located near areas of maximum concentration of workers.
Temporary buildings and structures are located in areas that are not subject to development by the main facilities, in compliance with fire safety standards and safety regulations outside the dangerous zones of operation of cranes, and also not closer than 50 m from technological productions emitting dust, harmful vapors and gases.
Premises for heating workers should be located no further than 150 m from workplaces, and shelters from solar radiation and precipitation - directly at workplaces or no further than 75 m from them.
The first-aid post is located in one of the blocks (containers) household premises and no further than 800 m from workplaces.
The distance from toilets to workplaces in the most remote parts of buildings should not exceed 100 m.
When developing a construction plan, it is necessary to strive to maximize the use of permanent buildings, structures and utility networks for the needs of construction and to minimize the amount of temporary ones.
Warehouse areas are determined for materials to be stored at the construction site, according to the nomenclature presented in the schedule for the receipt of building structures, parts, semi-finished products, materials and equipment at the facility (see Table 3).
The stock of materials in the warehouse is calculated by the formula:
where Rob is the amount of materials (parts, structures) required for the production of construction and installation works;
T - the duration of the work according to the calendar plan, days;
n - material stock rate, days. (when transporting material by road, it is assumed to be from 5 to 12 days);
K1 - coefficient taking into account the uneven receipt of materials at the warehouse, is taken equal to 1.1;
K2 - the coefficient of uneven consumption of materials, is taken equal to 1.3.
The required warehouse area is determined by the formula:
where Rsk - the amount of materials to be stored;
r - material storage rate per 1 m2 of area;
Kp - coefficient taking into account passes.
Stock of floor panels in stock:
![]() m3,
m3,
![]() m2.
m2.
For other materials, the calculation is performed in tabular form (Table 9).
Table 7
Calculation of the need for storage space
|
Need |
Norm |
Coefficient, |
Stock |
||||
|
Name of materials |
general |
subject to storage |
warehousing per 1 m2 |
pass-taking |
Area, m2 |
||
|
Window and door blocks | |||||||
|
Bricks in containers | |||||||
|
flights of stairs | |||||||
|
Landings | |||||||
|
Linoleum | |||||||
|
Ceramic tiles | |||||||
|
Gravel fraction 5-10 mm | |||||||
|
Timber | |||||||
4.4. Calculation of water demand at the construction site
Temporary water supply at the construction site is designed to meet industrial, household needs and fire fighting. The required water flow, l / s, is determined by the formula:
Q \u003d Rb + Rpr + Rpozh,
where Rb, Rpr, Rpozh - water consumption, respectively, for domestic and industrial needs, and for fire fighting, l / s.
Water consumption for domestic needs is made up of: R'b - water consumption for washing, eating and other household needs and R"b - water consumption for taking a shower.
Water consumption for domestic needs is determined by the formulas:
, ![]() ,
,




















