Monolithic structures are performed directly at the construction site. All types of concrete and reinforced concrete structures can be monolithic. Prefabricated structures are manufactured in factories and delivered to the construction site in a fully finished form.
Basic technical data of US aircraft F - 111A and F - 111B. Monolithic structures are structures made from one whole piece of material. A common example of such a design is a monolithic panel having a sheathing, a longitudinal or transverse set.
Basic technical data of US aircraft F - 111A and F - 111B. A monolithic structure with thick skin and often spaced ribs is less susceptible to deformation when heated at high flight speeds.
The monolithic design dramatically increases the sectional resistance and also simplifies production.
Monolithic structures are made at the construction site in the formwork of the required shape, in which steel reinforcement is laid, and then the form is filled with concrete.
Monolithic structures with flexible reinforcement are used in the lower tiers (pedestal) of whatnots, which perceive significant vertical and horizontal loads.
Monolithic structures with rigid reinforcement combine the advantages of steel and reinforced concrete structures; they are fire-resistant, the installation of rigid reinforcement is identical to the installation of a metal shelf, the concreting of columns and the inclusion of concrete in the operation of the columns reduces the consumption of metal, no bulky scaffolding is required to fasten the formwork during concreting.
Monolithic reinforced concrete frame of the reconstructed Cathedral of Christ the Savior in Moscow. Monolithic structures are constructed mainly from heavy concrete or lightweight concrete on porous aggregates. The walls of residential buildings are also erected from cellular concrete.
Time variation of loading characteristics. A monolithic structure, after being released from disturbing loads, enters a state of its own ordered free vibrations, and a composite structure enters a state of disordered vibrations characterized by the presence of high-frequency harmonics.
Location schemes.
Monolithic structures are concreted directly at the construction site in pre-installed formwork.
Design of ignition coils. The resulting monolithic structure is assembled together with the magnetic circuit.
Monolithic structures of thermal insulation are the most progressive, as they are most suitable for the organization of industrial production and installation of pipelines. Monolithic insulation is applied to pipes mainly at the factory using a technology that depends on the types of thermal insulation used in each specific case.
Double car dumper, interlocked with coal-receiving pits, built using a sink well. Cross section. Monolithic structures of the underground part are reinforced with welded reinforcing blocks, which significantly speeds up construction.
Distribution of shear stresses in a rubber-metal piston of a simple type. Monolithic structures of a rubber-metal piston (see Fig. 1) and a piston of a simple type (Fig. 14), in which the seating and supporting surfaces of the core are smooth without an annular protrusion and grooves, were studied with a radial clearance of 0.9 mm. Studies have shown that in the absence of pressure, the cuff contacts the sealing surface of the sleeve only in the lip area. The contact length /k increases under pressure.
The monolithic construction of the heat-insulating coating of pipelines is carried out by pouring the annular space (between the pipeline and waterproofing), for example, polyurethane resin, with special installations, followed by the formation of hardened foam.
Therefore, monolithic structures are currently being used more and more.
Steam heating of monolithic structures is carried out in steam jackets, or by passing steam through pipes laid in concrete, or grooves formed on its surface. Steam heating of prefabricated structures, in the case of their manufacture at the installation site, is carried out in portable collapsible chambers, and elements and products at landfills or factories - on stands or in stationary chambers.
In a monolithic structure, electrical insulating asbestos is used as body insulation and insulation between the plates, which significantly changes its physical, mechanical and dielectric properties during the collector manufacturing process after impregnation in an epoxy compound. This change primarily concerns the modulus of elasticity, which affects the stress state of the collector.
Steaming of monolithic structures is carried out using a steam jacket, which is a wooden casing arranged around the main formwork. Steam is passed into the space between the formwork and the casing.
The displacement of monolithic structures by prefabricated ones reflects the further growth of the industrialization of construction in our country. This process proceeds within the boundaries of technical and economic feasibility. Nevertheless, the absolute volumes of the use of monolithic concrete and reinforced concrete remain large in industrial and especially in hydraulic engineering and special construction, so questions further development and improving the technology of production of concrete and reinforced concrete works have a great practical value.
Concreting of monolithic structures is carried out continuously or intermittently, i.e. sections or blocks.
While this built-in economic incentive is the builder's choice, stricter environmental regulations on pollution also make this method a solid choice. In general, existing engineering know-how and building techniques should be used, as well as experience in developing safer building practices that are more cost-effective and consume less natural resources, energy and labor force.
Artificial and efficient use building materials will result in lighter, stronger, more earthquake-resistant structures. It's bad enough that catastrophic earthquakes cause collapse of buildings, great loss of life and numerous injuries. However, it also imposes an additional burden on our ecosystem in terms of further depletion of natural resources, as well as the addition of greenhouse gases from rescue operations, demolition, cleanup and subsequent reconstruction.
Concreting of monolithic structures is carried out continuously or intermittently, i.e. sections or blocks. Continuous laying of concrete is carried out in the case when increased solidity and uniformity of concrete is required and, therefore, the presence of working joints is undesirable.
The calculation of monolithic reinforcement structures is simpler, intermittent ones are more complicated.
Capacitors of a multilayer monolithic design without air gaps are a multilayer package consisting of alternating layers of dielectric and metal plates baked into a monolith.
Sections of walls 1 - 1 and 2 - 2 of a panel residential building. With monolithic structures at the construction site, it is installed according to the formwork drawings required form- formwork, in which steel reinforcement is laid in accordance with reinforcement drawings, and the form is filled with concrete. After reaching the required strength, the structures are demoulded.
In monolithic designs of pistons of mud pumps, the core is made with annular protrusions, which are designed to more firmly fix the cuffs on the core, since during the reverse stroke of the piston, the friction force directed against the movement tends to tear the cuff from the core. However, until now, the shape, size and placement of the annular protrusions on the core have been chosen arbitrarily. The results obtained in the study of the standard piston showed that the annular protrusion makes a significant change in.
In order to create monolithic structures in which the frame would work as one with the main body mass, the materials of the reinforcing elements and plastic castings must have the same linear expansion coefficients.
In order to create monolithic structures in which the frame would work as one with the main body mass, the materials of the reinforcing elements and plastic castings must have the same coefficients of linear expansion.
Comparative length of the working bodies of domestic PDM for the period 1960 - 2000 The most promising is the monolithic design of the RO, which ensures the simplicity and low detail of the machines. An increase in the active length of a monolithic working pair is mainly limited by the technological capabilities of casting and pressing equipment in the manufacture of the stator.
The most promising is the monolithic design of the RO, which ensures the simplicity and low detail of the machines.
During electrical heating of monolithic structures concreted in parts, non-concrete reinforcement associated with heated areas, as well as reinforcement of heated concrete, must be carefully grounded. In monolithic structures, this is carried out directly through the reinforcement of columns and foundations. When concreting individual elements, the reinforcement of which is not connected to the ground, it is necessary. To do this, each rod of the associated reinforcement is connected to the ground electrode, and in the case of welded reinforcement, it is sufficient to connect an individual welded element to the ground conductor.
Scheme of concreting foundations using concrete pavers. When concreting monolithic structures located slightly above or below the zero mark, self-propelled concrete pavers are widely used. The concrete mixture from the concrete truck 6 is fed by the skip hoist 5 to the conveyor 3 and then through the trunk 2 enters the formwork / concrete structure. This ensures wide maneuverability of concrete pavers during the construction of monolithic structures and structures.
For those monolithic structures that are made of materials with high internal friction, such as reinforced concrete, masonry and some types of plastics, the internal absorption of vibrational energy is determined mainly by internal friction in the material. For structures made of materials with low internal friction, for example, steel, big influence internal energy dissipation is affected by structural damping in the joints. The experimental and theoretical study of internal friction in materials, especially new ones - various types of plastics, and in various types of joints is still an important issue that needs to be further given due attention.
Construction of monolithic buildings and structures
Today, the growing demand for building more High Quality, the trend towards the adoption of more labor-saving designs, and the growing use of finished products and pre-assembled units in construction has meant that prices are maintained while maintaining quality.
With the gradual adoption of new building laws that establish minimum resistance values based on "principles of standardization, simplicity, and single integrated elements to achieve structural design." Standardized factory cast concrete components installed on site with simply made connection details in repeating grids are rated to significantly higher resistance ratings. These factors have forced the construction process to look for innovations in materials and technologies for industrial incubation.
In collectors of a monolithic design, the insulating material is not subjected to the noted effects; moreover, it is in the finished structure that it acquires its properties.
When concreting monolithic structures in winter conditions, it is possible to use methods of laying concrete with hardening due to exothermy, heating the concrete with steam or hot water, as well as various methods of electrical heating.
To create a monolithic structure, the coil is poured into plastic concrete.
Winter concreting of monolithic structures is designed using the most effective methods heat treatment of concrete: thermos and pre-heating of concrete mixtures, ensuring a steady pace of construction work, both in summer and winter conditions with minimal energy consumption.
Appearance bulk modules. To create a monolithic structure, the elements are filled with polyurethane foam. Sealing and mechanical strength are ensured by a metal casing and an epoxy resin filling of the structure.
A characteristic of monolithic structures is that with an increase in shear stresses at the base of the leading edge, the stresses in the gap region decrease. The reverse picture is observed with an increase in the shape factor of the elastic part: the stresses at the base of the leading edge decrease and increase in the gap region. The identified features of the stress state of elastic parts in monolithic structures contribute to right choice rational sizes of sealing devices.
When concreting monolithic structures of the underground part of buildings, self-propelled boom concrete pavers based on caterpillar tractors, cranes, excavators or special self-propelled pneumatic chassis are used.
The magnetic system of a DC machine. They have a monolithic design, since the value of induction under the additional poles is usually chosen small and when the armature rotates, eddy currents are practically not induced in their tips. However, in traction motors of AC electric locomotives operating at pulsating voltage, the cores of the additional poles are laminated - from insulated sheets of electrical steel with a thickness of 0 5 mm. This ensures a significant reduction in eddy currents that occur when additional pulsating current poles pass through the winding.
The insulation is a non-magnetically conductive monolithic structure and simultaneously serves as a power element of the armature. The strength of this element must be large, since during short circuits, mechanical forces act on the armature winding, approximately five times greater than in conventional generators. Due to the fact that the stray magnetic field in the generators under consideration significantly exceeds the biologically safe value, the stator in the generators under consideration is surrounded by a ferromagnetic cylindrical screen. This screen protects people and devices in the vicinity of the machine from the effect of alternating magnetic fields of the armature and constant excitation fields, and also prevents external electromagnetic fields from penetrating into the machine.
Plates in monolithic structures are made 50 - 100 mm thick, in prefabricated structures - perhaps thinner.
Metal pipes. Thus, a monolithic structure with a pressed mesh frame is obtained, on which the entire load falls during operation.
Prefabricated elements and monolithic structures made of heat-resistant concrete are widely used in various industries: energy, ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy, in chemical and oil refining, in the production of building materials; they are used instead of semi-acidic and fireclay products intended for temperatures of 800 - 1400 C, as well as instead of highly refractory products at temperatures above 1400 C.
Design and calculation according to SNiPs
Where do we see the world? However, to get the right idea, here is the work of the Indian Institute on monolithic concrete structures along with a construction company triptin with these projects.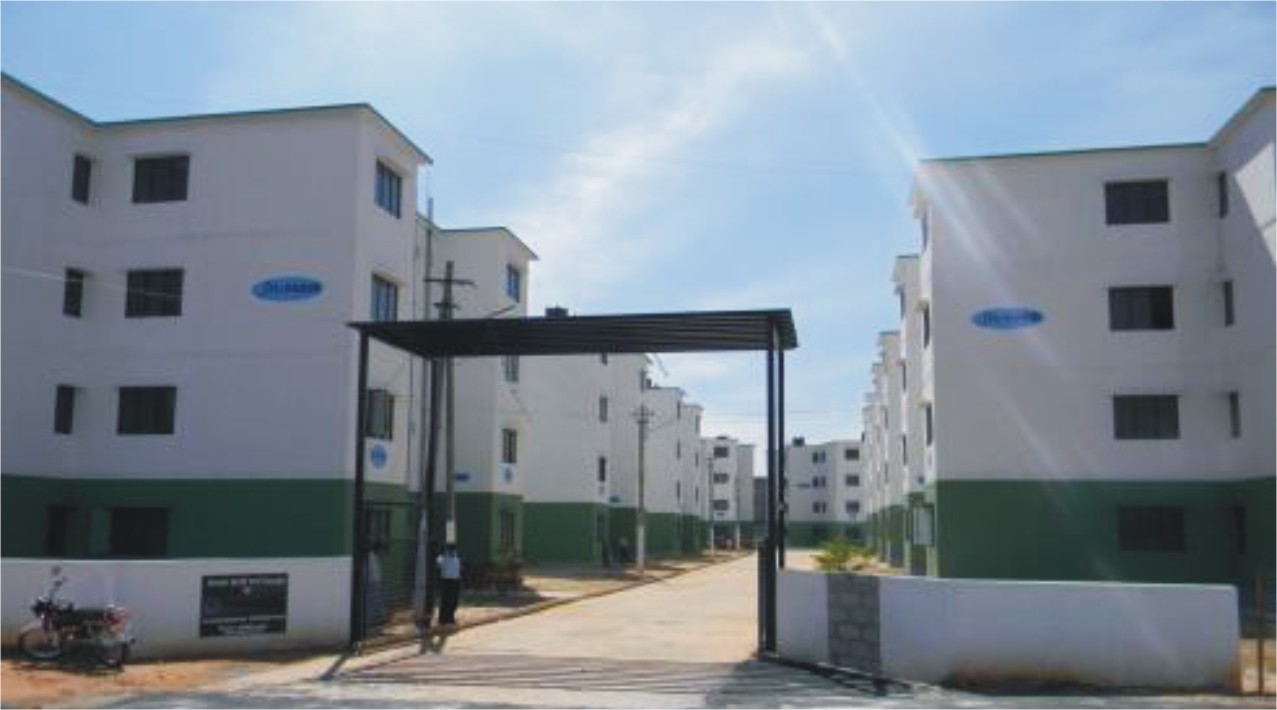 
The construction sector will host "game-changing technologies" in Singapore.
In Singapore, it has been suggested that developers who have successfully applied for projects on individual land sale sites should adopt more productive building practices towards the end. 
These methods can provide labor and time savings of between 35 and 50 percent compared to traditional methods, according to National Development Minister Hou Boon Wang.
The increased labor intensity of manufacturing monolithic structures, as well as the seasonality of work, leads to a lengthening of the construction time, and, consequently, to a slowdown in the turnover of funds invested in construction.
At the same time, for monolithic structures, it is necessary to increase protective layer by 5 - 10 mm against the tabular values. For large diameters and special reinforcement profiles, the thickness of the protective layer is assigned in accordance with SNiP P - V.
The design grade of concrete of monolithic structures is allowed to be established with special justification at the age of 90 or 180 days, depending on the timing of loading, which saves cement.
Prefabricated monolithic ceiling. / - prefabricated elements (old concrete. 2 - monolithic concrete (new concrete). For the erection of prefabricated monolithic structures, unlike monolithic structures, special formwork, scaffolding and scaffolding are not required.
The boilers are not a monolithic structure, which is of great practical importance when installing the boiler on a mobile base.
"We need gaming technology for construction to improve construction productivity and reduce our dependence on builders,” he said. It relies on factory-made building components, "thus reducing the need for workers and reducing noise and dust at the construction site," said Mr. Howe of the method, which is called prefabricated prefabricated construction.
Another method is to use cross-laminated wood, a multi-layered wood commonly used in Europe that meets the same fire safety requirements as concrete and steel. Commonly used for the construction of walls, lift shafts and floors, it can also support heavier loads than lumber and lighter than concrete.
Door classification
Classification and design of windows
Windows and doors
Classification and design of windows. - Classification of doors.
Windows are the enclosing elements of the building and not only provide the premises with natural light and ventilation, but also have the appropriate thermal and acoustic qualities.
To ease the push for these "game-changing technologies", the Building and Construction Authority will provide financial support to those who adopt them and organize experience building training in the area. “The desired outcome of these efforts is for our construction industry to be cleaner, quieter and faster, without sacrificing safety and quality,” says Mr.
"Prefabricated 3D Construction" is one of the game-changing technologies that support the concept of "Design for Manufacturing and Assembly" to greatly speed up construction. 

"Prefabricated volumetric structure" means a method of construction in which self-contained volumetric modules.
The composition of the filling of the window opening (window filling) includes: a window frame, bindings inserted into it, a window sill and an external drain. Window sashes, consisting of opening, blind or combined sashes, determine the type of window: one-, two- and three-leaf windows or a window with a balcony door.
Types and sizes of windows standardized and summarized in GOST. They are:
Built and assembled; or manufactured and assembled. . In an accredited manufacturing facility, in accordance with any accredited manufacturing method, and then installed in a building under construction. This can potentially improve productivity by up to 50% in terms of labor and time savings, depending on the complexity of projects. In addition, dust and noise pollution can be kept to a minimum as more work is carried out off site. When the bulk of installation work and labor moves off site to a factory controlled environment, site security will also improve.
a) single-sided;
b) double-leaf;
c) a window with a balcony door;
d) cuts on windows with separate and common boxes.
The window frame is an indispensable element of a window with wooden bindings and consists of side jambs, a top and a bottom trim. At large sizes box windows may have additional horizontal or vertical elements (mullions).
More detailed information on a mandatory requirement is indicated in the Code rules of thumb possible use. Construction Innovation Group. . Performance requirements are in line with the Code of Practice for Usability. Certificate of compliance from practice; Documentary track record of borrowing abroad; Specifications of materials or products; Quality certificates or retests from accredited laboratories. This is managed by the Singapore Concrete Institute and the Structural Steel Society of Singapore, which aims to increase self-regulation in the industry.
The box in the opening is fastened with crutches or long nails driven through the box into antiseptic wooden plugs, specially laid into the wall along the masonry. The gap between the box and the masonry from the side of the facade is sealed with mortar, with inside window slopes are plastered.
window construction shown in fig. 69.
An interview with this performance expert goes something like this. When was precast concrete adopted in Hong Kong? How does the use of precast concrete lead to increased productivity and quality in Hong Kong? These include water leakage problems, high maintenance cost, and concrete finishes on concrete. It was also labor-intensive, given the safety and environmental concerns, as wood materials were widely used for temporary work.
There are many advantages to a semi-basement construction system viz. 
The use of prefabricated elements reduces on-site concrete work and significant on-site wet areas. Since it is only the assembly of prefabricated elements and the installation of panel formwork with little concrete work, the construction project is completed on time. In addition, it is less affected by adverse weather. Upon completion structural structure building blocks, other work can be done at the same time, such as exterior trim and window framing, helping to mitigate critical activities and program delays.
Frame- the main part of the window, which consists of a multi-chamber profile made of wood, plastic or other material. The frame is installed directly into the window opening and must be particularly strong in order to support the weight of the sashes with double-glazed windows.
sash Made from the same material as the frame. The sash is necessary so that the window has opening parts. There can be several opening options: folding, turning, tilt-and-turn.
Quality is guaranteed because the prefabricated elements are manufactured in factories using a factory management system, which requires more precise tolerance to ensure best quality manufacturing. Leakage of water leakage is also eliminated by the monolithic casting of the facade with the floor slab, including the steel system formwork. Window frames are manufactured in a factory, which also helps to minimize the problem of water leakage, thereby reducing long-term costs for Maintenance. In this way, the precast concrete production process can be carefully controlled in the factory with a team of trained quality control personnel prior to product delivery.
Impost needed to divide a window into several sections, connecting the sashes in one window. It can be seen if you open a double-leaf window.
Shtulp directly connects several sashes to each other.
accessories- the internal mechanism of the window, which allows you to perform some of the movable functions of the window, such as opening or ventilating.
The semi-basement system is much safer as it can reduce a lot of work such as fixing rebar, setting up formwork and pouring concrete over height at construction sites. The steel structure design provides a safe working platform for workers.
Work of India - Monolithic construction. The aim here is to draw attention to filling the gaps that exist in India's and the world's approach, including the degree of equipment automation. This system replaces the traditional column and beam design with all walls, floors, slabs, columns, beams, stairs, and door and window openings applied on site in a single on-site operation using a specially designed, easy-to-handle, modular aluminum plastic mold. composite.
The hermetic construction of several glasses is called double-glazed window. Between the glasses there is a special perforated frame that absorbs residual moisture. There can be either air or gas (argon) between the panes.
Rubber seals serve to tightly connect the entire structure, improving tightness.
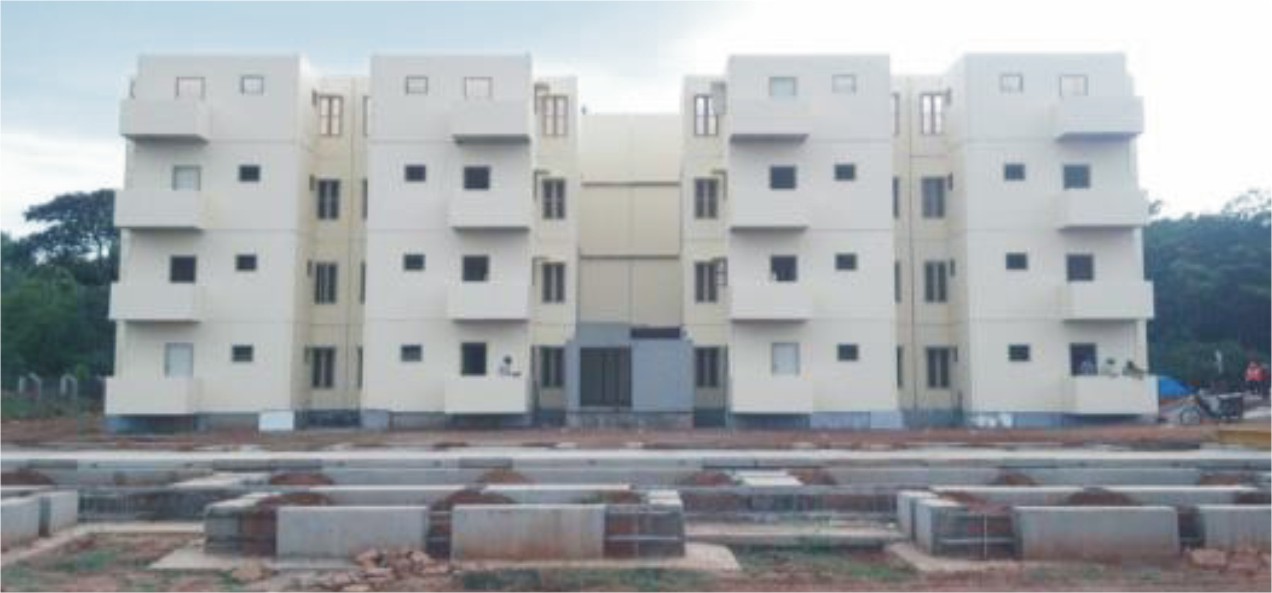



An example of work in the private sector. Shown here is a monolithic concrete sequence provided by a private Indian construction company. The structure has all the components such as walls, slabs, stairs, umbrellas, etc. Monolithic concrete used.
glazing bead the double-glazed window is fixed in the sash.
decorative elements can change the overall look of the window, which is sometimes important for the design style of the room.
Windowsill- a flat horizontal panel, usually made of PVC or wood.
Low tide- outer element windows in the form of a cornice or visor.
slopes- panels or plaster that cover the end parts of the wall from above and from the side.
Rice. 69. Details ( a) and cut ( b) window: 1 - frame; 2 - sash; 3 - impost; 4 - shtulp; 5 - accessories; 6 - double-glazed window; 7 - seals; 8 - glazing bead; 9 - layout; 10 - windowsill; 11 - low tide; 12 - slopes
Filling a doorway consists of a door frame and one or more door panels.
Doors distinguish by appointment: outdoor (entrance and balcony), indoor and closet.
Also by way of opening: swing, sliding, rotating and folded.

Rice. 70. Types of doors: a- swing; b- sliding; in- folded; G- rotating
The most common swing doors, which, depending on the number of canvases, are called single-leaf, double-leaf and, with two canvases of unequal width, one-and-a-half.
GOST provides for door heights from 200 to 240 cm, the width of single-leaf doors 60, 70. 80 and 90 and double-leaf doors - from 120 to 160 cm. The width of the doors is taken in accordance with GOST.
The width of the internal doors is taken depending on the purpose of the room. Doors designed to evacuate people when natural disasters should open outwards.
Door frames are made of bars with a thickness of 47, 57 and 77 mm.
They consist of jambs, a top and a threshold, in which quarters are selected according to the thickness of the door leaf. When arranging a light opening (transom) above the door, a horizontal impost is provided in the boxes, separating the door leaf and the transom.
double boxes balcony doors perform like window boxes. Fixing wooden door frames stone walls similar to fixing window frames. Boxes are attached to the partitions with nails. In gypsum partitions and in partitions made of slabs, the box is attached to the bars of the partition frame. The junction of the box to the partition is closed with platbands.
Door leaves can be panel, panel and carpentry. Panel and panel doors can be solid or glazed, with or without steel mesh protection for glazing.
Monolithic reinforced concrete structures, performed directly on construction sites, are usually used in buildings and structures that are difficult to divide, with non-standard and low repeatability of elements and under especially heavy loads (foundations, frames and ceilings of multi-storey industrial buildings, hydraulic, reclamation, transport and other structures). In some cases, they are expedient when performing work by industrial methods using inventory formwork - sliding, adjustable (towers, cooling towers, silos, chimneys, multi-storey buildings) and mobile (some thin-walled shells of coatings). The construction of monolithic reinforced concrete structures is technically well developed; there are also significant achievements in the application of the prestressing method in the production of monolithic structures. A large number of unique structures were made in monolithic reinforced concrete (television towers, industrial pipes of great height, reactors of nuclear power plants, etc.).
Installation of the reinforcing cage is carried out on the basis of the project or the instructions of the designer. Concreting starts only after the permission of the technical control engineer. With individual construction, technical control is practically absent at the expense of the quality of work. The most frequently repeated mistake is that during the concreting of monolithic reinforced concrete slabs, concrete workers flood the finished reinforcing cage. AT reinforced concrete slabs and beams, steel reinforcing bars should be located above and below, their number and location are calculated by the designer. Usually they are placed in a stretched belt, which is placed above or below, depending on how the beam works under the action of the load (Fig. 71).
To ensure continuous concreting of the structure, concrete is usually delivered over the top of the rebar, as freshly placed concrete is not capable of bearing loads. Rolling for transportation using stretchers, ordinary wheelbarrows, coolie wheelbarrows is arranged from boards in such a way that the wheels do not damage the reinforcement. It is very dangerous to damage the reinforcement in the upper tensile chord if the cantilever beam is rigidly fixed at one end to the supporting structure. These are balcony slabs (Fig. 72), galleries or the so-called cantilever stairs. The importance of reinforcing reinforced concrete structures in the upper chord is often misunderstood.
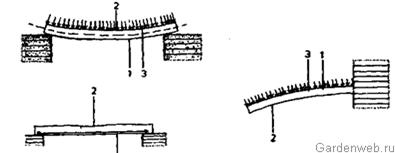
Rice. 71. Tensile and compressed chords in beams on two supports and in a cantilever beam; 1 - stretched belt, 2 - compressed belt, 3 - load
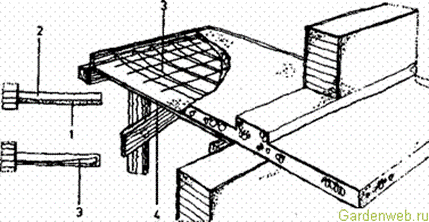
Rice. 72. Concreting of a balcony slab on crushed reinforcement
Even in the practice of state construction, sometimes reinforcement is carefully trampled down before concreting, not realizing that the reinforcement bars are arranged alternately according to the calculation - at the bottom and at the top.
 Accuracy during the installation of reinforcement is very difficult to maintain, especially in individual construction, where fixtures for bending and cutting reinforcement are much simpler than in the state. The most common mistake is the delusion that the designer calculates all structures with a large margin. Such a view breeds irresponsibility.
Accuracy during the installation of reinforcement is very difficult to maintain, especially in individual construction, where fixtures for bending and cutting reinforcement are much simpler than in the state. The most common mistake is the delusion that the designer calculates all structures with a large margin. Such a view breeds irresponsibility.
Rice. 73. Destruction of a beam due to lack of shear reinforcement; 1 - reinforced concrete beam, 2 - shear stress cracks, 3 - shear reinforcement, 4 - clamp, 5 - beam support, 6 - load
Incorrect placement of shear reinforcement in a beam near supports is an example of poor reinforcement. The greatest values of shear stresses are located just at the supports, they are balanced by the strength of concrete, the use of so-called clamps and the bearing capacity of the reinforcement, designed for shearing forces (Fig. 73).
The lower and upper steel rods located in this place also participate in the perception of the transverse shear force. Incorrect placement of shear reinforcement in the most dangerous places near the supports weakens the cross section and the reinforced concrete beam "shears" because the combined resistance of concrete and stirrups is often not enough to balance the shearing forces.
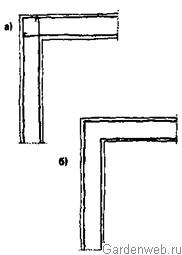
Incorrect reinforcement has already caused the destruction of many monolithic reinforced concrete stairs, when tensile reinforcement was laid along the fracture line of the structure (Fig. 74). In this case, under the action of the load, the reinforcement straightens, the beam collapses. During normal laying of the reinforcement, the lower tensioned rods are brought out into the compressed belt, where they are fixed. A mistake similar to the one described above is made when reinforcing the corners of frame structures (Fig. 75). Incorrect reinforcement also causes difficulties in concreting: it is impossible to lay concrete between the reinforcement bars of heavily loaded beams. After stripping, it is found that there is no concrete under the steel inserts and the beam is unsuitable for bearing the load, and the reinforcement is not protected from corrosion.
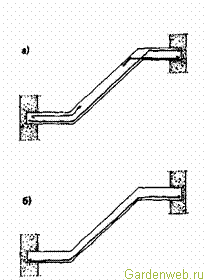
Rice. 74. Arrangement of reinforcement in a reinforced concrete staircase: a - correct, b - incorrect
Rice. 75. Arrangement of reinforcement in the corners of a reinforced concrete beam: a - correct; b - wrong
Repair requires careful work. If a defect is found, weak sections of concrete are removed, the place is cut for re-concreting. The voids prepared for repair are equipped with formwork; it is desirable to use the so-called formwork with pockets, the essence of which is that the voids are filled with "overflow" and no air bubbles remain in the concrete. Excessive protrusions of concrete are chipped off after hardening. After the formwork, the place prepared for concreting is cleaned of dust and dirt; the cleaned surface is thoroughly moistened, otherwise the hardened concrete absorbs moisture from the freshly laid concrete mixture and there is not enough water to set, the concrete “burns out” and the structure does not gain the required strength.
The composition of the concrete mixture to eliminate imperfections is determined depending on the needs. The repair is taken as the basis concrete mix, prepared with a minimum amount of water to avoid increased shrinkage, which causes cracks to open along the border of old and new concrete.




















