Mortar for bricklaying: proportions and composition
The mortar for laying bricks must contain the so-called binders and aggregates. Most often, cement or lime is used as a binder. Sand acts as a filler - for masonry mortar, clean sand without impurities (roots, grass, etc.) is considered the best option.
In the construction business, solutions of air and water hardening are used.
The preparation of the mortar is an extremely serious matter, because if it is made incorrectly, one cannot be sure of the safety of the building. For example, the composition of the mortars that were used in the construction of ancient temples is not known thoroughly until now, and yet it allowed them to stand for thousands of years. Given this fact, it is necessary to pay special attention to the preparation of the solution.
Rules for the manufacture of a quality solution:
Are you going to build a house? About how to prevent the most common mistakes the foundation for a house with your own hands can be read in our article from the "Foundation" section.
You have built a house and are thinking about outdoor decoration? Finishing a house with siding is a great solution, read about how to do it yourself here.
Before answering the question of which mortar to choose for laying bricks, you need to figure out what types of mortars exist and what are their characteristics. The composition of the solutions for brickwork most often divided into lime, cement-lime or cement.
- lime mortars warm and plastic, however, their strength is lower than that of cement. A solution is prepared from the so-called lime paste, sand and ground quicklime.
Grades of masonry mortar
The classification of the solution by brand is widely used.
- Marks 0 and 2 are rarely used.
- Grades 75, 25, 4, 10, 50 are the most popular.
- Grades 100, 200, 150 - used for specific construction work.
The brand is assigned by checking the hardened solution cubes for compression.
Solution mobility is another important feature. This value is determined by the method of practical tests. A special cone is immersed in a freshly prepared solution - the lower the cone is immersed in the material, the higher the mobility. For laying a solid brick, a mortar with a mobility of 9-10 is optimal, for a hollow brick - 7-8. In hot weather, it is recommended to use a solution with a mobility of 12-14.
The composition and proportions of a quality solution
 The proportions of the mortar for laying bricks are determined based on such indicators as the number of storeys of the building, the type of structure being erected, the type of soil, and so on.
The proportions of the mortar for laying bricks are determined based on such indicators as the number of storeys of the building, the type of structure being erected, the type of soil, and so on.
For laying one-story buildings, lime mortar is used, which is distinguished by ease of installation and excellent "tenacity". The optimal proportions of sand and lime are 4:1.
Cement mortar is used when laying walls with a thickness of less than 0.25 meters. The ratio of sand-cement should be from 3:1 to 6:1, depending on the characteristics of the structure being erected and on the brand of cement.
The mortar for laying bricks is prepared in two stages: first, dry ingredients are mixed, then water is poured. Water must be clean and cold.
The optimal water consumption for a cement-sand mortar is considered to be 0.8 parts of water per one part of cement.
The popular brand of mortar for laying bricks 75 is prepared from cement, lime and sand in the following proportions: 1. 0.8. 7. Special dyes can be added to the facing brick mortar to achieve certain design ideas, such as combining yellow facing bricks with brown joints.
For refractory brick structures that are expected to be impacted high temperatures, a special sand-clay mortar is used with the addition of refractory clay or fireclay powder. This solution is perfect for laying fireclay stoves or fireplaces.
Preparation of high-quality mortar for brickwork
 Proper preparation of mortar for laying bricks is carried out in stages:
Proper preparation of mortar for laying bricks is carried out in stages:
- First you need to prepare the components - cement, sand, water and slaked lime.
If you are going to build a garage, then you can find out how to do it without resorting to the help of specialists here.
The construction of the house is completed and it's time to think about protecting the foundation and arranging the territory. You can learn how to make a blind area around the house by reading this article.
How to calculate the consumption of mortar for brickwork?
One of the most popular mortars for laying bricks - cement-sand, has the following indicators for the consumption of this material. For one square meter brickwork one brick thick consumes about 75 liters of mortar. If the laying is carried out in one and a half bricks, about 115 liters of mortar per square meter will be consumed.
The twenty-first century offers many different dry mixes for brick work. However, a simple cement-sand mortar is still out of competition. When planning construction work, it should be remembered that it is best to carry it out in the summer, then nature itself will help you.
More information
Mortar is used to fasten the bricks together. Any solution consists of a binder, aggregate and water. Mortars for masonry can be used on a lime, cement-lime or cement base.
lime mortars warmer, but their strength is significantly inferior to the strength of cement mortars. It is prepared from lime dough or ground quicklime and sand. The dough is mixed with sand and water until a homogeneous mass is obtained. The solution can be passed through a sieve to weed out lumps. Lime mortars for brickwork are usually made in a ratio of 1:2 to 1:5, depending on the fat content of the lime.
Lime mortar masonry is less durable, so they are rarely used for masonry walls.
Cement-lime mortars composed of cement and lime mortar. Lime dough (slaked lime) is diluted with water to the density of milk and filtered on a clean sieve. A dry mixture is prepared from cement and sand, it is mixed with milk of lime and thoroughly mixed. The addition of lime milk increases the plasticity of the solution.
(cement: lime: sand)
|
Grade of cement |
Solution grade | ||||
| 200 | 150 | 100 | 75 | 50 | |
| 500 | 1: 0.2: 3 | 1: 0.3: 4 | 1: 0.5: 5.5 | 1: 0.8: 7 | |
| 400 | 1: 0.1: 2.5 | 1: 0.2: 3 | 1: 0.4: 4.5 | 1: 0.5: 5.5 | 1: 0.9: 8 |
The plasticity of cement-lime mortar makes it preferred for almost all types of masonry.
cement mortars prepared from sand and cement in a ratio of 1:3 to 1:6 (cement:sand), depending on the brand of cement and the requirements for the solution.
To do this, first knead a dry mixture of sand and cement in the required ratio. Stir it thoroughly and then add water to mix until smooth. Compared to lime or cement-lime mortars, the cement mortar is less mobile and with almost any brand of cement it turns out to be unnecessarily strong and rigid.
(cement: sand)
|
Grade of cement |
Solution grade | ||||
| 200 | 150 | 100 | 75 | 50 | |
| 500 | 1: 3 | 1: 4 | 1: 5.5 | 1: 6 | - |
| 400 | 1: 2.5 | 1: 3 | 1: 4.5 | 1: 5.5 | - |
The ratio between the amount of binder and sand is given by volume. The mixing of the mixture of binder and aggregate must be done in batches, each time visually assessing the mobility of the mortar mixture after thorough mixing.

To prepare the mortar mixture, take a pure cold water(from +15 to +20˚С). When preparing the solution, the dosage should be strictly observed.
The optimal water consumption for mixing is:
For cement-sand mortars - 0.8 parts of water per 1 part of cement;
For concrete grade M-100 (B7.5) - 0.5-0.7 parts of water per 1 part of cement.
As a filler should be used:
Sand for construction work with a grain size of not more than: 2.5mm
Portland slag cement is not recommended for use in winter.
Approximate consumption of cement for the preparation of 1 meter of cubic (m3) mortar for brickwork, kg.
| Grade of cement | Consumption of cement brand M100 |
| M400 | 300 |
| M500 | 250 |
| Consumption of cement brand M150 | |
| M400 | 400 |
| M500 | 330 |
| Consumption of cement brand M200 | |
| M400 | 490 |
| M500 | 410 |
| Consumption of cement brand M300 | |
| M400 | 600 |
| M500 | 510 |
The mobility of the mortar mixture is determined by the depth of immersion of a metal standard cone
 AT this moment on the market building materials a wide range of ready-made dry mixes appeared. The dry mixture is mixed with the required amount of water, according to the technical data. Mixing is carried out in a mortar mixer or hand mixer in a container. Mixing time 5-7 minutes. It is not allowed to introduce any foreign additives or fillers into the composition of the mixture.
AT this moment on the market building materials a wide range of ready-made dry mixes appeared. The dry mixture is mixed with the required amount of water, according to the technical data. Mixing is carried out in a mortar mixer or hand mixer in a container. Mixing time 5-7 minutes. It is not allowed to introduce any foreign additives or fillers into the composition of the mixture.
The strength of the hardened mortar depends not only on its correct preparation, but also on what base it is applied to. When laying the mortar mix on a porous base that intensively absorbs water from the solution, the strength of the hardened mortar will be significantly higher than that of the same mortar laid on a dense base that does not absorb moisture well.
Before use, the solution must be thoroughly mixed, because over time, heavy particles settle, the solution separates and becomes heterogeneous.
In order for mortars and concretes to be best quality, had certain properties, organic additives are added to them - these are sand, crushed stone, marble, clinker and inorganic compounds. Inorganic additives are synthetic substances. The mobility, rigidity, setting of cement mortars, as well as concretes, depends on how many additives in the mortar mixture.
- Basic requirements for masonry mortar
- What are masonry mortars
- Mortars based on cement
- lime mortars
- Cement-lime mortars
- Features of the preparation of a refractory solution
No matter how high-quality the brickwork is, but without a properly prepared masonry mortar, not a single building will stand idle for a long time. If the solution is prepared correctly, then a brick building can stand for many years, as evidenced by the thousand-year-old Orthodox churches built during the time of Kievan Rus.
This fact alone is enough to approach the preparation of the solution very seriously, not allowing any gag either in the proportions of the components or in the technique of its preparation.
Basic requirements for masonry mortar
Method for preparation of lightweight masonry mortar and composition for lightweight masonry mortar.
The mortar prepared for masonry must meet three basic requirements. Firstly, in order to completely fill all the voids and crevices in the bricks (with the exception of the voids in the hollow bricks, which should just remain unfilled), the prepared mixture must have sufficient plasticity.
Secondly, the prepared mixture should not set for a long time so that it can be used in work. Thirdly, after hardening, it should remain hard and rigid for as long as possible, ideally the entire existence of a brick building.
If the solution, under the influence of the environment or due to miscalculations in its preparation, after the completion of the masonry begins to soften, this will inevitably lead to deformation, and even to the complete destruction of the building.
Back to index
What are masonry mortars
The composition of any solution in a certain proportion includes three main components: aggregate, binder and water. Depending on the type of binder, solutions can be:
- cement based;
- lime-based;
- on a mixed cement-lime base.
The most common filler is sand. It must be of fine fraction (grains of sand no more than 2 mm), clean and free of impurities. To bring it to the desired condition, it is advisable to sift it immediately before use, otherwise small lumps in the prepared solution cannot be avoided.
Not only sand, but also clay can be added as a filler. Such a mixture has high plasticity, but it is not always suitable for masonry, especially if the masonry is made of hollow bricks. In this case, the plastic mixture will fill the cavities of the brick, thereby worsening the thermal insulation of the masonry being performed.
To date, in building stores there is a fairly wide range of various ready-made dry mixes. In such a mixture, you just need to add the amount of water indicated on the package and mix everything thoroughly for 5-7 minutes.
If the amount of solution needed is small, then a bucket and a construction mixer can be used to prepare it. If the volume of brickwork is to be large, then it is faster and more practical to use a concrete mixer, but it must be washed clean, since the addition of foreign elements to the mixture is strictly prohibited.

When preparing the solution, it should be borne in mind that its plasticity and strength depend, in addition to the type and correct preparation, and on the masonry material. If the material is porous, then it will more intensively draw water out of the mixture, therefore, the strength of the solution hardened in such a masonry increases significantly. And when using a mixture similar in preparation to make masonry from a material that does not absorb water well, its hardened strength may be lower than required.
Water for the preparation of the solution should be used only clean and best of all cold (from 15 to 20ºС). The optimal consumption for cement-sand mixtures is taken from the calculation for 1 part of cement 0.8 parts of water. In order for the solution to come out of high quality, the indicated dosage should be strictly observed.
In order to acquire in sufficient quantities the components necessary for the preparation of the masonry mortar, you need to know in advance the norms of its consumption. The calculation of consumption per 1 m³ of brickwork depends on the thickness of the wall to be extruded and the type of brick.
Back to index
Mortars based on cement
Cement-based mortars are the coldest of all three types. Despite this, due to the ease of their preparation, they remain the most popular with private developers who do their own masonry. Prepare them by carefully mixing dry sand and cement. Then the mixture is diluted with water to the desired density, constantly stirring until lumps disappear and a homogeneous mass is obtained as a result.
When preparing a solution in large volumes, a concrete mixer is usually used. The technology of its preparation in a concrete mixer is slightly different from the classical one. Initially poured into the concrete mixer right amount water, and then, constantly stirring, add cement and sand in the right proportions.
If the mixture does not come out plastic enough, then a little water is added to it, if, on the contrary, it turns out to be too liquid, then a little sand and cement, maintaining the given proportion of the mixture. The total mixing time should not exceed 3 minutes.
When masonry is used for the preparation of mixtures, the water tends to seep down to the bottom of the container, so the solution must be mixed all the time, swapping the lower and upper layers. The prepared solution hardens in 1.5-2 hours, so it will not work to prepare it for the future. You need to prepare such a volume of the solution as you can use in the time allotted for hardening.
Depending on the brand of cement and the requirements for masonry mortar, the ratio of sand to cement can vary from 3:1 to 6:1. Cement mortar is the strongest, but at the same time the most rigid and immovable of all types of mortars. Moreover, the smaller the ratio of sand and cement, the more durable the solution will be.
To classify the solution, its marking is used. In private construction, mortar grades M25, M50 or M75 are most often used. For industrial construction, where special strength is required, mortar grades M100, M150 or M200 are used.
To prepare a mortar of grade M25, the ratio of sand to cement of grade M300 should be 5:1, for grade M50 this ratio is reduced to 4:1, and for grade M75 to 3:1. To obtain higher grades of mortar, the ratio remains 3:1, but cement of higher grades is used.
It is difficult for a non-specialist to perform accurate calculations of the volume of sand and cement to obtain a high-quality mixture of the required grade.
Back to index
lime mortars

Lime mortars are distinguished by great warmth, but they are significantly inferior in strength to cement mortars. For its preparation, either ground quicklime or lime dough mixed with sand and water is used.
The solution is mixed until a homogeneous plastic mass is obtained. It is better to pass it through a sieve to obtain a more uniform consistency and to eliminate lumps. It is best to take a sieve with a mesh size of 1x1 cm for this. Smaller cells will clog, and small lumps of lime may fall through large ones. Depending on the fat content of lime, the proportions of sand to lime can vary from 2:1 to 5:1.
To obtain lime dough, quicklime is taken and diluted in water in a ratio of 1:3. Properly prepared lime dough has a density of 1400 kg/m³. However, it is not recommended to cook it yourself, because. without experience with quicklime, you can easily get serious burns of your hands and respiratory tract along with the lime test, or even instead of it.
Due to insufficient strength, lime mixtures for laying exterior bearing walls practically not used. The scope of their application is the foundations of stoves and fireplaces, as well as brick chimneys, where other types of solutions do not withstand and crack or crumble due to frequent significant temperature changes.
Back to index
Cement-lime mortars
Cement-lime mortars are prepared from cement, sand and lime milk. First, slaked lime is diluted with water until the mixture resembles milk in composition. Cement and sand are mixed dry, after which the prepared milk of lime is filtered through a sieve, removing the smallest lumps, after which it is added to the cement-sand mixture and everything is mixed very thoroughly.
Such a solution, due to the addition of lime milk, is much more plastic and warmer than cement, and much stronger than pure lime, so professionals prefer to use it for brickwork.
In comparison with cement mortar, its hardening time is almost 3 times longer - up to 5 hours. Therefore, it is more convenient and practical to use a concrete mixer to prepare the mixture.

Using a concrete mixer greatly simplifies the process of preparing the mixture. First, 2/3 of the required volume of water is poured into the concrete mixer, then lime and cement are poured in and everything is thoroughly mixed. Then sand and the remaining water are added to the concrete mixer and the concrete mixer is turned on again for 3-5 minutes. Clay is often added to this mixture for better plasticity.
To prepare such a mixture, cement M400 is usually used, much less often - M500. Higher grades of cement are not used, because. a mortar with similar characteristics is much easier to prepare from a mixture of sand and cement of lower grades.
The ratio of cement, lime and sand in the M25 cement-lime mixture should be taken as follows: part cement, 1 part lime and 4 parts sand. For a solution of brand M50, this ratio will be 1: 0.5: 4.5.
Performing the calculation of the required volume of cement-lime mixture and required amount ingredients, you need to build on the following values: to prepare 1 m³ of the mixture, you will need 1760 kg of sand, 470 liters of water, 191 kg of cement and 106 kg of lime.
Such solutions, due to their strength and plasticity, are simply indispensable for forcing foundations and plinths below the waterproofing layer. But often it is also used for forcing external walls in one- and two-story cottages.
The strength of the solution is determined by its brand, i.e. the ability to withstand a certain compressive load, measured in kilograms per square centimeter. To obtain a solution of the same composition, all the components included in it are measured in certain doses, using different dishes or scales for this. There are lean, normal and fatty solutions. The skinny has a lot of aggregate, it is inconvenient to work with and does not have the proper strength. A normal solution contains an abundance of binder and aggregate, while in a greasy one there is an excess of binder, so it cracks. Fat content is determined mainly in clay and lime mortars with the help of an oar, with which it is mixed. If the solution does not stick to the oar, but only stains it, then it is skinny; if it sticks in separate clots - normal; when the solution strongly envelops the paddle, it is greasy.
Astringents are added to the lean solution, and filler is added to the greasy solution. All materials used to prepare the solution are pre-sieved on a sieve. When preparing a mortar for plastering, a sieve with 5x5 mm cells is used, for stone work - with 10x10 mm cells. From clay or lime dough, the solution is prepared immediately, and from cement, first a dry mixture is prepared, and then a solution. You can make a mixture in a box; but it is better on a striker - a wooden shield measuring 2x3 m. Any solution must be prepared carefully. A poorly mixed solution is not homogeneous, and where it is weaker, structural failure can begin. Accurate dosing of materials is essential. Dry mixes, such as cement with sand, are best prepared this way. Sand and cement in the form of a bed are poured in layers, which are brought to a total height of 200-300 mm. This bed is shoveled with shovels several times until smooth, and then the mixture is sieved through a fine sieve with cells of 3x3 mm, no less.
To prepare the solution, the mixture and water are also measured in doses and thoroughly mixed until completely homogeneous. From excess water, a more liquid solution is obtained and, after drying, it is less durable than a thick solution of the same composition. From properly prepared mixtures, homogeneous solutions are obtained. It is much easier to lay them than heterogeneous ones.
Materials and solutions for foundations and plinths
These parts of the buildings are built from durable materials that can serve for a long time without collapsing. Tables 6 and 7 list materials and mortars for foundations and plinths in various operating conditions.
Table 6 Mortars for laying foundations and plinths below the waterproofing layer:
| Grade of cement | Soil type | |||
| low-humidity | wet | saturated with water | ||
| cement-lime mortar brand "10" (cement, lime paste, sand) | cement-clay mortar brand "10" (cement, clay dough, sand) | cement-lime and cement-clay mortar brand "25" (cement, lime or clay, sand) | cement mortar brand "50" (cement, sand) | |
| 50 | 1:0,1:2,5 | 1:0,1:2,5 | - | - |
| 100 | 1:0,5:5 | 1:0,5:5 | 1:0,1:2 | - |
| 150 | 1:1,2:9 | 1:1:7 | 1:0,3:3,5 | - |
| 200 | 1:1,7:12 | 1:1:8 | 1:0,5:5 | 1:2,5 |
| 250 | 1:1,7:12 | 1:1:9 | 1:0,7:5 | 1:3 |
| 300 | 1:2,5:15 | 1:1:11 | 1:0,7:8 | 1:4,5 |
| 400 | 1:2,1:15 | 1:1:11 | 1:0,7:8 | 1:6 |
Note: Solution compositions are given in volume units.
Table 7 Materials for the underground part of the house and the basement below the waterproofing layer:
| materials | Material grade, kgf / cm 2 | ||
| Priming | |||
| slightly humidified | wet | saturated with water | |
| at the level of groundwater at a depth from the surface of the earth, m | |||
| 3 or more | 1 to 3 | 1 | |
| Natural stone, weighing more than 1600 kg / m 3 (limestone, dense sandstone, granite, diorite, basalt) | 100 | 150 | 200 |
| Natural stone weighing less than 1600 kg / m 3 | 50 | 75 | Cannot be applied |
| Heavy concrete weighing more than 1800 kg / m 3 and products from it, except for concrete on fuel slag | 75 | 75 | 100 |
| Clay brick plastic pressing | 100 | 125 | 150 |
| cement mortar | Application not justified | 25 | 50 |
| Cement-lime mortar | 10 | 25 | Cannot be applied |
| Cement-clay mortar | 10 | 25 | Same |
Most often, rubble concrete is used for foundations. The filler is usually a stone from quarries, coarse gravel, crushed stone, brick-ladder, brick fight, etc. The filler is laid in layers of 20-25 cm thick against the walls. Each layer is poured with a solution of the desired brand and tightly rammed.
Cement-lime mortar is prepared from cement, lime paste and sand. The lime dough is diluted with water to the density of milk and filtered on a clean sieve. A dry mixture is prepared from cement and sand, it is mixed with milk of lime and thoroughly mixed. The addition of lime milk increases the plasticity of the solution. Instead of lime dough, clay dough can be used, which is taken in the same amount. Compositions (in volume parts) and brands of cement-lime and cement-clay mortars are given in tables 8, 9, 10. Both those and other solutions are used both for laying elevated walls and foundations in dry soils. If underground masonry is carried out in low-moisture soil, then for 1 m 3 of sand in cement-lime mortars take at least 75 kg of cement, in cement-clay - 100 kg; in very wet and water-saturated soils - 100 and 125 kg.
Table 8 Composition and grades of cement-lime and cement-clay mortars:
| Grade of cement | Brand of solution, kgf / cm 2 | ||||
| 100 | 50 | 25 | 10 | 4 | |
| The ratio of the parts of the solution | |||||
| 400 | 1:0,2:3,5 | 1:0,7:6,5 | 1:1,9:12,5 | - | - |
| 300 | 1:0,1:2,5 | 1:0,4:5 | 1:1,3:10 | - | - |
| 200 | - | 1:0,2:3,5 | 1:0,7:6,5 | 1:2:16 | - |
| 150 | - | - | 1:0,3:4,5 | 1:0,8:7 | - |
| 100 | - | - | 1:0,1:3 | 1:1,5:10,5 | 1:1,8:13 |
| 50 | - | - | - | 1:0,2:3,5 | 1:1:9 |
Note: the numbers 1:0.7:6.5 mean that they take 1 part of cement, 0.7 parts of lime or clay dough and 6.5 parts of sand.
Table 9
| Grade of cement | Solution grade | |||
| 100 | 75 | 50 | 25 | |
| 600 | 1:0,4:4,5 | 1:0,7:6 | - | - |
| 500 | 1:0,3:4 | 1:0,5:5 | 1:1:8 | - |
| 400 | 1:0,2:3 | 1:0,3:4 | 1:0,7:6 | 1:1,7:1,2 |
| 300 | - | 1:0,2:3 | 1:0,4:4,5 | 1:1,2:9 |
| Cement-clay mortars | ||||
| 600 | 1:0,4:4,5 | 1:0,7:6 | - | - |
| 500 | 1:0,3:4 | 1:0,5:5 | 1:1:3 | - |
| 400 | 1:0,2:3 | 1:0,3:4 | 1:0,7:6 | 1:1:11 |
| 300 | - | 1:0,2:3 | 1:0,4:4,5 | 1:1:9 |
Table 10
| Brand | Solution grade | |||
| 100 | 75 | 50 | 25 | |
| Cement-lime mortars | ||||
| 600 | 1:0,4:4,5 | 1:0,7:6 | - | - |
| 500 | 1:0,3:4 | 1:0,5:5 | 1:0,7:8 | - |
| 400 | 1:0,2:3 | 1:0,3:4 | 1:0,7:6 | - |
| 300 | - | 1:0,2:3 | 1:0,4:5 | 1:0,7:9 |
| Cement-clay mortars | ||||
| 600 | 1:0,4:4,5 | 1:0,7:6 | - | - |
| 500 | 1:0,3:4 | 1:0,5:5 | 1:0,7:7,5 | - |
| 400 | 1:0,2:3 | 1:0,3:4 | 1:0,7:6 | 1:0,7:8,5 |
| 300 | - | 1:0,2:3 | 1:0,4:5 | - |
| cement mortars | ||||
| 600 | 1:4,5 | 1:6 | - | - |
| 500 | 1:4 | 1:5 | - | - |
| 400 | 1:3 | 1:4 | 1:6 | - |
| 300 | - | 1:3 | 1:4,5 | - |
Cement mortars are prepared in the following sequence. A dry mixture is preliminarily prepared from cement and sand, and from 2.5 to 6 parts of sand can be taken for 1 part of cement (depending on the brand of cement). The dry mixture is closed with water, mixed and used for 1-1.5 hours. Cement mortars are most often used for laying foundations and other structures that are below the groundwater level. Walls can also be laid on the same solutions. They are quite strong, but very cold. Depending on the brand of binder and the amount of filler taken in volume parts, a cement mortar of one brand or another is obtained (Table 11). The need for cement is determined depending on its brand and the brand of the prepared solution (Table 12).
Table 11 Brand of mortar depending on the brand of cement and the amount of aggregate:
| Grade of cement | Brand of solution, kgf / cm 2 | ||||
| 100 | 50 | 25 | 10 | 4 | |
| The ratio of the parts of the solution | |||||
| 400 | 1:3,5 | 1:6 | - | - | - |
| 300 | 1:2,5 | 1:5 | - | - | - |
| 200 | - | 1:3,5 | 1:6 | - | - |
| 150 | - | 1:2,5 | 1:4 | 1:6 | - |
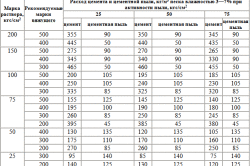
Table 12 Consumption of cement per 1 m 3 of sand to prepare a solution of the desired brand:
| Grade of cement | Brand of solution, kgf / cm 2 | ||||
| 100 | 50 | 25 | 10 | 4 | |
| Consumption of cement, kg | |||||
| 400 | 340 | 185 | 90 | - | - |
| 300 | 435 | 240 | 120 | - | - |
| 200 | - | 350 | 185 | 75 | - |
| 150 | - | - | 230 | 95 | - |
Comments: 0
The cement mortar of brickwork must be elastic and viscous - this is the main condition for its preparation. An “obedient” solution will greatly facilitate the work of a bricklayer, and provide high performance masonry. To prepare a “successful” solution is a whole art that only professionals can do. Since there are many nuances and little secrets. The quality of the mortar depends on the brand and quality of the cement, the composition of the sand, and of course the skill of the mason.
Brand of concrete mix
Depending on the material used, the load and other features of the future masonry, various grades of mortar are used during construction. The grade of concrete usually varies from 100 to 500, depending on the purpose of the structure and the requirements for its operation.
What is their peculiarity? It's simple: the brand of cement mortar directly depends on the amount of sand in it, that is cement mixture classified according to the proportions of the components contained in it. For example, to prepare a solution of grade 100, it is necessary to mix grade 400 cement, sand and water in a ratio of 1:4. If cement is used brand 500 proportions - 1:5. The calculation is carried out as follows: we divide the brand of cement by the amount of sand - we get the brand concrete mix. Everything is simple. Builders usually use a bucket as a unit, this container is accessible to everyone and has a small, at the same time convenient volume. In a similar way, you can calculate the grade of the solution individually for each type of work.
How to prepare a mortar for laying bricks, based on its properties, what brand of concrete to use?
To be whole Brick wall homogeneous in terms of strength properties, theoretically it is necessary to use a solution of grade -100. In this case, you should not take into account the brand of brick. For example, if a brand-350 brick is used, it will be enough to confine itself to a “weaving” solution.

Solution preparation technology
Any concrete consists of water, cement and sand. Sometimes special additives are added to improve elasticity or other indicators. For example, to create an "oily" solution, experienced masons add any concentrated detergent - dishwashing detergent, liquid soap, Trialon. In the cold season, especially in frost, an anti-freeze powder is used; it does not allow the water contained in concrete to turn into ice. For viscosity, lime is often added, it gives the solution an “obedient” consistency.
How to prepare a mortar for laying bricks correctly and prevent unpleasant oversights will help a few tips.
1. Water for the solution must be used only clean, free of impurities and dirt. It is not advisable to add rain water or already used water to concrete, for example, for washing buckets, barrels, etc.
2. To make the solution airy and not settle, detergents are added to it, but you should be careful with this additive, since a large amount of it can, on the contrary, spoil the masonry mortar - make it brittle, and after a few weeks the cement joints will crumble.
3. Sand is an important component of concrete; the quality of future walls depends on its quality. Sand with clay impurities or small pebbles is definitely not suitable, as the masonry will begin to collapse. In this case, it is better not to save money and buy sand of the appropriate quality.
4. The brand and quality of cement also affects the strength of the walls being built. To do this, you need to choose.

Cooking process
Pour the required amount of water into the mixing container or into the concrete mixer. In this case, it is worth considering the moisture content of the sand. An excellent guideline for the correct calculation of water - cement - in a 1: 1 ratio. For example, on a bucket of cement - a bucket of water, but it is better to ensure that the concrete is not too liquid. However, if this still happened, you can correct the situation by adding sand and cement to the container in the original proportions.
The detergent is added to the water, stirred, and only after that cement and sand should be introduced. If the detergent is added after kneading, it will not dissolve.
After dissolving the detergent, sand is added, more precisely half of it. Then pour all the cement into a container or mixer and mix until a homogeneous mass is obtained. Next, add the rest of the sand. In the event that the solution turned out to be thick, you can add water until the desired consistency is obtained.
The result should be a creamy mixture of moderate density to keep its shape and not blur.
It is important to consider that the quality factor and stability of the future home depends on how to prepare a mortar for brickwork. Mortar is the basis of brickwork.




















