Life modern man impossible without the use of various devices. Every home is filled with electronic and home appliances, tools and lighting fixtures. But, unfortunately, problems with power supply have again become commonplace.
Electricity can be turned off on schedule or without any warning, and simple accidents on the networks happen. And any power surges and interruptions in the flow of "light" not only disrupt the usual course of life, but also increase the risk of equipment failure.
The device of a backup power system (PSS) based on a storage battery (AB) allows you to solve this problem once and for a long time. It is important to do this reasonably, thoughtfully and with a proper approach to the quality of installation work.
What to connect?
With the help of PSA, it makes sense to provide uninterrupted power supply only to the main consumers, characterized by either low power or intermittent operation for a short time. This, in particular, can be:
- gas or solid fuel heating (automatic control, circulation pumps);
- water supply (pump);
- emergency lighting (3-5 electric lamps per building);
- 2-4 additional sockets for appliances (refrigerator, computer, internet router).
It is not worth reserving continuous loads from the operation of powerful devices (electric boiler, boiler, air conditioner or electric oven). After all, this will entail the need to use several high-capacity batteries, and the equipment accompanying them also needs to be strengthened. Thus, for the arrangement of the system, very large and unjustified financial costs will have to be incurred.
The best option is to follow the principle of reasonable sufficiency, that is, to establish a PSA of the required performance and use only the equipment that is really necessary in this moment. This will enable you to save on initial stage and extend the time battery life technology.
Energy storage
Batteries are the most important element of the PSA, as they ensure the operability of equipment in the event of malfunctions or outages in the network. These devices are used for reusable accumulation and further distribution of electricity.
The most common for a long time were acid (lead-acid) batteries., the principle of which is based on the immersion of two or more lead plates in a solution of sulfuric acid (electrolyte). The chemical reaction that occurs between them causes the accumulation of electricity. These devices are also called traction or starter, since they are able to provide increased values of starting (initial) current. In this regard, they are widely used in cars. But to create a home autonomous system, it is not recommended to use traction devices. The fact is that a liquid acidic electrolyte can boil at high currents, so the battery case is made leaky. And this, in turn, leads to the risk of fires and even explosions in the room.
In contrast, gel batteries use acid in a thixotropic gel state (similar in texture to wax). The body of the devices is made integral, but even if it is damaged, the gel will not be able to spill. There is no danger or harm to the environment. For this reason, the gel battery can be installed in any room.
And the most modern are AGM-batteries (Absorbed Glass Mat). The electrolyte in them is bound with a special glass fiber. These devices have the same advantages as gel devices. Yes, and the cost is approximately equal (and 2 times higher than that of acidic ones). In addition, AGM batteries practically do not heat up, since the internal resistance in them is negligible.
Essential detail: while charging acid batteries up to 20% of the energy goes into a thermal state, for gel models this figure is about 10-15%, and for AGM models it is only 3-4%. That is, the latter practically do not heat up, and this is a positive characteristic in terms of safety and lower power consumption. In addition, gel and AGM devices are more efficient in case of long downtime: they lose no more than 1-3% of energy per month, and acid ones - up to 1% per day.
Thus, gel and AGM batteries can be recommended for use in home SRPs. Moreover, they do not require periodic addition of electrolyte and generally any maintenance during operation.
To increase the capabilities of the PSA, several batteries are purchased and installed in a parallel-connected circuit to increase the output of electricity.

Batteries of different types are very similar in appearance, so it is important to buy equipment from specialized companies or in construction hypermarkets

Only the most necessary equipment needs to be provided with autonomous power: heating and water supply pumps, lighting. It is not advisable to connect powerful devices to batteries, without which you can easily do without for some time - air conditioners, electric ovens
Important Features
AB is chosen taking into account several parameters. Weight is important in determining the location of the battery. Modern batteries weigh about 10-20 kg. The relative severity is associated with the design features of the devices, in particular, the use of an electrolyte in a viscous consistency. Therefore, light shelves for installing AB will not work - you need a more solid support, for example, a rack made of metal corners. The output voltage for most modern models is 12 V. There are also modifications for 24 and 48 V. For domestic use, experts recommend choosing batteries that produce direct current with a voltage of 12 V.
The maximum starting current value indicates whether the battery can generate the current required to start the motors. The fact is that almost all electrical devices at the moment of switching on require much more energy than in operating mode. This value is measured in amperes (A). At home, a battery with a starting current of 200-400 A is enough. This is enough to turn on, for example, a pump for a well or household models of power tools.
Battery capacity is the amount of charge that the battery is able to accumulate and then give away during its work. The capacitance is measured in ampere-hours (A x h), and the larger it is, the longer the devices connected to the battery will work.
To find out what kind of practical return a battery has, you need to perform a simple arithmetic calculation. For example, a battery with a capacity of 200 A x h and a voltage of 12 V accumulates 12 x 200 = 2400 W x h = 2.4 kW x h. the power in this case is no more than 75-80% of the nominal, that is, about 2 kWh. In practice, this means the ability to provide lighting from four lamps of 50 W each for 10 hours or an electric stove with a power of 2 kW for 1 hour. The calculation of the required battery capacity is carried out in conjunction with the selection of other PSA devices, so they need to be considered separately.
Estimated budget
One gel battery with a capacity of 150-200 Ah costs about 200-250 USD. e. For a suitable UPS, you will have to pay 400-700 USD. e., a optional equipment"pull" another 30-50 cu. e. Thus, the total cost of the PSA will be about 2500-2700 USD. e. At the same time, you can limit yourself to buying a simple 1 kW UPS and a 150 Ah battery. The total cost in this case will be approximately 300-400 USD. That is, and the system will keep the refrigerator, computer and a pair of electric lamps working for 2-3 hours. True, heating from such a PSA will not be able to work.
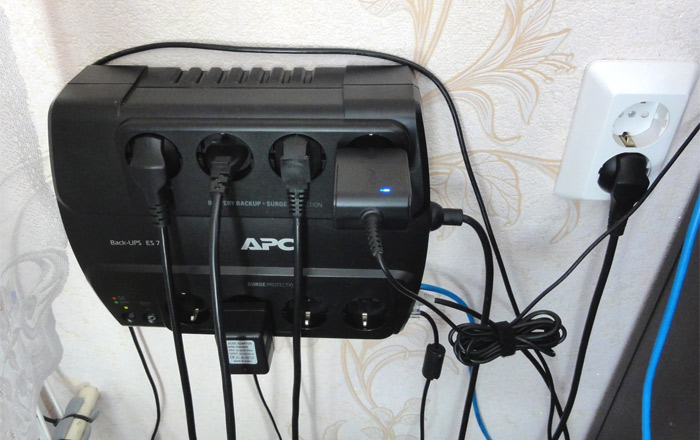

Low-power UPSs in one case combine a battery, an inverter, and automation. Consumers are connected to them directly - through a plug. Such systems are enough for very a short time(up to an hour) and only on a computer, charger, lamp.
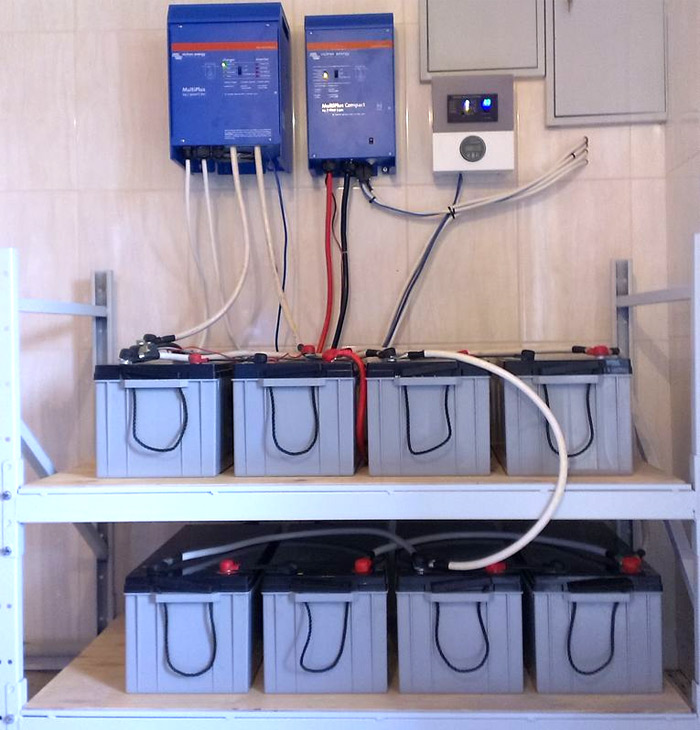

To provide a large number of consumers, separate dial-up systems are used that are connected not to a socket, but to a power supply panel.
System Components
In addition to batteries, the PSA includes several other very important devices. An uninterruptible power supply (UPS, or UPS) is an auxiliary device that is paired with a battery. It is used to compensate for peak loads and short-term power supply of household appliances in case of jumps and voltage drops in the network. This device is constantly connected to the outlet, and all the others are powered after it.
There are two constructive types of UPS depending on the electronic control circuit - offline and online. The first ones are simpler and cheaper, but they will provide power supply from the battery only in case of a power outage or a sharp drop in the voltage in the network. In addition, their response time is about 30-40 ms. The second ones are more expensive, but they "straighten" even small jumps. Thus, they provide the best protection for the devices connected to them, which is especially important not only for computers, but also for other modern high-precision equipment (for example, refrigerators, washing machines, TVs with electronic control units). The response time rarely exceeds 2 ms. Of course, an online-type UPS is better and more reliable, although an offline-UPS is quite sufficient in terms of response time.
An inverter is a current converter. In normal mode, it consumes a minimum amount of electricity and provides battery charging. When an emergency occurs, the inverter automatically switches to compensation mode. The need for it is due to the fact that ABs give out direct current with a voltage of 12, 24 or 48 V, and most electrical appliances require an alternating voltage of 220 V. There are modified (with a modified sinusoid) and sinusoidal devices. The former are good only for video and audio equipment, while the latter are needed for household devices. They cost more, but they also give out, saying plain language, higher quality current.
In addition, PSA is equipped with additional devices - charge controllers, as well as electronic devices for automatic control, regulation and protection. AT recent times, as a rule, they are all placed in the inverter housing.
Selection of general parameters
When calculating the parameters of the PSA, it is necessary to determine the required power of the equipment and the capacity of the battery. But before you do the calculations, you should clarify the difference between two similar terms. In the general case, the power of electrical equipment is determined in Watts (W). But the output power of the UPS is the product of the current and voltage values, this parameter is indicated in volt-amperes (VA). Part of this energy goes to the operation of the device itself, but the lion's share is beneficial. This useful power is usually additionally entered in the data sheet (measured in W).
To calculate the required values, first calculate the static power consumption of equipment that operates constantly or regularly (computer, refrigerator, boiler circulation pump, electric lamps), taking into account its quantity and average operating time during the day. Short-term requests of power consumers (for example, a water supply pump, a gate drive, an electric kettle) are added to the result.
True, the simultaneous inclusion of all these devices is unlikely, therefore, the power of only the strongest is added to the first digit (in the above example, the pump). Finally, it is necessary to take into account the dynamic (starting) power of the powered equipment. It is reached at the time of device startup and can exceed the static values by 3-4 times. Again, there is no need to add up all the starting indicators, the probability of their joint (up to fractions of a second) switching on is negligible. So it is enough to focus on the highest indicator. As a result, a specific inverter and UPS are selected.
However, it is not necessary to make an accurate calculation. If there is no goal to provide backup power for absolutely all devices, but only the most important devices, then for a private house with an area of 150-300 m2, models with a total capacity of 3-6 kVA are sufficient, withstanding starting power up to 9-12 kVA.
Calculating the required battery capacity is quite simple. For this, the volume of consumption is divided by the voltage of the battery, taking into account the coefficient of incomplete discharge of the device. For example, to guarantee the consumption of electricity in the amount of 4.5 kWh, 500 Ah (4500 W / 0.75x12 V) is required. Thus, in order for the equipment in the house to work for 4 hours, a battery with a capacity of 2000 Ah (4 x 500 Ah) is required. At the same time, the fact that an increase in the capacity of the battery automatically leads to an increase in the cost and increase in the mass of the device is taken into account, so it is better to install several batteries of a lower capacity.
In addition, when the external power supply is turned off, almost no one uses all the equipment at the same time. So in fact, the above values will be sufficient to ensure a comfortable stay in the house for 8 hours.
In the general case, experts recommend purchasing eight 12 V batteries for 200 Ah each or ten batteries for 150 A x h for such a building. And if you want to save money, four such batteries will be enough - they will "hold" the entire building 1-1, 5 hours and ensure the operation of the required minimum of devices for 3-4 hours. If power outages are more protracted and can last 1-2 days, the first thing to do is to calculate which equipment can be saved on the work, and only then plan to build up battery sections.

Mounting
Despite the apparent complexity of the PSA, the amount of electrical work required to connect it is practically minimal. After all, all household "loads" are brought to the electrical panel. It is only necessary to install a nearby UPS with battery and inverter and connect the latter to the network between consumers and the shield.
The SRP needs little space. Approximately 0.5-1 m2 is enough. It is important to choose the right room. PSA can be installed in unheated rooms, since most of the modern battery models can easily tolerate cooling down to -20 ° C. However, they perceive dampness and moisture condensation worse. In addition, with a decrease in external temperature, the AB capacity drops by 10-20%. The charging time also increases. So it is better to locate the PDS in a place where the temperature is constantly maintained around 0°C and there is good ventilation. It can be a garage, a properly executed basement, a utility room.
An inverter and a UPS are mounted on the wall, batteries are installed nearby - most often along the wall or in a chain on a shelf or rack. On sale there are special redundant power supply units with prepared places for placing equipment. It is also allowed to install the PSA in a closed perforated cabinet, where it will be protected from children and pets at the same time.
In the course of the work, it is important to ensure high-quality wire connections of all components - then the PSA will last for many years. After installation, intervention in the operation of the system during the entire period of operation is not required. You just need to periodically wipe the dust.
System advantages
Virtually instant response (within milliseconds) in the event of a power outage. Most modern, even high-precision electrical appliances do not "notice" the transition from a standard power supply to an autonomous one,
- Ability to withstand significant overloads.
- Protection of equipment from voltage surges, phase imbalance and other "whims" of the network.
- The ability to perform their duties at low loads without compromising the durability of the system.
- Virtually silent operation.
- Environmental friendliness, no harm to the environment compared to the use of diesel generators.
Why does the cottage need an inverter?
Have you noticed that without electricity in your copper veins, your beloved home turns into a zombie? Instead of warming and protecting, it begins to suck energy from your nerves.
It is not a problem to physically survive the night without light, without heat, without water and with a toilet in the yard (if the sewerage is forced). You can even survive the comments of your wife and loved ones.
But moral humiliation - "Well, what ... ?!" So much money has been invested in engineering systems and perimeter security!!! And all this is easily and naturally turned off by drunken negligence, the installer of the local substation Vasily(with an annual salary less than the price of the boiler), which you do not even know about and do not want to know.
Let's say you're in good shape, and poking into the house left without protection will regret that he met you, and not your dog. Or you are perspicacious, so even when you were building you took care of the backup power supply, bought a generator and can quickly “reanimate” the dead house (let the neighbors curse for the noise, this is their problem).
But did you build a house in order to WORK there yourself as a diesel security guard? Monitor the oil level, change diesel fuel, candles in the fall-spring, wait not for friends to visit on weekends, but for "colleagues" - diesel workers from the service?
It is our deep conviction that backup power supply should require no more attention from the owner of the house than water from a tap or heat from batteries!
Do you think if there watchman or servant, is it logical to entrust the Generator to them? One of our customers had an experience where he was glad that the embarrassing culprit of the fire at least did not burn himself.
The less the house depends on the person, the better. This is true even for the owner himself. And the English, back in the 19th century, knew that this was even more true for servants - the less "crooked hands" work, the calmer - let the servants rest better.
Inverter 12/220 is the best addition to the engineering systems of the house, because it provides backup power just as QUIETLY, INDIRECTLY and WITHOUT HUMAN participation.
How to choose inverter power?
For right choice The inverter 220 needs to know which load can be turned on at the same time, as well as the nature of this load (active or reactive - this affects the power calculation). The total total power of the load will determine the required power rating of the Inverter.
About types of load and features of power calculation for active and reactive load.
For a rough estimate of the power of your equipment, you can use
Calculation examplereserved powerbased on typical data
An example of calculating the load power of a house requiring uninterruptible power supply can be downloaded here:
- (.xls 39 kB)
- (.xls 39 kB)
In continuous mode (that is, a high probability of simultaneous operation), the following main electrical appliances will work:
| electrical appliances | Working mode | Power | Qty | Starting power VA | Hours per day | Consumed per day, kVAh | ||
| Television | continuous | 400 W | 1 | 400 | 2,000 | 5 | 2,000 | 250 |
| Fridge ** | 15 min/h | 250 W | 1 | 357 | 1,071 | 6 | 2,142 | 89 |
| Electric lamps *** | continuous | 75 W | 4 | 300 | 1,500 | 5 | 1,500 | 188 |
| Boiler** - burners and automation | continuous | 150 VA | 1 | 150 | 450 | 24 | 3,600 | 150 |
| Circulation pump ** | continuous | 90 W | 4 | 516 | 1,548 | 24 | 12,384 | 516 |
The total power of constantly operating devices is 1723 VA.
Powerful consumers can also be switched on for a short time. The most obvious are the water supply pump and the gate drive. Of course, when running on batteries reasonable person will not turn on the washing machine or electric oven. But it hardly makes sense to refuse a cup of coffee or tea, because in terms of average hourly indicators, this will not affect the battery drain too much:
| electrical appliances | Working mode | Power | Qty | Starting power VA | Hours per day | Consumed per day, kVAh | ||
| Electric kettle | 4 min. | 1000 W | 1 | 1,000 | 1,000 | 0.3 | 300 | 38 |
| Toaster | 5 min. | 600 W | 1 | 600 | 600 | 0.3 | 180 | 23 |
| Submersible pump (art.skv)** | ~6 min/h | 2000 W | 1 | 2,857 | 8,571 | 0.3 | 857 | 107 |
| Electric motors (gates)* | 1 min. | 500 W | 1 | 714 | 2,142 | 0.1 | 71 | 9 |
Simultaneous operation of all these devices is unlikely, therefore, in addition to the total power of constantly operating devices, we add only the most powerful of those briefly turned on - the well pump. With it in mind the maximum power of the simultaneously switched on load reaches 4580 VA.
Starting power must also be taken into account. It is not necessary to add up all the starting powers, because the probability of simultaneous (up to fractions of a second) switching on of electrical appliances is negligible. We focus only on the largest of the starting powers - 8571 VA
For uninterruptible power supply of such a load, a set of two modules is suitable. OutBack VFX3048 with a total power of 6 kVA, capable of withstanding starting power up to 12 kVA.
There is another, most reliable way - measuring currents with the load on. You can make them yourself or call our specialist.
For advice on power assessment, the choice of uninterruptible power supply equipment at home, the features of operation, as well as to order the departure of a specialist estimator -
UPS time at home
To estimate the operating time of a backup power supply system at home, you need to know two parameters:
calculated because the maximum total load calculated in the example above does not reflect the actual load on the battery. Devices turn on and off, and in some periods the power taken from the batteries is several times lower than the maximum.The principle of calculating the average hourly load is quite simple.:
Taking into account the operating mode of the device (continuous, continuous with on-off periods, rare switching on), the approximate duration of its operation per day is calculated. The operating time is multiplied by the power of the device - we get the consumption of the appliance per day (in kVA-hours). Next, we divide the value of consumption per day:
- / for 24 hours - for continuously operating devices,
- / for 8 hours - for devices that operate only during the active time of the day (that is, in the morning 7-10 hours and in the evening 18-24 hours intervals)
An example of calculating the load power and average hourly load at home can be downloaded here:
- (.xls 39 kB)
- (.xls 39 kB)
In general for a rough estimate we recommend focusing on the rating of the inverter and the size of the batteries not less than those indicated in the table:
| Maximum load power at home | UPS power for home | Inverter voltage rating | Number of batteries 12V for 220Ah | Inverter battery energy | Autonomy time at continuous supply max. loads* |
| 1.0 kW | 2 kW | 12V or 24V | 2 | 4 kWh | 4 hours |
| 2.0 kW | 3 kW | 24V or 48V | 4 | 8 kWh | 4 hours |
| 3.0 kW | 3 kW | 48V | 8 | 16 kWh | 5 o'clock |
| 4.0 kW | 6 kW | 48 V | 8 | 16 kWh | 4 hours ** |
| 5.0 kW | 6 kW | 48 V | 12 | 24 kWh | 5 o'clock |
| 6.0 kW | 6 kW | 48 V | 12 | 24 kWh | 4 hours |
* Minimum operating time. The actual operating time is, of course, longer, because the average hourly load is always less than the maximum.
** The line in italics corresponds to the example considered above.
For the example in question:
- average hourly load power = 1369 VA
- battery capacity = 16 kVAh
Estimated UPS Time = 12 hours
If long (more than a day) outages are not uncommon, then it is more profitable not to build up the battery, but to supplement the UPS for the home with a generator.
It is possible to create a fully automatic backup power supply system, if with auto start. The OutBack Inverter can independently command such a generator to start when the batteries are discharged, and turn off the generator after the batteries are charged. In this case, you can configure the prohibition on turning on the generator at night.
For advice on assessing power, choosing UPS equipment for the home, operating features, as well as ordering a specialist visit -
What is the difference between a UPS for a boiler and a house?
When choosing a UPS for a boiler and water supply, especially a powerful one, they often ask - Can the same Inverter be used for uninterruptible power at home? - Of course you can.
True, the cottage does not need a “pure sine” inverter. In the house, most of the load is not as sensitive to the shape of the current as the boiler. Modified sine wave (pseudo-sine, approximate sine) inverters 220 will provide a backup power supply acceptable to most electrical appliances. Of the critical loads from the "bad" sine, perhaps only the refrigerator will suffer. At the TV, in the worst case, interference is possible.
Therefore, if the task is a backup power supply only for lighting-TV-refrigerator, then a budget Inverter with a pseudo-sine will be a more profitable solution than increasing the capacity of a high-quality Inverter 220 “pure sine” of a boiler room.
But cheaper does not mean more efficient. than buying a separate cheap inverter, it is better to increase the power of a more expensive common Inverter, because a common resource is always exploited more efficiently than individual resources. More efficient in the sense everything is squeezed out of the shared resource, and it does not rest without load. And this postulate of the theory of queuing is confirmed by any practice - whether the resource is at least a general Inverter, at least a general office manager.
In addition, when using two Inverters, you will either have to connect both to the same battery, or buy separate batteries for the second Inverter.
In the first option, the charger of the budget Inverter will negate the entire effect of the intelligent 4-stage algorithm for charging a high-quality Inverter. That is, to reduce the life of expensive batteries.
In the second, the cost of an additional battery will negate all the benefits of a separate budget Inverter (it will be more expensive than the Inverter itself).
How is installing a UPS for a home different?
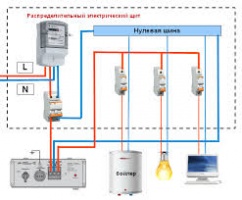
For backup power supply to the boiler, a minimum of electrical work is often needed. The UPS for the boiler can simply be included in the break in the line going to the boiler room. If the wiring in the boiler room is open, it is enough to “break” the line and connect the end of the cable coming from the switchboard to the input of the Inverter, and the other end of the cable to the output of the Inverter.
For uninterrupted power supply at home, there is more electrical work. All household loads are brought to the power grid at home. Therefore, power must be supplied from the shield to the Inverter and returned back to the shield in order to supply the backup power supply line to the circuits of the redundant loads. Requires a "loop" between the Inverter and the shield, that is, laying a cable (one five-wire or two three-wire) from the shield to the installation site of the Inverter.
Uninterrupted power supply at home requires re-switching of the house shields to bring redundant consumers to the Inverter 220. Therefore, the installation of a backup power supply system requires prior consultation, as well as a specialist visit for an engineering assessment of the installation work. In addition to assessing the work, it is recommended to measure the starting power of electrical appliances at home in order to more accurately select the power of the backup power supply system.
For advice on assessing power, choosing inverter 220 equipment for backup power supply at home, operating features, as well as ordering a specialist visit -
Power outages in our power grids, unfortunately, are a frequent occurrence, especially outside the city. Outages typically last from a few minutes to several hours. In the event of power outages, you can be left without electricity for several days.
Usually, gasoline or diesel generators are used to provide electricity to consumers in the house. However, their use is limited - they cannot be placed in an apartment, they need a special, well-ventilated place. The noise and exhaust gases from their operation can be an obstacle to the use of generators - neither you nor your neighbors are likely to like the noise and stench. Fuel for them also needs to be stored somewhere - and this immediately raises questions about fire safety.
We have installed hundreds of such backup systems
Therefore, a more correct solution would be to install an inverter-battery backup power supply system. Such a system will ensure reliable and uninterrupted operation of consumers in your home, including security and fire alarm systems, communication systems, heating systems and other critical loads. The inverter-battery system will provide electricity to your home, office, shop, and can be used as a power source for mobile power consumers. There are practically no restrictions on the use of such an uninterruptible power supply system - you can install it in a house or apartment, and it requires virtually no maintenance.
If your power grids experience power outages, voltage fluctuations, or other power grid parameters that do not meet load requirements, you need modern system with an uninterruptible power supply (UPS). We have installed many such backup power systems, you can see some examples in the section "Our installations"
INVERTER converts direct current from batteries into alternating 220 V with a frequency of 50 hertz. The inverter is the core of a backup power supply system, which usually consists of:
- an inverter that converts direct current from the battery into alternating voltage 220V
- rechargeable battery (AB), which is recharged during the presence of electricity from an external source
- a charger that provides a multi-stage high-quality charge of batteries
- controller (usually the controller is built into the uninterruptible power supply), which monitors the charge and discharge of the battery, as well as the voltage in the external network. If the quality (voltage value and frequency) is out of range or the voltage disappears, the controller instructs the system to switch to battery power through the inverter.
There is 2 types of backup power systems— with transfer relay and on-line systems. Firstly, if there is mains voltage, the UPS passes the available mains voltage to the load and at the same time recharges the batteries with a built-in charger. Some BBPs can also stabilize output voltage when the AC input voltage fluctuates. However, if the fluctuations are strong, then it is better to use a special stabilizer at the system input - this will ensure best options output voltage, because usually the stabilizers built into the BBP have only coarse voltage regulation with a large stabilization step.

At the time of power outage, the system almost instantly switches to battery operation and converts their energy into alternating current of a stabilized voltage of 220 V with a frequency of 50 Hz. When electricity appears, the system, after analyzing the quality of the incoming voltage, automatically switches to charge mode or continues to work in conversion mode (if the network parameters do not match the set ones) until normal voltage is restored.
If the network quality is very poor, then it is better to use an online backup uninterruptible power supply system. In online systems, the inverter is always on, and it is he who provides high-quality electricity to consumers. The network is used only to charge the batteries. Such systems are usually somewhat more expensive, and the battery operation modes in them are more difficult, but they must be used if the mains voltage cannot be corrected by a stabilizer, or it has strong distortions - unfortunately, this is not uncommon in our rural networks.

Continue Reading

Despite the progress moving forward, the shortage of electricity is increasing every year. And this happens not only in remote villages and villages, but also in large cities that even have their own hydroelectric power station. Why is this happening? The answer is very simple. The number of powerful consumers is growing, which simply did not exist before. Networks designed back in the USSR have practically not changed. Here, in order not to overload the line, during peak hours, power services turn off third-class consumers, that is, residential buildings. And it happens most of the time without warning. You sit on the Internet or in front of the TV, and bam ...! the light went out. In such a situation, in addition to nerves, dear Appliances, and you will not find the extreme.
But there is a way out. Buy an uninterruptible power supply for your home. What they are and how they work - these and other questions, the answers to them, will be discussed later in the article.
Purpose
The main task of an uninterruptible power supply is to supply power to a house or apartment in the event of a power outage or an accident on the main power line. When voltage is applied to the main network, the UPS will automatically, without human intervention, switch the power back to this line. In addition, the UPS has protection against voltage surges and stabilizes it:
UPS types
- UPS is redundant. This is the most commonly used uninterruptible power supply. This is due to: low price, high efficiency and low heat generation. The disadvantage of this type of device is: slow switching from the mains to the battery, poor-quality input and output noise filters, switching the load power with minor fluctuations in the mains voltage. This leads to premature wear of the relay contacts and frequent battery replacement.
- Line-interactive UPS. With a higher switching speed than the first. Equipped with an automatic voltage regulation device. This device tries to the last to stabilize the voltage in the network, and only when this fails, it switches the power to the batteries. Hence the long life of all nodes and blocks, as well as the high cost of the UPS.
- Online UPS. The most expensive type of UPS. Switching from power sources occurs almost without delay. It is used in industrial structures at critical facilities, such as automatic telephone exchanges and server rooms.
Execution
UPSs come in different types. In some, the batteries are built into the same housing with other blocks, in others, the batteries are located separately and are connected with an additional cable. What are the differences, pros and cons of such structures?
If the UPS is of low power, then the batteries are usually small-sized, and are located in the same cabinet with the inverter and charger. The advantage of this design is that it takes up little space and mobility. Minus - in case of replacement, it is necessary to install the same batteries, which can not always be found. It is also not possible to increase the operating time by replacing it with more capacitive batteries.
Important! When choosing batteries, pay attention to voltage. It must be what is needed for this device.
Another thing is a UPS with an external battery. Here you can experiment. In addition, external batteries can be placed in a separate, well-ventilated room with a stable temperature. After all, batteries can emit harmful fumes and do not tolerate temperature changes.
UPS device
Almost every uninterruptible power supply consists of blocks such as:

The input filter consists of capacitors and coils that remove mains noise while at the same time suppressing its own from the inverter.
The rectifier converts the alternating voltage of the network 220 Volts into the constant voltage necessary for operation charging block and inverter. The rectifier consists of a diode bridge, electrolytic capacitors and additional elements that improve current smoothing.
Charger. It consists of electronic units that regulate and control the optimal charge of the batteries.

Rechargeable batteries are a must in this device. In the event of a power failure in the network, they feed the inverter, which generates an emergency voltage. It is the quality and capacity of the batteries that determines the operating time of the UPS during a power outage.
The inverter consists of a generator of pulses of a given frequency, which are fed to the primary winding of the transformer, exciting a magnetic field in it. Voltage is removed from the secondary winding, which is rectified and stabilized. It is also used to power electrical appliances at home. Due to such a long conversion path, the output current has the correct shape and high stability. Home equipment is reliably protected from power surges and surges.
Important! The UPS must necessarily have protection against a short circuit at the output, otherwise the inverter will fail when shorted.
The switching device incorporates high-speed relays, which, at the time of a power outage, quickly switch from one power source to another.
Control devices, depending on the UPS model, can be both electronic and mechanical voltmeters, and ammeters. Thanks to them, it is possible to control the voltage and current both at the input and at the output of the device.
The output circuits are the same as at the input - inductors and capacitors that remove noise. In addition to the above, these are output terminals or terminals for connecting a home electrical network.

Of course, to protect all these blocks, a reliable and aesthetic case is needed. For different models, the case has its own characteristics. Therefore, when choosing a UPS, you should pay attention to the material, whether there are enough slots for cooling the indoor units and, of course, the color, if this is important to someone.
Principle of operation
As already partially described above, the principle of operation is as follows:
- the alternating voltage of the network is rectified by a rectifier;
- rectified DC voltage is used for battery charger and inverter power supply;
- the rectifier charges the batteries, which, when switched off, feed the inverter;
- the inverter, in turn, outputs a stabilized alternating voltage of 220 volts to the house network.
Installing and connecting a UPS for the home
Connection is not difficult. Each device has an instruction with a diagram and recommendations for connection and installation. In any case, a cable is connected to the input of the device immediately from the output of the meter, and the output from the UPS is connected to the house network. That is, the UPS is simply installed in the gap between the meter and the home network. You can put the device, if it does not interfere, right in the corridor of a private house near the meter, and make all connections along the shortest path. This is the easiest option. If aesthetics are lost, you will have to install the UPS where it does not spoil the view, and lead the input and output cables to the meter.
Important! Be careful when working near the counter so as not to accidentally break the seal.
Sometimes a gasoline or diesel generator is also included in the circuit, which, of course, must stand separately in non-residential premises or on the street. He is needed when the batteries have already exhausted their charge, but the electricity has not been supplied. The generator will additionally provide energy and charge the batteries.
How to choose a UPS for home and garden
Before choosing this device, you need to calculate the power consumption of your network. To do this, we take the power of all household appliances that are used in the house and summarize it. We add 10-20 percent to this value, and we get the maximum power. For example, in your house: refrigerator - 200 W, TV - 100 W, computer - 300 W, washing machine - 2500 W and iron - 2000 W. We summarize, and we get a value of 5100 W (5.1 kW). Throw in 20% and get about 6 kW. This is the power you need to choose a UPS for your home. It is clear that all devices cannot be turned on at the same time, but it is better to take it with a margin for the future, and the ratings on UPS devices are most often overstated than they actually can give.
Also important point of choice is the quality of the batteries. They are the most expensive in this device, so you need to choose famous brands with a guarantee and the ability to find a replacement.
Attention! Power is indicated both on the body and in the data sheet of the device.
UPS for gas boiler

In principle, if you already have a UPS for the whole house, then there is no point in buying another one for the boiler. But. if the first option is too expensive for you, then you can buy a UPS separately for the boiler.
It is worth choosing according to the criteria described above, the only difference is power. Here you can take the UPS cheaper. Usually, a power of 500 W (0.5 kW) is enough for a boiler, but it is better to look at the passport of your particular device. It is necessary to take into account not only the consumption of the boiler electronics, but also the pumps:
Choosing a UPS for a computer.
This type of UPS has been used for a long time and has gained considerable popularity.
What to consider when choosing it:
In general, the heavier the block, the better. Take exactly the one that weighs more, with the same indicated power on the case.
Do-it-yourself UPS for home and summer cottages
Yes, you can make this device yourself. The easiest way is to find an old computer UPS with dead batteries and use its inverter and case:
What else needs to be done?
- Remove body.
- Disconnect the old battery and draw these conclusions with access to the outside. To do this, you can make holes in the body and put these ends on the terminals. Now external batteries can be connected to these terminals for the same voltage as the old ones. The larger the capacity, the better.
- We mount sockets on the case or on the rear panel and connect them, first to each other, and then to the inverter output.
- We break off the speaker on the board. Otherwise, he will constantly squeak.
- For better cooling, we cut a 120 mm hole in the case and insert a standard fan into it. It is needed to cool the inverter.
This is how you can build your own backup power system. The main thing is to choose quality batteries voltage for the inverter. You can calculate the voltage using the old ones.
Attention! Be careful. When making changes to the circuit, disconnect both the cord from the outlet and the battery.

IPB is undoubtedly a necessary thing. It will protect your equipment, and in emergency situations will not leave you in complete darkness. Even if you do not have blackouts, it is better to be ready for this now.
Many things in our Everyday life seem to us so ordinary and self-evident that it is difficult for us to imagine even their fleeting absence. One such thing is electricity. We cannot see and feel it, it is inconspicuous and silent, and we can determine its presence only by indirect signs, such as the operation of electrical appliances, the presence of light and heat in our house.
The civilization of the modern city owes its existence, for the most part, to electricity, but at the same time we very rarely think about where this electricity comes from. In order for such a vital potential difference of 220 volts to appear in a small electrical outlet in our house, somewhere in other places, sometimes quite distant, huge turbines of hydroelectric power plants are spinning and thousands and thousands of tons of minerals are burned.
Before getting to our house, the current travels hundreds or thousands of kilometers through the vast expanses of our state, jumping over countless power line masts and squeezing through substations.
Now imagine for a moment that some link in this huge chain fails, and the light goes out in our house. Worse yet, the power goes out throughout the city, which can lead to chaos and even casualties.
 Is it possible to protect yourself from this? While the state and large energy companies will deal with putting things in order, which in itself can drag on for many years, we can secure ourselves in our particular, single dwelling.
Is it possible to protect yourself from this? While the state and large energy companies will deal with putting things in order, which in itself can drag on for many years, we can secure ourselves in our particular, single dwelling.
Generator Substation
There are several ways to protect your home from power outages. All of them are connected with the construction of a certain autonomous system capable of supporting life in the absence (short-term or long-term) of an external source of electricity.
The first way is already well known to all of us - this is a generator power plant. An internal combustion engine running on gasoline or diesel generates electricity that powers our entire home. If our light is “cut off”, we just go into the yard, turn on the generator set and say “let there be light!”, Returning to household chores as if nothing had happened. If we are willing to spend a little more money, then we can buy and install a generator with an automatic start system that will start the generator automatically in the event of an outage. In this case, we will know about the disappearance of the network by the fact that our entire house will be plunged into darkness for half a minute - the time required to start the generator and supply backup power.  If you have a generator in the house, you need to ensure that there is fuel in the fuel tank and carry out service from time to time. In addition, the installation of a generator requires a separate room with exhaust gases, and preferably away from living rooms due to the noise of a running engine.
If you have a generator in the house, you need to ensure that there is fuel in the fuel tank and carry out service from time to time. In addition, the installation of a generator requires a separate room with exhaust gases, and preferably away from living rooms due to the noise of a running engine.
inverters
Is there an alternative to a generator? Recently, battery systems have become increasingly popular in our country, which have a number of undeniable advantages over generators. When there is an external network, the batteries accumulate energy (recharge), and when a power outage occurs, the whole house receives electricity from its own reserve, and it can be made as big as you like. Such a system is silent, does not require a special room, takes only about 1 sq. m and switches to the reserve instantly, so you may not know about the accident at the substation. This system does not need to be monitored, filled with fuel, it is not flammable and its service life is very long - about 10 years and more.
 Such systems are called inverter (or battery) uninterruptible power systems. Their basis is an inverter, a device that converts the direct current of batteries into alternating current 220 volts of a home network. As a rule, the inverter also has a built-in charger, which allows you to quickly charge and monitor the condition of the batteries. In houses with three-phase power supply, one of the phases is connected through an inverter, becoming the so-called "reserve phase". All loads inside the house are switched to it, which should work in uninterrupted mode. These can be, for example, light sockets, heating boiler power, alarms, security systems, gates, and so on. That is, those household appliances, without which we may experience inconvenience or even outright problems.
Such systems are called inverter (or battery) uninterruptible power systems. Their basis is an inverter, a device that converts the direct current of batteries into alternating current 220 volts of a home network. As a rule, the inverter also has a built-in charger, which allows you to quickly charge and monitor the condition of the batteries. In houses with three-phase power supply, one of the phases is connected through an inverter, becoming the so-called "reserve phase". All loads inside the house are switched to it, which should work in uninterrupted mode. These can be, for example, light sockets, heating boiler power, alarms, security systems, gates, and so on. That is, those household appliances, without which we may experience inconvenience or even outright problems.
Union of inverter and generator
Some of the more "advanced" inverters, such as the Xantrex XW, can automatically drive a connected generator to recharge batteries if external power is not provided for too long. This feature allows the use of such systems in places where there is no or no electricity at all. If built Vacation home where there is no mains power yet, it is possible to install both a generator and an inverter system, which will be effectively combined with each other. In this case, in order not to drive the generator all the time, it can be automatically turned on by the inverter to charge the batteries as needed or at a predetermined time, after which the energy from the batteries can be used through the inverter. At the same time, the service life of the generator is noticeably increased, not to mention the fact that we can live in silence for at least some time without sacrificing electricity. ![]() If we talk about the choice - a generator or an inverter, then, first of all, two factors matter: the required power of the loads and the duration of autonomous operation. When there are interruptions for more than a day, then, most likely, we cannot do without a generator. The longer the system has to run, the more batteries are required, and good battery is a rather expensive component.
If we talk about the choice - a generator or an inverter, then, first of all, two factors matter: the required power of the loads and the duration of autonomous operation. When there are interruptions for more than a day, then, most likely, we cannot do without a generator. The longer the system has to run, the more batteries are required, and good battery is a rather expensive component.
A powerful generator is indispensable if you need to power loads over 10 kW, although Xantrex does have three-phase redundancy systems up to 18 kW. The problem with high capacities is that the batteries will drain very quickly and, accordingly, their capacity must be made very large. For continuous operation of loads above 10 kW, the cost of batteries becomes astronomical.
The Xantrex XW Inverter has a feature to automatically turn on the generator if the load rises above a certain threshold. Thus, the inverter does not allow the battery to discharge too quickly when “heavy” consumers are turned on, such as, for example, heaters, stoves, air conditioners, etc.
Other useful features of the Xantrex XW inverter include its ability to add power in weak networks. If you have a weak substation or there is a demand limit such as 3kW, then a 6kW Xantrex XW Inverter can add power to loads in your home up to 12kW peak. At the same time, he will take from the network no more than the power that you allow him, and in addition he will add from the battery. At night, when consumption is minimal, the batteries can be automatically charged.
Another function is mixing alternative energy to the network. In the presence of, for example, solar panels or a windmill, the generated energy will automatically compensate for the consumed energy. This will happen with fully charged batteries, when there is an excess of energy from an alternative source.
Batteries for uninterruptible power systems
 Batteries for uninterruptible systems are expensive. Not every battery will fit. Cheap car batteries are called starter batteries and are not designed for long discharge-charge cycles due to the insufficient thickness of the lead plates. Nothing prevents, of course, from using them, but, most likely, they will quickly fail, since they are designed only for the short pulse mode (starting the car). Of the batteries that can be used for home power systems, there are two types: open (serviceable) and sealed (unattended). Open batteries have longer lifespans but require a separate room with forced ventilation. If these batteries are lost in capacity over time, they can be "refreshed" using a special charge algorithm called "equalization". During such a charge, the electrolyte is mixed and restores its density. Sealed batteries cannot be subjected to such procedures, and if they are lost in capacity, then you can only put up with this or change them to new ones. Sealed batteries are convenient in that they do not require any attention. They are divided into 2 types: AGM and GEL. Gel batteries are more suitable for use in cold temperatures, but they are also the most expensive. Modern batteries for uninterruptible power systems can cost from 12 to 30 thousand rubles. When installing a home uninterruptible power supply system based on an inverter, which has a so-called 48 V DC rating, you will need 4 or 8 12-volt batteries. If the inverter is rated at 24 V, then two 12-volt batteries can be dispensed with.
Batteries for uninterruptible systems are expensive. Not every battery will fit. Cheap car batteries are called starter batteries and are not designed for long discharge-charge cycles due to the insufficient thickness of the lead plates. Nothing prevents, of course, from using them, but, most likely, they will quickly fail, since they are designed only for the short pulse mode (starting the car). Of the batteries that can be used for home power systems, there are two types: open (serviceable) and sealed (unattended). Open batteries have longer lifespans but require a separate room with forced ventilation. If these batteries are lost in capacity over time, they can be "refreshed" using a special charge algorithm called "equalization". During such a charge, the electrolyte is mixed and restores its density. Sealed batteries cannot be subjected to such procedures, and if they are lost in capacity, then you can only put up with this or change them to new ones. Sealed batteries are convenient in that they do not require any attention. They are divided into 2 types: AGM and GEL. Gel batteries are more suitable for use in cold temperatures, but they are also the most expensive. Modern batteries for uninterruptible power systems can cost from 12 to 30 thousand rubles. When installing a home uninterruptible power supply system based on an inverter, which has a so-called 48 V DC rating, you will need 4 or 8 12-volt batteries. If the inverter is rated at 24 V, then two 12-volt batteries can be dispensed with.
It should also be mentioned here that Xantrex microprocessor chargers allow you to increase the life of batteries using a three-stage charging technology and monitoring the condition of the batteries.
 Quasi and pure sine
Quasi and pure sine
Inverters are also different. Cheaper inverters produce a stepped (quasi) sine wave at the AC output. The more expensive ones have a more advanced converter that produces a "pure sine" current - a current with minimal harmonic distortion - the same as in a conventional 220 V network. Pure sine is better for demanding electronic devices (plasma panels, expensive audio equipment, etc.). ) and is better suited for the functioning of the electronics of imported heating boilers.
Virtually all home appliances will work on quasi-sine, with the exception of dimmers, microwave ovens with a power of more than 1000 watts, some chargers for cell phones.  In addition, there may be such inconveniences as the noise of fluorescent lamps. All Xantrex inverters have sufficient electromagnetic shielding and will not interfere with TV or radio operation. It is also worth noting that the network failover time is approximately 16ms, which is enough to ensure that the computer is not overloaded.
In addition, there may be such inconveniences as the noise of fluorescent lamps. All Xantrex inverters have sufficient electromagnetic shielding and will not interfere with TV or radio operation. It is also worth noting that the network failover time is approximately 16ms, which is enough to ensure that the computer is not overloaded.
The cost of inverters depends on their power and functionality. For example, the most “fancy” Xantrex XW6048E (6.0 kW) with a built-in powerful charger, the ability to control a generator and the ability to work with alternative energy sources costs about four and a half thousand dollars. Combined with a 400-600 amp hour battery bank, this inverter can provide up to 12 hours of uninterrupted power to your home.
It is also recommended to equip a home uninterruptible power system with a voltage stabilizer, since the inverter itself does not solve the problem of stabilization during surges or when the external network voltage is low.
 Inverters and solar energy
Inverters and solar energy
Inverter systems are ideally combined with solar-powered current sources, being an accumulating link for energy coming from solar panels. Although solar panels and remain an extremely expensive pleasure, but even at a cost of about 150 rubles per 1 W, they can be an effective help for autonomous power supply of cottages in the sunnier southern regions of Russia.
In Russia, a fuel generator is the most popular option for solving electricity problems. Few people know about inverter systems. Despite the fact that the described uninterruptible power systems are somewhat more expensive than generator sets of similar power on gasoline or diesel fuel, these systems are designed to different situations. With short interruptions, the convenience of an inverter system is undeniable. With long interruptions, you can’t do without a generator, but again, if the generator is supplemented with an inverter system, you get a combination worthy modern technologies"smart home".
Text: Nikolai Plekhanov, CEO of Inverta




















